Vital Signs & Oxygen
advertisement

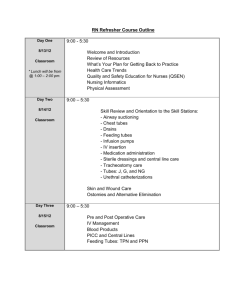
Patient Vital Signs DRAFT Rad Tech A – Week 13 Patient Assessment &Vital Signs • Patient Interview • Role of Radiologic Technologist • Elements of the Clinical History • Vital Signs • Oxygen Therapy • Oxygen Devices • Chest Tubes and Lines Vital Signs • • • • Body Temperature Respiratory Rate Pulse / Heart Rate Blood Pressure Vital Signs • Indication of Homeostasis • Primary Mechanisms – Heart beat – Blood pressure – Body temperature – Respiratory rate – Electrolyte balance • Physical assessment include measurement of vital signs Body Temperature Pulse Respiration Blood Pressure Mental Status Homeostasis • Our bodies are always trying to maintain HOMEOSTASIS – a constancy in the internal environment of the body, naturally maintained by adaptive responses that promote healthy survival. • Ex: sweating to cool body temperature Body Temperature • The human body has an ideal temperature, and it works to maintain it, this is called: THERMOREGULATION • Ideal temperature: 98.6 degrees F (oral) • Acceptable range: 97.7 to 99.5 degrees F • Measurement: oral, axillary, tympanic, rectal Body Temperature • Normal average body temperature: 98.6 F Humans can survive between 106 F and 93.2 F. –Hyperthermia Fever, febrile –Hypothermia below normal range Measuring Body Temperature – Oral – Rectal – Axillary – Tympanic Pulse • Pulse rate: Adult = 60 to 100 beats per minute • Children under 10 = 70 to 120 beats per minute • Tachycardia • Bradycardia Blood Pressure Measure of the force exerted by blood on the arterial walls during contraction & relaxation. Measured pressure when the heart is relaxed: Diastolic Measured pressure when the heart is contracted: Systolic Measured with a Sphygmomanometer Blood Pressure Systolic pressure = 95-140 mmHg Diastolic pressure = 60-90 mmHg 120/ 80 Normal Blood Pressure cont’d Recorded in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) with systolic over diastolic Normal adult systolic: 95-140 mm Hg Normal adult diastolic: 60-90 mm Hg Persistent elevation of BP: Hypertension Persistent low BP: Hypotension Respiratory Rate Respiratory System delivers oxygen to the body’s tissues & eliminates carbon dioxide. Major muscle of ventilation: diaphragm Measured in “breaths per minute” 12 – 20 bpm Children: 20 – 30 bpm Newborns: 30 – 60 bpm Adults: Respiratory Rate • Breaths per minute: Adult = 12 to 20 • Children under 10 = 20 to 30 per min • Dyspnea- difficulty breathing • Apnea- no breathing • Bradypnea – decrease is breathing Pulse Oximeter • Normal Pulse Oximeter = 95% to 100% Methods of Delivering Oxygen Nasal Cannula Masks Ventilators Oxyhood Oxygen • Oxygen constitutes 21% of atmospheric gases • If O2 levels in the body drop below 21% homeostasis is altered. • Hypoxia: Inadequate amount of oxygen at the cellular level. Chest Tubes & Lines The Rad Tech’s Role • Early detection of problems associated with malpositioned lines. • X-rays assist physicians in determining if tubes and lines are placed correctly • Correct positioning and technical exposure are crucial Chest Tubes and Lines ENDOTRACHEAL TUBES CENTRAL LINES CHEST TUBES NASOGASTRIC TUBES Tubes & Lines cont’d • • Endotracheal Tubes (ET tubes) – Known as “intubation” -translaryngeal -tracheostomy -nasotracheal Must be precise in placement: 1-2 inches superior to the tracheal bifurcation (carina) Intubation of the rt main-stem bronchus with complete occlusion of the lt bronchus causing lt lung atelectasis. (A) Distal tip of endotracheal tube in rt main bronchus; (B) Central venous catheter in the lt subclavian vein. CHEST TUBES Tubes & Lines (last one) • Common insertion sites for CV lines: -subclavian vein -internal jugular vein -femoral vein • Most evaluated by a chest x-ray • Extreme caution must be used when positioning for images! NASOGASTRIC (NG) TUBE CENTRAL LINES Rt hydrothorax caused by displacement of a central venous line during dressing change; 1300 ml of intravenous fluids were evacuated via thoracentesis. Review • Vital Signs • Homeostasis • Body Temperature • Pulse • Respiration • Blood Pressure • Mental Status • Electrolyte balance • Pulse Oximeter • Oxygen • Oxygen Devices • Chest Tubes • Chest Lines