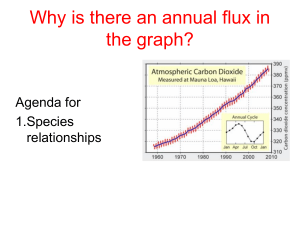
ES10 11 Population Interactions (Nicole)
advertisement
POPULATION INTERACTION animalsversesanimals.yuku.com Predation www.techtimes.com Herbivory Consumption of plant materials by animals Drives adaptions in both the Herbivore and Plants Plants have evolved defenses (Thorns and Chemicals) Scientist identified thousands of Chemical Defenses (Nicotine & Cocaine) Herbivores have evolved as well (Butterflies & Mammalians) www.courseimage.com Parasitism Parasites consume nutrients from other Organisms Effect to the Host (Decreasing of its Fitness & Diseases (referred as Host)) Endoparasites (Inside the body) Examples :(Flukes, Tapeworms, Fungi, Bacteria, and Protozoa) Ectoparasites (Outside the body) Examples : (Ticks and Lice, Plants, Protozoa, Bacteria, and Fungi) Do not kill their hosts Parasitoids : Draws the line between Parasitism & Predation (Several species of wasps) freepngimages.com www.willows.uk.net Mutualism http://www.eoearth.org/ 3 Types of Mutualism Trophic Mutualism • Interaction where both species receive benefit of resources • Requires both nutrients and energy to survive Example : ( Plant provides energy with photosynthesis, Partner then provides the plant with increased access to nutrients) 3 Types of Mutualism Defensive Mutualism • Interaction where one species receives food & Shelter. The partner then gets protected from its Predators or Parasites • The Prey involved benefits from predators avoiding them. Example : (Pseudomyrmex ants & Acacia shrubs) 3 Types of Mutualism Dispersive Mutualism • Interaction where A species receives food from moving the pollen or seeds of it’s partner • Seede Dispersers benefit from energy and nutrients found in fruits Example : (Insects, Birds, and Mammals, who are involved in pollination and seed dispersal) Commensalism http://www.eoearth.org/ 4 Basic Types of Commensalism Chemical – Most often associated with but not always (One bacterium metabolizes a chemical not useful to the second) Inquilinism - Use of a second species as a platform or cavity (Attachment of barnacles to other marine creatures is a prominent example) Metabiosis – circumstance where one species creates a useful habitat feature for a second species. (reuse of holes made in saguaro cactus by many different birds and mammals) Phoresy – Attaches for temporary transport (attachment of burs or seeds, plants to (chiefly) furry land animals for the purpose of seed dispersal) Example :(Epiphytes, Anemones and clownfish, Barnacles, Bacteria ) en.wikipedia.org Symbiosis fortcapitalresou Symbiosis Literally means ‘Living together’ But when the term is used in biology it means a close, longterm interaction between two different species Some examples of the many different types of Symbiotic Relationships (Mutualism, Parasitism, Commensalism & Amensalism) Competition www.glogster. Competition Between Species www.pinterest.com en.wikipedia.org uldissprogis.com www.glogster.com Does nature favor competition C o m p e t i t i o n? en.wiki hqdefault What is resource specialization and how does it relate to competition? What is resource specialization and how does it relate to competition? en.wiki Examples on Population Interaction? And how does this relate it to our daily lives? en.wiki REFERENCES http://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/predationherbivory-and-parasitism-13261134 http://www.eoearth.org/view/article/51cbee7b7896bb431f698251/ http://www.eoearth.org/view/article/51cbf2687896bb431f6a929c/ http://study.com/academy/lesson/symbiotic-relationships-mutualismcommensalism-amensalism.html http://www.globalchange.umich.edu/globalchange1/current/lectures/ecol_com/ecol _com.html