Operations - Providence University College
advertisement

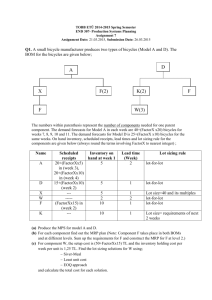
Operations 11 473.31 Fall 2015 Bruce Duggan Providence University College Summary Materials Requirement Planning ties together all the major functions of a firm. MRP system takes information from • the master schedule • bill of materials, and • inventory records and “explodes” the process into detailed schedules that show the exact timing of needed parts in the future. Learning Objectives Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is MRP is and where is it best applied? What is the source of the information used by the MRP system? How do you do an MRP “explosion”? How do you calculate order quantities in MRP systems? What are the extensions of MRP? 11-26 Material Requirements Planning • Materials Requirements Planning (MRP) is a means for determining the number of parts, components, and materials needed to produce a product • MRP provides time scheduling information specifying when each of the materials, parts, and components should be ordered or produced • Dependent demand drives MRP • MRP is a software system Where MRP Can Be Used MRP System Structure MRP system has 3 sources of info: 1. Master Production Schedule (MPS) 2. Bill Of Materials (BOM) 3. Inventory Record File MRP System Structure Info sources: 1. Master production schedule states the number of items to be produced during specific time periods. o creates schedules identifying the specific parts and materials required to produce end items o determines exact unit numbers needed o determines the dates when orders for those materials should be released, based on lead times MRP System Structure Info sources: 2. Bill Of Materials (BOM) identifies the specific materials used to make each item and the correct quantities of each. o Materials, parts, components o Production sequence o Modular BOM is the term for a buildable item that can be produced and stocked as a subassembly. o Super BOM includes items with fractional options. MRP System Structure Info sources: 3. Inventory Record File o contains data such as # of units on hand # of units on order o cach inventory item carried as a separate file status according to “time buckets” o pegging identify each parent item that created demand MRP System Structure MRP System Structure MRP System Structure MRP System Structure MRP System Structure An Example Using MRP Copyright © 2013 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited An Example Using MRP An Example Using MRP An Example Using MRP An Example Using MRP An Example Using MRP An Example Using MRP Lot Sizing in MRP Systems Lot sizes are the part quantities issued in the planned order receipts and planned order release sections of an MRP schedule. • Lot-for-lot (L4L) sets the planned order to exactly match the net requirements. • Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) explicitly balances set-up and holding costs. Lot Sizing: Lot-for-Lot Lot Sizing: EOQ 11-22 Extensions of MRP Capacity Requirement Planning (CRP) • revises the MRP schedule based on capacity requirements Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP) • refers to an MRP system linked to the other functions in the firm Distribution requirement planning (DRP) • uses MRP logic in the planning of distribution inventories LO5 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Copyright © 2013 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited 11-24 End of Chapter 11