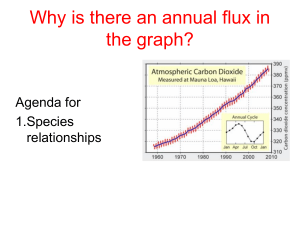
Ecology: Mutualism, Commensalism, Predation Worksheet
advertisement

Mutualism Commensalism 1. What is symbiosis? 1. What is commensalism? 2. What is mutualism? 2. Why is commensalism harder to demonstrate than parasitism and mutualism? 3. Describe the relationship between bacteria and the cows whose intestines they reside in. 3. Describe 5 examples of commensalism. In your description, explain the specific benefit received by one of the organisms involved in this relationship. 4. How is mutualism important in ecology? 5. What are the 3 types of mutualism? Explain how they’re different. 6. Describe 2-3 examples of each type. In your example explain the benefit that each organism receives. 4. Why do some scientists feel that close interactions between organisms are unlikely to be completely neutral for either party? Parasitism 1. What is parasitism? 2. How do parasites differ from their host? 7. What are parasitoids? How is their behavior connected with predation? 8. List 4 examples of parasitism. In each example explain the benefit that the parasite receives and how it harms its host. 3. Why do you think parasites do not immediately kill their host? 4. Explain the difference between ectoparasites and endoparasites. Competition 1. What is competition? 2. What is necessary for competition to occur? 5. What are vectors? 6. What are epiparasites? 3. How is competition connected to natural selection (survival of the fittest)? 4. What is detritivory? 4. Explain the difference between interference, exploitation and apparent competition. 5. How is a “true predator” defined? 5. How are intraspecific and interspecific competition different? Explain an example of each. 6. What characteristics/adaptations do you think make certain predators more successful at capturing their prey? 7. How is grazing different from “true predation”? 8. How is parasitism different from grazing? Predation 1. What is predation? 2. Do predators always kill their prey? 3. What is herbivory?