Notes--Classification and Taxonomy 1011
advertisement

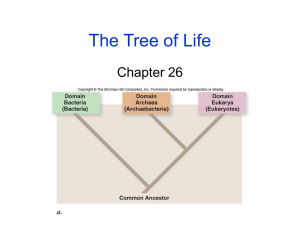
QUIZ: Tuesday 10/18 TEST: Fri. 10/28 Taxonomy a branch of biology that deals with classifying and naming organisms Scientists look at similarities and differences in organisms Aristotle (~360 BC) came up with a system of classifying organisms. o ANIMALS and PLANTS o Based on habits o Very inconsistent Carl Linnaeus (~1735) improved Aristotle’s classification system and his is still used today o Founder of taxonomy For order and organization Ease of adding newly discovered organisms Shows relationships between organisms Beyond language barriers and common names Prokaryote o Organisms that DO NOT HAVE a membrane bound NUCLEUS Eukaryote o Organisms that HAVE a membrane bound NUCLEUS Unicellular Multicellular o Uni- means ONE o Multi- means MANY o Organism made o Organism made up of up of ONE CELL MANY CELLS Autotrophic Heterotrophic o Create their own o Rely on other energy from sun or chemicals o Producers organisms for energy o Consumers Cell structure that surrounds a cell Provides support and protection Can be made up of: chitin, cellulose, peptidoglycan, silica, proteins Kingdom King Phylum Phillip Class Came Order Over Family For Genus Species Good Spaghetti 9 LINNAEAN CLASSIFICATION OF HUMANS Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primates Family: Hominidae Genus: Homo Species: sapiens Two word system using the genus and species of an organism o Genus is always capitalized…species is always lowercase o Both genus and species are underlined or italicized EX: Humans o Homo sapiens o Homo sapiens Ursus arctos (italics) Ursus arctos underlined Always capitalize the first letter of the Genus name!!! 12 Genus - first part of name Always use a capital letter and underline or italics Ex: Homo - humans Felis - cats, tigers, lions Ursus- bears Canis - dogs, wolves, coyotes 13 Species - second part of the name Always with a lower case letter and underline or italics. Ex: sapien - thinking domesticas - cat tigris - tiger familiaris - dog lupus - wolves latran - coyotes 14 Full binomial nomenclature: Genus species Homo sapiens Canis familiaris Felis domesticus Canis lupus 15 Scientists group organisms based on their evolutionary connections A “Family Tree”… Limpets Barnacles Which ones are most closely related?? Crabs Appendages Crab Crustaceans Conical Shells Barnacle Limpet Crab Gastropod Barnacle Limpet Molted exoskeleton Segmentation Tiny free-swimming larva CLASSIFICATION BASED ON VISIBLE SIMILARITIES CLADOGRAM 18 A cladogram is a diagram used to show ancestral relationships between organisms Evolutionary tree of life Derived Characters in Organism Organism 1. Identify which organism is least closely related to the others. 2. Create your branches based on the differences in characters. 3. What trait separates the least closely related organism from the other animals? Derived Character Backbone Legs Hair Earthworm Absent Absent Absent Trout Present Absent Absent Lizard Present Present Absent Human Present Present Present ANALYZING Does your cladogram indicate that lizards and humans share a more recent common ancestor when compared to an earthworm? Where would you insert a frog if you added it to the cladogram? 20 Frog Lizard Earthworm Trout Amniotic Egg Human Hair Legs Backbone 21 Dichotomous Keys Archaebacteria Archaebacteria Protista Bacteria Eubacteria Fungi Eukarya Animalia Plantae Cell Type: prokaryote Cell Wall: not composed of peptidoglycan Body Type: unicellular Nutrition: autotrophic vs. heterotrophic Examples: Ancient bacteria--Extremophiles methanococcus; halophiles Cell Type: prokaryote Cell Wall: composed of peptidoglycan Body Type: unicellular Nutrition: autotrophic & heterotrophic Examples: Common bacteria E. coli, streptococcus, staphylococcus Cell Type: Eukaryotic Cell Wall: silica, calcium carbonate, proteins Body Type: unicellular & multicellular Nutrition: autotrophic & heterotrophic Examples: Misfits like--paramecium, euglena, amoeba Cell Type: eukaryotic Cell Wall: chitin Body Type: unicellular & multicellular Nutrition: heterotrophic (not a plant!) Examples: yeast, morel, puffball, Rhizopus stolonifer (bread mold) Cell Type: eukaryotic Cell Wall: composed of cellulose Body Type: multicellular Nutrition: autotrophic Examples: corn; ferns; roses; pine tree Cell Type: eukaryotic Cell Wall: no cell wall Body Type: multicellular Nutrition: heterotrophic Examples: manatee, shark, snakes, worms, coral, hummingbird, insects….