The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale
advertisement

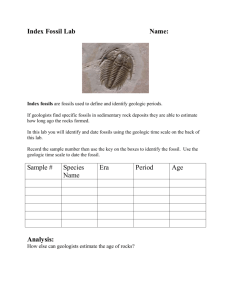
The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale KEY CONCEPT Specific environmental conditions are necessary in order for fossils to form. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale Fossils can form in several ways. • Permineralization occurs when minerals carried by water are deposited around a hard structure. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale • A natural cast forms when flowing water removes all of the original tissue, leaving an impression. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale • Trace fossils record the activity of an organism. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale • Amber-preserved fossils are organisms that become trapped in tree resin that hardens after the tree is buried. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale • Preserved remains form when an entire organism becomes encased in material such as ice. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale • Specific conditions are needed for fossilization. • Only a tiny percentage of living things became fossils. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale Radiometric dating provides an accurate way to estimate the age of fossils. • Relative dating estimates the time during which an organism lived. – It compares the placement of fossils in layers of rock. – Scientists infer the order in which species existed. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale • Radiometric dating uses decay of unstable isotopes. – Isotopes are atoms of an element that differ in their number of neutrons. neutrons protrons The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale • Radiometric dating uses decay of unstable isotopes. – Isotopes are atoms of an element that differ in their number of neutrons. – A half-life is the amount of time it takes for half of the isotope to decay. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale KEY CONCEPT The geologic time scale divides Earth’s history based on major past events. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale Index fossils are another tool to determine the age of rock layers. • Index fossils can provide the relative age of a rock layer. – existed only during specific spans of time – occurred in large geographic areas • Index fossils include fusulinids and trilobites. The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale The geologic time scale organizes Earth’s history. • The history of Earth is represented in the geologic time scale. 100 250 550 1000 2000 PRECAMBRIAN TIME This time span makes up the vast majority of Earth’s history. It includes the oldest known rocks and fossils, the origin of eukaryotes, and the oldest animal fossils. Cyanobacteria The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale • Eras last tens to hundreds of millions of years. – consist of two or more periods – three eras: Cenozoic, Mesozoic, Paleozoic The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale • Periods last tens of millions of years. – most commonly used units of time on time scale – associated with rock systems. • Epochs last several million years.