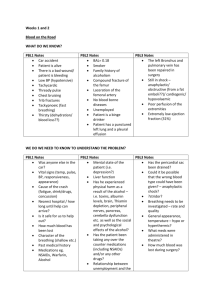
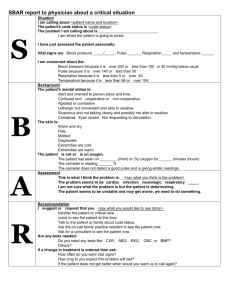
Infection Control, Medical Emergencies, Vital Signs & Oxygen
advertisement

Vital Signs, Oxygen & Medical Emergencies Warning: blood and guts to follow ! Vital Signs Vital Signs Oxygen Therapy Oxygen Devices Chest Tubes and Lines Vital Signs Indication of Physical assessment Homeostasis Primary Mechanisms include measurement of vital signs Body Temperature Pulse Respiration Blood Pressure Mental Status Heart beat Blood pressure Body temperature Respiratory rate Electrolyte balance Body Temperature Normal average body Measuring Body temperature: 98.6 F Humans can survive between 106 F and 93.2 F. Temperature Hypothermia Axillary Hyperthermia Tympanic Oral Rectal Pulse Pulse rate: Adult = 60 to 100 beats per minute Children under 10 = 70 to 120 beats per minute Tachycardia Bradycardia Respiratory Rate Breaths per minute: Adult = 12 to 20 Children under 10 = 20 to 30 per min Tachypnea Bradypena Dyspnea Apnea Pulse Oximeter • Normal Pulse Oximeter = 95% to 100% Blood Pressure • Blood Pressure • Systolic pressure = 95-140 mmHg • Diastolic pressure = 60-90 mmHg • Hypertension • Hypotension Oxygen Oxygen constitutes 21% of atmospheric gases If O2 levels in the body drop below 21% homeostasis is altered. Hypoxia: Inadequate amount of oxygen at the cellular level. Oxygen Devices Nasal Cannula Masks Nonrebreathing mask Aerosol mask Air-entrainment mask Tent and Oxyhood Chest Tubes and Lines • Endotracheal Tube (ET) – Ventilator • Chest Tubes • Nasogastric tube (NG) • Central Lines Review Vital Signs Electrolyte balance Homeostasis Pulse Oximeter Body Temperature Oxygen Pulse Oxygen Devices Respiration Chest Tubes Blood Pressure Chest Lines Mental Status Winston Churchill "The pessimist sees difficulty in every opportunity. The optimist sees the opportunity in every difficulty." Winston Churchill Questions? • Vital Signs Medical Emergencies TRAUMA = X-RAY IS READY SPINAL INJURY PT GSW to the Abdomen Compound Fx of Femur Medical Emergencies • Definitions • What should the RT know? • Common Radiology Emergencies Medical Emergencies Definition: Sudden change in medical status requiring immediate action. For RT’s medical emergencies are rare, however as medical personnel we must be prepared to recognize emergencies. Fractured Forearm What an RT should know….. How to….. Avoid additional harm to the patient Obtain appropriate medical assistance quickly Recognize emergency situations Remain calm and confident Anaphylactic Reaction An immune response to foreign material Bronchospasm – wheezing and edema in the throat and lungs Can lead to shock Requires prompt recognition and treatment from the technologist Why do RT’s care about Anaphylactic RXN’s….? Water Soluble Iodine • High atomic # 53 • Radiopaque • Used to radiograph – – – – Vessels Arteries Veins Function of internal organs Iodine Contrast Material • Ionic Iodine Contrast – Anion – Cation + – More patient allergic reactions • Non-Ionic Contrast – Less patient allergic reactions Radiology Department Patients are usually sent to the radiology department only after they have been stabilized. However…… General Priorities Ensure an open airway Control Bleeding Take Measures to Prevent shock Attend to wounds or fractures appropriately Provide emotional support Continually reevaluate and follow up ABC • A = Air Way • B = Breathing • C = Circulation CPR • C = Cardio • P = Pulmonary • R = Respiration • Must be certified for the “Health Care Provider” • Cards good for 2 years are available. Become familiar with……….. • In your work environment: – Emergency assistance protocol (how to get help) – Emergency Cart/Crash Cart Location Important Conditions to be Aware of…… Level of Consciousness: ALOC Altered Level Of Consciousness Anaphylactic Shock: vasogenic shock Hypoglycemic/Hyperglycemia NPO – Nothing by Mouth Medical Terms to Know….. Pallor = paleness; absence of skin coloration Shock = failure of the circulatory system CPR = cardiopulmonary resuscitation For program must be for Health Care Provider Continued…………… Stroke = Cerebrovascular Accident (brain) Heart Attack = Myocardial Infarct (heart) N/V = Nausea & Vomiting Epistaxis = nosebleed Vertigo = dizziness Syncope = fainting And more…… Hemorrhage = bleeding outside a vessel Radiologic Technology • You never know when a medical emergency may occur. • Helping your patients depends on your abilities to stay calm and perform you duties! Questions? • Infection Control • Vital Signs • Medical Emergencies