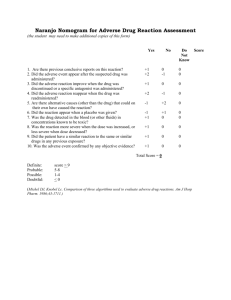
Chapter 18 Drugs Used for Psychoses Learning Objectives Identify
advertisement

Chapter 18 Drugs Used for Psychoses Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of psychotic behavior Describe major indications for the use of antipsychotic agents Identify common adverse effects observed with antipsychotic medications Develop a teaching plan for a patient taking haloperidol and one receiving clozapine Psychosis Clinical descriptor; no exact definition Characteristics include: Being out of touch with reality Perceptual deficits Deterioration in social functioning Psychotic symptoms: Can be associated with many illnesses Are common in mood disorders Can be caused by many drugs Symptoms Delusions Hallucinations Disorganized thinking, loosening of associations Disorganized behavior Changes in affect Treatment Perform thorough initial assessment Consider both drug and nondrug therapies Determine baseline level of functioning Define treatment goals Identify and document target symptoms Target Symptoms Frequency and type of agitation Degree of suspiciousness Delusions Hallucinations Loose associations Grooming habits/hygiene Sleep patterns Speech patterns Social skills Judgment Drug Therapy Antipsychotic (neuroleptic) agents Phenothiazines and nonphenothiazines Low potency and high potency Typical and atypical Other agents Benzodiazepines Control of adverse effects Beta-adrenergic blocking agents Antiparkinsonian agents Anticholinergic agents Actions Blocks dopamine from acting on the brain Stimulate or block cholinergic, histaminic, nicotinic, and alpha and beta adrenergic neurotransmitter receptors (cause of adverse effects) Adverse Effects Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) Dystonic reactions/acute dystonia Pseudoparkinsonism (tremor, muscular rigidity, masklike expression, shuffling gait, loss/weakness of motor function) Akathisia (pacing, rocking, subjective feelings of anxiety and restlessness) Tardive dyskinesia (hyperkinetic abnormal movements) Neuroleptic malignant syndrome Nursing Process: Assessment History of behavior Basic mental status Interpersonal relationships Mood/affect Clarity of thoughts/perception Thoughts of death Psychomotor function Sleep pattern Dietary history Nursing Process: Planning History of psychotic behavior Basic mental status Mood/affect Clarity of thought/perception Thoughts of death Psychomotor function Sleep pattern Dietary needs Nursing Process: Implementation Create individualized interventions Provide safe, structured, accepting environment Provide opportunity for expression Allow opportunity for patient to make decisions (if capable) Involve the patient in self-care activities Do not reinforce hallucinations, delusions Be open and direct when handing suspicious patients Nursing Process: Implementation Set limits and enforce them kindly Provide diversionary activities for patients with altered perceptions Monitor suicidal patients Use physical restraints within guidelines Provide for nutritional needs Handle manipulative behavior in consistent manner Antipsychotic Agents Used to treat schizophrenia, mania, psychotic depression, and psychotic organic brain syndrome Typical Phenothiazines Nonphenothiazines (haloperidol, molindone, loxapine, thioxanthenes) Atypical Clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, ziprasidone Premedication Assessment Obtain blood pressures in supine, sitting, and standing positions Check Electrolytes Hepatic function Renal function Cardiac function Thyroid function Perform baseline clinical evaluation rating scales and adverse effect scales Side Effects to Expect Chronic fatigue/drowsiness Orthostatic hypotension Blurred vision Constipation Urinary retention Dry mouth/throat/nose Weight gain Side Effects to Report Seizure activity Parkinsonian symptoms Tardive dyskinesia Hepatotoxicity Blood dyscrasias Hives/rash Photosensitivity Drug Interactions Increase toxic effects: Antihistamines Alcohol Analgesics Tranquilizers Decrease therapeutic effects: Carbamazepine Cimetidine Phenytoin Insulin/oral hypoglycemic medications Venlafaxine