2014-2015 Formula Writing Note Packet
advertisement

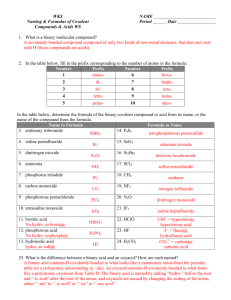
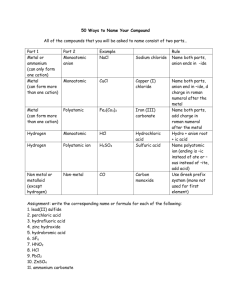
Name: ________________________________ IONS – MONATOMIC CATIONS Main Group Elements 1A I & II II & III II & IV Charge 1+ 2A 2+ 3A 3+ Examples: d –block elements Name Ag+ Silver Cd2+ Cadmium Mn2+ Manganese (II) Ni2+ Nickel (II) Zn2+ Zinc Stock Latin Cu+ Copper (I) Cuprous Cu2+ Copper (II) Cupric Hg2 2+ Mercury (I) Mercurous Hg2+ Mercury (II) Mercuric Fe2+ Iron (II) Ferrous Fe3+ Iron (III) Ferric Co2+ Cobalt (II) Cobaltous Co3+ Cobalt (III) Cobaltic Cr2+ Chromium (II) Chromous Cr3+ Chromium (III) Chromic Pb2+ Lead (II) Plumbous Pb4+ Lead (IV) Plumbic Sn2+ Tin (II) Stannous Sn4+ Tin (IV) Stannic IONS – POLYATOMIC Polyatomic Ions Name NH4 + Ammonium C2H3O2 - Acetate BrO4 - Perbromate BrO2 - Bromate BrO3 - Bromite BrO - Hypobromite ClO4 - Perchlorate ClO3 - Chlorate ClO2 - Chlorite ClO - Hypochlorite IO4 - Periodate IO3 - Iodate IO2 - Iodite IO - Hypoiodite CN – Cyanide HCO3 - Bicarbonate (Hydrogen carbonate) HSO4 - Bisulfate (Hydrogen sulfate) MnO4 - Permanganate NO3 - Nitrate NO2 - Nitrite OH - Hydroxide CO3 2- Carbonate SO4 2- Sulfate SO3 2- Sulfite CrO42- Chromate Cr2O72- Dichromate PO4 3- Phosphate IONS – ANIONS The anions are determined by the group number they are located in on the periodic table. This can be easily completed by subtracting the group number the element is located in from the number eight. When naming the anion, the ending portion of the name (such as –ine) is removed and –ide is added. Nonmetal Anion Name of Anion Fluorine F- Fluoride Chlorine Cl- Chloride Bromine Br- Bromide Iodine I- Iodide Oxygen O2- Oxide Sulfur S2- Sulfide Nitrogen N3- Nitride Phosphorus P3- Phosphide Prefixes 1 mono 2 di 3 tri 4 tetra 5 penta 6 hexa 7 hepta 8 octa 9 nona 10 deca 3 Naming systems: 1. Ionic Naming – Used when a metal or polyatomic cation and a nonmetal or polyatomic anion bond. This system uses the charge of the ions to determine the name and/or formula. 2. Molecular Naming – Used when two nonmetals bond. This system uses prefixes to determine the name and/or formula. 3. Acid Naming – Always starts formula with H and always has Acid in the name. Uses the anion’s name to determine the name and/or formula. Ionic Naming: Used when a metal or polyatomic cation and a nonmetal or polyatomic anion bond. This system uses the charge of the ions to determine the name and/or formula. When given a formula: Say or write the cation’s name followed by a space and then the anion’s name. When given a name: Write down each ion’s symbol including its charge. Use the numeric part of the cation’s charge to tell how many anions you need (Cross charges). Use the numeric part of the anion’s charge to tell how many cations you need. Reduce if possible to the lowest whole number ratio. When a hydrate is present: Name or write the formula for the ionic compound just the same as you would otherwise. Use the prefixes to determine the correct number of hydrates (waters) and write H2O if writing the formula or prefix - “hydrate” if naming the compound. Practice problems: 1) Ferrous oxide -FeO 6) CuO Cupric Oxide 2) Calcium fluoride CaF2 7) 3) Aluminum sulfide Al2S3 8) Hg2I2 Mercurous Iodide 13) CoO Cobaltous Oxide 4) Cobalt (II) bromide CoBr2 9) Sr3N2 Strontium Nitride 14) NiF2 Nickel (II) Fluoride 5) Chromic nitride CrN 10) PbS2 Plumbous Sulfide 15) CdO Cadmium Oxide MgCl2 Magnesium Chloride 11) Sn3P2 Stannous Phosphide 12) Cr2S3 Chromic Sulfide Polyatomic Ionic Compounds Practice Problems: 1) Zinc Nitrite Zn(NO3)2 4) Sn(BrO2)2 Stannous Bromite 2) Calcium Permanganate Ca(MnO4)2 5) Ag2CO3 Silver Carbonate 3) Iron (III) Carbonate Fe2(CO3)3 6) Al(NO3)3 Aluminum Nitrate Hydrate Practice: 1) MgSO4· 7H2O Magnesium Sulfate heptahydrate 5) Sodium carbonate monohydrate Na2CO3 ∙H2O 2) CuSO4 · 5H2O Cupric Sulfate pentahydrate 3) Pb(C2H3O2)2 · 3H2O Plumbous Acetate Trihydrate 6) Potassium carbonate decahydrate K2CO3 ∙10H2O 7) Ferric chloride hexahydrate FeCl3∙ 6H2O 4) MgCl2 · 6H2O Magnesium Chloride hexahydrate 8) Barium chloride dihydrate BaCl2∙ 2H2O ∙ Molecular Naming: Used when two nonmetals bond. This system uses prefixes to determine the name and/or formula. When given a formula: Say or write the prefix for the number of the first element present (if more than one) followed by the first element’s name. Next write the prefix for the number of the second element represented in the formula followed by the name of the second element as if it were an anion (see the chart on page 3). When given a name: Write down each ion’s symbol. Use the prefixes of each to tell how many you need. Practice problems: 1) NO Nitrogen Monoxide 2) BI3 Boron triiodide 5) PCl4 Phosphorous tetrachloride 9) Carbon monoxide CO 10) Diphosphorus pentaoxide 3) NO2 6) SeCl4 11) Carbon tetrafluoride 4) AsCl5 7) SBr6 12) Tetraphosphorus decaoxide 8) Dinitrogen monoxide Acid Naming: Always starts formula with H and always has Acid in the name. Use the anion’s name to determine the name and/or formula. 1. Binary Acid – Starts with “H” and has no “O” When given a formula: Always start with “hydro” then the name of the name of the element minus its ending and add “ic”. Always add the word acid to the end. When given a name: Write the symbol of the element referenced between “hydro” and “ic”. Determine the charge it would have as an anion. Then write H and the number from the charge before the symbol from the first step. 2. Oxy-Acid – Starts with “H” and has at least one “O” When given a formula: Write the name of the anion (after the H). If it ends with “ate” replace with “ic”. If it ends with “ite” replace with “ous”. End with the word Acid. Be careful with sulfur and phosphorus anions because they gain a syllable. When given a name: Write the formula of the anion referenced before acid. Remember if it ends with “ic” replace with “ate”. If it ends with “ous” replace with “ite” Determine the charge, then write H and the number from the charge before the symbol from the first step. Practice problems: 1) HI 8) H3PO4 2) H2S 9) Hypochlorous Acid 3) HBr 10) Perchloric Acid 4) Hydrochloric Acid 11) Carbonic Acid 5) Hydrofluoric Acid 12) Nitrous Acid 6) H2SO4 7) HNO3