Ancient Greece and Rome The Ancient Greek City
advertisement

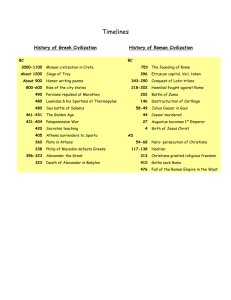
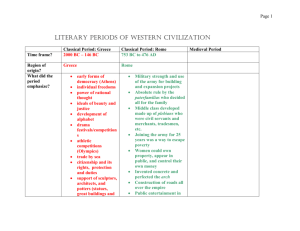
Ancient Greece was not a unified country City-States An independent town or city that governs itself and the land around it. Polis Typical Polis Town or small city Farmland Population less than 20,000 Approximately 100 square miles 500 BC Mostly in Greece along the Aegean Sea Others scattered along the Coast of Asia Minor Asia Minor: another name for the Anatolian Peninsula, where much of Turkey is located Along the coast of the Black Sea Southern Italy Northern Africa The people in the city-states all spoke Greek Some difference in dialects Dialect is a regional variety of a language Non-Greeks were called barbarians When the barbarians spoke only meaningless syllables could be heard Religion Greek Gods Zeus Chief God Hera Wife of Zeus Apollo The sun god Poseidon Sea god Aphrodite Goddess of Love Spent most of their time on Mount Olympus Came down time to time to influence human affairs Marvelous stories were told about the adventures and misadventures of the gods Temples were built to honor the gods Own distinctive forms of government Very innovative when it came to government We still use many of their terms Politics The art of governing a polis Policeman A person who preserves order in the state In the genesis most Greek city-states were ruled by kings. 500 BC Many different forms of government Tyranny Aristocracy Oligarchy Democracy •One man is a dictator •Power is gained illegally •Popular at times Opposition to the rich and helping poor •Few wanted to be ruled by tyrants all of the time Power by the few noble and upper-class families Aristocracy means rule of the best Power was sometimes shared with an assembly made up of citizens, not always Similar to aristocracy Power by only a few people Oligarchy means “rule of the few” The few were not noble families They were wealthy men Power is shared by a large number of citizens Citizens took part in the government Debates Policy Elected officials Greeks seemed to be the first people to experiment with this type of government Very popular among the Greek city-states The city-states loved their independence and individuality They thought it was better to have a local government than to be ruled by a king that lived far away Many of the city-states would get into disagreements and wars This made it easy for foreign countries to invade Greece During times of crisis they might join together to fight the foe but this was the exception Alliances between city states were fragile and short lived Rivalries among them were sturdy and long-lasting Athens vs. Sparta Two of the largest and most powerful citystates One of the largest Greek Polis’ One of the most democratic Not always democratic Monarch Aristocracy Oligargy Democracy Even a few tyrants People were able to participate in the government by 500 BC All citizens were allowed to participate in the Assembly Before making decisions the merits would be debated Decision would be made by a vote Pass by a majority The assembly passed laws, levied taxes and voted on issues such as war and peace The Assembly also had the power to ostracize citizens who might be a problem Ostracize- to banish or send away Votes took place on an ostrakon or piece of pottery If enough people wrote the same name the person had to leave the polis for 10 years The ostracized person was allowed to keep their property during that time The Boule was a smaller council that assisted The Assembly Made up of 500 members chosen by lots Terms were 1 year No-one could serve more than one term They decided which issues need to be brought before the Assembly Athenian Law was divided into two sections Public Laws Had to do with the city state Fine or penalty decided by the Assembly or the Boule Private Laws For people to work out their disagreements Take your neighbor to court and have a jury decide the case Much larger than todays Sometimes as big as 501 citizens The bigger the jury was the less likely to have problems with bribery Most citizens served on a jury at one point in their lives. Strategoi Leaders of the military Elected officials by the Assembly Athens was not completely democratic by modern standards Not everyone in the polis was a citizen Male Atleast 18 years Not a slave Son of two athenian parents All others could not vote in the Assembly or serve on juries Played an important role in religious affairs No political rights No owning of property Always under the control of a man Decided who she would marry Could not participate in the debates Could not attend certain public events Not sent to school Women were to bear children and tend to their families Foreign residents Artisans Craftsmen and merchants Made up a quarter of the population or a third of the population Rich citizens had hundreds of slaves Did not have political rights Freedom could be bought Citizenship could not After slaves, women and children are subtracted there are only about 40,000 people that qualified as citizens. Athens should be remembered as having many people involved in politics Young men were prepared to become good citizens Rhetoric The Art of using language to persuade others Logic, reading, writing, arithmetic and music Learned to play instruments and memorized epic poems Epic poems: long poem that tells the adventures of legendary heroes 2 years of Military instruction Many years of PE Lots of exercise in gymnasiums Gymnasium- to exercise naked Participation in Symposiums The goal of Athenian education was produce solid citizens and well-rounded individuals Spartans required 23 years of military education Education system emphasized military training Inspection at birth Treatment of children Crying Shoes At age of 7 children began their military training Taught to obey without question Little time was spent with reading writing and poetry PE most important subject Taught how to endure great pain Food rations cut when they became teenagers Marriage at 20 Barracks until 30 Dinner with army until 60 Could not fight Could own land Encouraged to participate in sports Expected to raise their sons as warriors Expected to be prepared to lose sons in war “ I bore him so that he might die for Sparta, and that is what has happened, as I wished” Protection against enemies Wall of men the most effective defense Spartans ruled large numbers of slaves Helot Had is much worse than Athenian slaves Spartans made fun of Athenians for treatment of slaves Called helots Outnumbered Spartans 10 – 1 Treated like farm animals Beaten regularly Put to death for complaining Spartan society produced the desired results. The people care more about the polis than their own personal well-being Oligarchy Ruled by 2 kings Suppose to keep each other from becoming tyrants In charge of the army Council of Elders Assembly Elements of monarchy, aristocracy and limited democracy Much less democratic than the Ecclesia of Athens Citizens could not debate Shouting for the candidates Loudest crowd wins Athenians thought this was funny Spartans thought that their traditional way of life was much better than Athenian Society ATHENS SPARTA Held in the city of Olympia Every 4 years A sacred disk was carried to all of the Greek City States Truce An agreement where two or more people agree to stop fighting The truce lasted as long as it took the athletes to travel to Olympia, attend the games, and return home The Olympics were a religious festival in honor of Zeus 776 BC a foot race was added 200 yard race Other events were added and the Games became a regular event Prize for winning was a wreath of olive leaves Honor Athletes became heroes and were immortalized in songs or sculptures They dressed Athenian Style Not even shoes Runners felt that clothing would slow them down Only males and priestesses were allowed to watch Slaves and women put to death for watching Most events were based on skills that were needed for survival Javelin Distance Accuracy while riding a horse Run Wrestle Horse Riding Discus Long Jump Involved carrying weights Pentathlon Pankration 5 events: discus, javelin, long jump, wrestling, 200 yd foot race No rules Except no biting and sticking fingers into opponents eyes 400 yard race While wearing helmet shin guards and carrying a shield The Games lasted until 393 AD Theodosius I Did not like the religious rites in honor of Zeus First Modern Olympics were held in 1896 in Athens The Olympics have been held every 4 years since Not during WWI and WWII 499 BC Miletus Rebels against Persian rule Needed the help of Greek City States Athens agrees to help 498 BC Athenians cross the Aegean Sea and defeat the City of Sardis The other Greek Polis’s decide to join in Athenians went home 495 BC Darius puts down the revolt in Asia Minor Angry with the Athenians Crosses the Aegean sea for revenge Marathon 26 miles from Athens Athenians were badly outnumbered CHARGE Persians broke ranks and fled to their ships 6,000 Persians/192 Athenians After the victory Messenger to Athens announce victory “Rejoice, We Conquer!” And died of exhaustion Marathon was an extremely important battle because the Athenians were filled with pride. Persians didn’t like defeat 480 BC Xerxes determined to conquer all of Greece 100,000 men 600-700 Ships Athens and Sparta Unite 200 -300 Ships 10,000 Men Led by King Leonidas of Sparta The Greeks realized that they could win without a strategy Thermopylae 75 miles north of Athens Narrow pass between high cliffs Only one part of the army could attack at a time Greeks held the pass for 2 days A traitor (Ephialtes) showed the Persians how to slip around the Greeks Leonidas ordered the majority of the army to retreat. 300 left behind The heroism of the Spartans slowed the Persians but did not stop them Xerxes burns Athens to the ground Most of the citizens had been evacuated Persians are set to conquer Greece Xerxes leads with his navy Fleets crash at Salamis Athenian navy lured them to shallow waters Rammed and sunk Persian ships Greek boats were filled with soldiers Defeat of the Persians Xerxes sails home Pausanias The battle of Plataea Persians out of Greece After the Persian War Sparta hurries home to their helots Athens begins to build a mighty empire Many of the poleis feared that the Persians would invade again Wanted to protect themselves from future invasions The Delian League is Established Sparta refused to join Athens plays the leading role Each polis agrees to: Send money or ships to support the league Amount sent determined by Athens Athens begins to treat allies more like colonies Each member of the league had to swear allegiance to Athens No one was allowed to resign from the league Used to fund the Golden Age of Athens This period lasts 75 years From the Persian Wars (479 BC) to the end of the Peloponnesian War (404 BC) Athens produces some of the greatest artistic and achievements the world has ever known One of the leading citizens during the Golden Age Elected to the Strategoi for 30 years An amazing orator “his words were like lightning and thunder” People were swayed by his opinion Hard Worker, and dedicated He did not spend time walking on roads that did not lead to government buildings He did not believe in wasting time attending parties or social events Led the military in victorious campaigns Kept members of Delian League in line Established and supervised Athenian Colonies Convinced the Ecclesia to build bigger and stronger walls to protect Athens Walls to Piraeus Strengthened Athenian Democracy Convinced Ecclesia to pay citizens for government work Enabled the poor the opportunity to participate in the government. Patron of the Arts Rebuild the temples and buildings in the Acropolis Wanted to use money from the Delian League Controversial Pericles used his oratorical skills to persuade the allies The most famous building built under the leadership of Pericles Temple to Athena the Greek Goddess of Wisdom Built between 447 and 432 BC One of the Greatest Treasures of human culture Pericles wanted the building to be a symbol of the wealth, power and prosperity of Athens 2 Architects were recruited Iktinos and Kallikrates, They designed a building that was 230 x 100 x 60 20,000 tons of marble were used Each side of the Parthenon had a row of columns Doric columns Carvings on the side were done by Pheidias The most famous sculptor of Ancient Greece Inside the Temple 40 ft statue of Athena Covered with Gold and Ivory Statue of Athena cost more than the building it was housed in. Destroyed in ancient times A smaller copy still exists Large Theatres were built for drama performances Drama began as Festival in honor of the Greek god of wine Two Types of Drama Dionysus Comedy Tragedy The Theatre of Dionysus 3000 participants each year Comic Aristophanes Tragic Sophocles Euripides Aeschylus Oldest of the four dramatists Fought in the Persian Wars and wrote plays about them Wrote a trilogy called the Orestiea Sponsored by Pericles One scene caused children to go into convulsions and pregnant women had miscarriages Wrote more than 80 plays Only 7 have survived Teenager during the Persian Wars Played roles in performances celebrating the victory Aeschylus’ biggest rival Oedipus the King Most famous play Produced 80-90 plays Won fewer awards than Aeschylus and Sophocles Admired for his psychological insights Comic playwright Made fun of statesmen Pericles Made fun of Dramatists Euripides Made fun of Scholars Socrates Distinctive Pottery Hippocrates Herodotus Father of Medicine Hippocratic Oath Father of History Thucydides History of the Peloponnesian War Sparta and some of its allies form the Peloponnesian League Named that way because of its location Democratic relations between Athens and the Peloponnesian League Deteriorated 431 BC War Breaks out Pericles knew that the Spartan Army was much stronger Athens has a stronger navy Athenian Strategy Avoid meeting Sparta in a land battle Hole up in the walls of Athens Supply the people within the walls via the Navy Attack towns along the coast of the Peloponnesus Pericles convinces the citizens to follow his plan Everyone leaves and seeks refuge in Athens Sparta marches in to find a deserted countryside Burn everything Athenians wanted to fight “Crops will grow back, dead men will not” The strategy is successful in the 1st year Sparta give up Year two Another Spartan land attack Athens retreats behind the walls A plague sweeps through the city 1/4th of the population is killed Lasts 3 years Pericles Dies Pericles is replaced Sparta could not attack Athens would not leave Alcibiades Attack the island of Sicily Renew supplies Attack Sparta on Both sides Some people didn’t trust Alcibiades Athens met a strong resistance Sicily is much stronger Athenian army is divided Those that weren’t killed became slaves in the quarries Alcibiades is ordered to return to Athens Flees to Sparta Tells Sparta of Athens plans Sparta did not trust him Flees to Persia Battle at Sicily shifts the balance of power in the favor of the Spartans Spartans ally with Persia First Naval Victory in 405 BC Athens surrender in 404 BC Sparta and it Allies win the Peloponnesian War Athenians are forced to tear down the walls that once protected them Not allowed to have a navy any more New government set up by Sparta Rule of 30 nobles The nobles were corrupt Athenians Rebel Democracy is restored Sparta allows Athens to be as long as they are peaceful End of the Athenian Empire and the Golden Age As the Athenian Empire crumbles Athenian philosophy bursts into bloom Athens becomes the home of brilliant and influential philosophers Socrates Aristotle Plato All of life’s early questions were answered with Greek Mythology Storm at Sea Poseidon Thunderstorm Zeus World’s Problems Pandora 6th Century BC many people become disenchanted with the explanations that mythology provides Greeks begin to use reason to understand the world The beginning of Philosophy The love of Wisdom Everything is always changing You never step into the same river twice To live long it was important to keep your soul from becoming to wet. 24 at the end of the Peloponnesian War Tried to record the early conversation of Socrates Dialogues were based on things that Socrates might have said Much more idealistic than Socrates Tried to understand what the ideal of goodness was and less time trying to help people recognize whether they were actually living it Started the Academy Lasted 900 years Closed by Justinian because it didn’t teach Christianity Mastery of Mathematics Plato thought it led to pure abstract truth Two worlds Perfect one of forms and ideals Imperfect one that we live in The purpose of philosophy was to identify the perfect forms that life really has in its ideal state By studying mathematics and philosophy we can learn what things are really like. Philosophers should play a central role in society They understand the meaning of truth and justice Did not believe in the idea of Democracy It gave people power that didn’t understand justice Democracy executed Socrates Plato thought that citizens should spend their lives training to be good people Ideal society would teach citizens to control themselves and to act for the good of others Born in 384 BC Studied with Plato for 20 years Started his on school called the Lyceum Collected animals insects and plants Loved to study and dissect them He learned that there is always more than one way to explain things All explanations were important He developed that basics of the scientific research Wrote the Nicomachean Ethics “Virtue, therefore is a kind of moderation or mean as it aims at the mean or moderate amount.” People should avoid extremes of all kinds Studied to see which form of government was the best The responsibility of the government was to create the good life for its citizens Not all people are created equal Men vs. women Aristocrats vs. non-aristocrats Slavery Legacy of the Philosophers Taught us to examine our lives Taught us about observation Beginning of Rome is vague Myth Romulus and Remus Farmers United to form a town Early Rome was ruled by kings 509 Revolt Monarchy is replaced with an aristocratic republic Consuls Senate 2 men that replaced the king Elected by the Senate every year Assembly of 300 Aristocrats Republican Rome is ruled by men chosen from among the Roman elite 2 unequal groups Plebeians Plebeians Patricians Members of the Roman lower class Had few rights No representation Patricians Members of the ruling class or aristocracy Received the best education Were the only members of the senate Plebeians wanted rights They left the city and elected their own officials Tribunes The plebeians forced the patricians to treat them better and to give them a voice in the government Class distinctions faded away Slavery Rights of Women Initially Rome was always defending itself from its enemies 275 BC Rome had conquered all central and northern Italy. Early Roman society was based on its army. Romans loved valor, and bravery, loyalty, duty, honor and fidelity Army began as farmers that were forced to fight to keep their land Later soldiers were given land for service in the Army Fringe benefits Conquered people were organized into provinces Governed by magistrates Troops were left behind to keep order No tribute Conquered people were made citizens of Rome Serve in the Army instead Reward for fighting well Gained rights Better life Rome had a purpose in all of this Everything goes through Rome Rome becomes very rich because of all the plunder Senate became more and more powerful Romans did not have to pay taxes Generals became wealthy Built temples to celebrate their victories Success of the Republic depends on the success of the army Carthaginians are people from Carthage Carthage is in Northern Africa Modern Day Tunisia Wanted to conquer Sicily They were originally Phoenicians Had problems in their attempt Sicilians asked Rome to help them Rome agrees They want to conquer Sicily secretly Beginning of the Punic Wars Battle for control of the western Mediterranean Lasted for more than a century Rome wins the First Punic War Stopped Carthage Took over Sicily Rome had stopped Carthage in Sicily Carthaginians take over Spain Not anywhere else Hamilcar Barca Hannibal Son of Hamilcar Barca Grows up hating the Romans because of defeat in the 1st Punic War Wanted to conquer Rome completely Begins to make plans at the age of 26 The treaty that ended the Punic War established boundaries for Carthage’s empire Hannibal chooses a city close to the border to conquer Saguntum Romans try to protect Sagantum Second Punic War begins Hannibal attacks Rome By land Hannibal and his army are attacked again and again War Elephants through the Alps Hannibal's men suffered greatly People whose territory they marched Hannibal hoped that people would join him on the way No one helped out Rome refuses to surrender The Roman Army attacks the Carthaginians in Spain Completely driven out of Spain Scipio Africanus Wants to go to Carthage and conquer it. Hannibal and his men abandon Rome Return to Carthage 202 BC Scipio is victorious Carthage is forced to pay Rome for its losses Hannibal will not give up After the 2nd Punic war Carthage was still trouble Senator Cato Considered Rome’s #1 enemy Wanted Carthage destroyed completely “Carthage must be destroyed” 150 BC Carthage defends itself against a small army Treaty is broken Rome sends in its armies Carthaginians did not want to fight They were willing to give up their weapons Romans told them they would have to leave Away from the trade routes Rome Attacks Carthage Scipio Aemilianus Adopted Grandson of Scipio Africanus Long and bitter battle Rome wins 250,000--50,000 Survivors sold into slavery City is leveled Land is ploughed Salt is poured in the furrows Rome becomes the dominant power of the Mediterranean Conquered all of Alexander’s kingdoms Greece Greek culture wins the battle Wealthy Romans had Greek sculpture brought to Italy Copies and imitations were made Roman authors imitated Greek authors Roman students studied Greek literature and philosophy Greeks are Romanized Romans are Hellenized Roman culture created youth that looked for power and wealth and honor. This was only possible through the military Julius Caesar was one of these young men Patrician Family Not wealthy Many of the Governors were ruling poorly Rome had to rely on military strength to hold the republic together The army had become professional Became a career for men who joined Most men joined to get rich and achieve higher status They had more loyalty to their generals than Rome Generals could attack their own city Senate created a law to prevent this Foreshadowing Tall Well built Dark brown eyes Intelligent Good Sense of Humor Liked to look good Hair trimmed Shaven face Almost bald First comb-over Commanded part of the Army Began to make friends and allies Spent money to become popular Pompey and Crassus Schemed together Pass laws Kept power from their enemies Caesar is Elected to consul Becomes one of the most successful Generals Caesar expands the Roman Republic Conquers Gaul Invaded Britain in 55 After conquering Gaul Caesar wants to be in the Consul again Not good the first time No alliance with Pompey and Crassus Pompey realized Caesar was using him Caesar told to come to Rome for his election Caesar Crosses the Rubicon River Not allowed to bring his army Pompey would have him arrested “the die is cast” “crossing the Rubicon” Civil war begins Caesar Becomes a dictator Legally dictatorships could only last 6 months Placed his face on coins Changed the name of month Quintilis Julius (July) Always wore a laurel wreath Something only kings did Symbol of conquerors and victors Other work Worked to make more people citizens of Rome Improve court system Help others avoid debt Caesar had a hard time trusting others and wanted complete control Many people blamed Caesar for the collapse of the Roman Republic All of the pressure made Caesar constantly sick Epilepsy Not a great dictator Too arrogant Dismissed his body guards 44 BC Forced the Senate to vote for him as dictator for life Caesar never noticed the pain that he caused for others Romans did not want to see kings again One month after being elected dictator for life 60 “friends” came to pay him a visit Dozen of them drove their weapons into him Brutus and Cassius “Et tu, Brute?” Great General Increased the Power of Rome Destroyed the Republic Link between what Rome was and would become Another Civil War broke out Lasted 13 years Octavian becomes sole ruler Defeats Cassius and Brutus Marc Antony Becomes the first roman emperor Named Caesar Augustus JULIUS CAESAR Tall Well built Dark brown eyes Intelligent Good Sense of Humor Liked to look good CAESAR AUGUSTUS Short Not good looking Small teeth Dirty, widely separated Didn’t care how he looked Bad Health Liked to sleep in Avoids battle Not known as a great soldier Very good administrator Romans no longer had pride in the Roman Empire Felt like the government didn’t care Make Rome Strong Get the people to believe in the Empire Ambitious Building Program Architects, sculptors, artists Build beautiful buildings Copied the Greeks Created a new image for Rome that the citizens could be proud of “inherited brick and left it marble” Built arches celebrating Roman history Rebuilt the temples Re-established religion Romans could believe in the old gods and goddesses Gave the Romans a sense of identity A New Beginning for Rome Augustus became a patron of the arts Friend named Maecenas Invited poets to write about Augustus and what he was doing for the empire. Publius Vergilius Maro, AKA Virgil Virgil wrote a poem that celebrated the glory of Rome. The poem isn’t completely about Augustus The poem that Virgil wrote Becomes the greatest epic poem of Ancient Rome Story of Aeneid Aeneas Founds Rome Trouble along the way Dido Nothing could stand in his way Virgil dies before completing it Augustus loves the poem Shared responsibilities with the Senate Tried to not become too arrogant Called himself Princeps “First Citizen” Senate calls him Imperator “He who commands” Augustus strengthens roman law 2 groups Roman Citizens 30 Legions Commanded by senators that had to report to senators Non Citizens Commanded by noblemen No more getting money solely by plunder Special Treasury Avoiding another Julius Military was mainly used to keep order Pax Romana Roman peace Lasts 200 years Establishes the Empire and Rules it well Worked well with the senate Helped the Citizens to feel proud for Rome Used army for peace Peace lasted Centuries