Theory X
advertisement

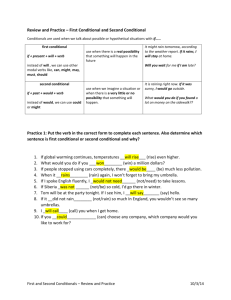
Managing people Socialising and entertaining Douglas McGregor formulated the famous Theory X and Theory Y: Theory X is the idea that people instinctively dislike work and will do anything to avoid it Theory Y is the view that everybody has the potential to find satisfaction in work Some people have suggested the Theory W (“whiplash”) which is the idea that most work is done under conditions of slavery Most managers still choose the Theory X: They believe that their subordinates need constant supervision if they are to work effectively They think that decisions must be imposed from above without consultation The managers who work in this way are called authoritarian managers Different cultures have different ways of managing people: Some cultures prefer frequent consultations in decisionmaking (all members contribute to this process) This is called management by consensus: a group decision that is acceptable to all members of the group, a general agreement A recent trend in managing people is To encourage workers to use their own initiative (to make decisions on their own without asking managers first) This is called empowerment (employees improve operations, reduce costs and improve product quality) Empowerment is used to establish better relationships with customers Empowerment is linked to the idea of delegation: Delegation is handling a task over to a subordiante If you delegate you transfer the decision-making responsibility to some subordinate organisations You give someone the authority to undertake specific activites or decisions Another trend is virtual management: In virtual management the teams of people are not physically present at the work site, they are linked by e-mail and the Internet and they work from their own premises (homes) Another word for virtual management is off-site management In managing people the managers need to be good at: Observing: they must understand the behaviour, the strengths and weaknesses of their staff Listening: in order to learn about their staff’s problems Asking questions: to find out all the information they need to make the right decisions Speaking: in order to communicate their objectives clearly to all their staff “The international manager” In recent years, many companies have expanded globally through mergers (uniting), joint ventures (two or more companies or people doing business together) and cooperation with foreign companies. This means that many managers work abroad as a part of a multicultural team Still, many of them have difficulties adapting to the new culture. The first example of failure in this segment is a German manager with IBM who took up a position as product manager in England. He stopped the employees from leaving the company building at lunchtime (they had the habit of going to a pub). This made him unpopular. The problem is he didn’t think of cultural differences. It is true that IBM didn’t allow drinking during working hours, but he didn’t understand that staff in other countries might be more flexible in applying the rule. The second example is about an American manager who came to France. He was unable to win the trust of his staff although he tried all kinds of ways to do so. He set clear goals, worked longer hours, participated in all the projects, visited offices and even took employees out to lunch one by one. To them, he seemed more interested in getting the job done. By walking around and visiting everyone in their offices, he gave the impression that he was “checking up” on staff. Socialising and entertaining Some useful expressions Socialising is an important part of good management: Being on time: how late do you have to be before you are considered “late”? The way people dress: the company’s policy might also be smart-casual (dressing smartly but in casual clothes). What about dress-down Friday? Does it exist in your country? (a company allows people to dress less formally than on other days) How you address people (first names or family names?) Giving gifts: What should you give? Does the person unwrap them immediately or wait till later? (to say thanks you usually say: That’s very kind of you.) Shaking hands/kissing/hugging/bowing : when is it appropriate? Making excuses: conversation: It’s very kind of you, but... I’d like to take it easy if you don’t mind. It’s very kind of you, but another time perhaps. Making What do you like to do in your spare time? Where are you going for your holiday this year? Can you tell me about any interesting places to visit? What about you? Showing interest: Saying goodbye: Interesting! Really? Thanks very much for your hospitality. I really enjoyed the meal. Thanks for showing me round the city. I’ll be in touch soon. Goodbye. All the best. Word building Conditionals Word building: complete the missing words in the columns NOUN Patience Calmness Weakness Toughness Emotion Consistency Sympathy ________ Enthusiasm _________ ADJECTIVE patient ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ formal ______ creative OPPOSITE ________ nervous strong ______ _______ ________ ________ ________ ________ __________ Conditionals: First conditional: a possible condition and its probable result if + present simple, will + base form of a verb If we meet our sales target, we’ll get a bonus. Second conditional: an unlikely condition and its probable result if + past simple, would + base form of the verb If he listened more, he would be a better manager. Conditionals are often used when negotiating. Complete the sentences with: will, would, won’t, wouldn’t I’m sure they ____ continue doing business with you if they weren’t satisfied. If he was able to deal with pressure, he _____ be an excellent negotiator. If I lose this order, I’m afraid it _____ affect my commission. If you don’t increase the discount, we _____ be able to increase the size of our order. We ____ have to turn to another supplier if you were able to deliver this month. Complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs in brackets: We ____ (give) you a 15% discount if you pay cash. If they ____ (pay) late, we would close their account. If you ______ (deliver) this week, we will place a bigger order. We _____ (deliver) this week if you paid cash. We will give her a free gift if she ______ (increase) her order. If they make a concession, we _____ (do) the same. If you place regular orders, we _____ (cover) insurance.