Colonial War and the War in the Middle east
advertisement
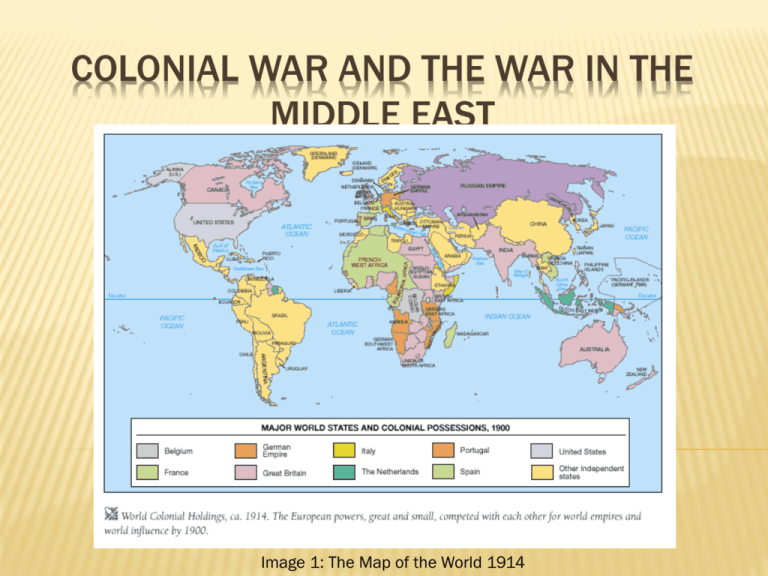
COLONIAL WAR AND THE WAR IN THE MIDDLE EAST Image 1: The Map of the World 1914 BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Africa Germany’s new policy of Weltpolitk changed the balance of the major powers Germany now also wanted their “place in the sun” Before World War 1 Germany had acquired colonies all over the world, but did not match the empires of France and especially Britain However, German Generals were sure that with a War in Africa they could keep a multitude of British troops away from the Western Front Middle East After the Balkan Wars and conflicts with Russia the Ottoman Empire had lost over one third of their Empire The Young Turk movement sought to modernize the Ottoman Empire and after their revolution in 1908 they had gained considerable power The new Ottoman Empire saw Germany as a potential ally and Kaiser Wilhelm the second saw himself as a friend to the Muslim World AFRICAN THEATRE OF WAR 1. 2. Three Main Campaigns 1. West Africa Campaign (Togoland and Kamerun) 2. East Africa Campaign (German East Africa: Modern day Tanzania, Rwanda and Burundi) 3. South West Africa Campaign (German South West Africa: Modern day Namibia) The Main Belligerents 1. 2. German Empire and the Boers United Kingdom (South Africa and Australia), France, Belgium, Italy, Portugal, Liberia. Image 2: Map of Colonial Africa Before World War 1 WEST AFRICA CAMPAIGN The German colonies of Togoland and Kamerun were completely surrounded and poorly equipped. However they held strategic importance (4 long wave radio transmitters used in naval warfare and coal refueling points) The small colony of Togoland was conquered by British and French troops in only 20 days. (August 7th to August 27th 1914) Only 44 European forces died (all French and British) but over 2500 Africans The Fight for Kamerun was much more difficult The British attack from Nigeria had failed on all three attempts (guerilla warfare was favored by German troops all over Africa as they were outnumbered and outgunned) With the assistance of Belgian and French troops they were able to capture the capital in 1914 The War in West Africa was pretty much over by November after German troops fled to the neutral Spanish colony of Guinea Image 3: African troops fighting for Germany SOUTH-WEST AFRICA CAMPAIGN British Troops tired to invade German South West Africa on the 25th of September 1914 but were defeated and pushed back. A Second attack was stopped short after the Boers revolted Over 12 thousand rebels under Maritz, supplied and supported by Germany rose up against the British colonialists. It took nearly half a year until the British could silence the rebellion but by February 1915 the leading Boer rebels had been arrested. In the March of that year the second and final offensive on German South-West Africa began The German troops were completely outnumbered (only around 3000 troops supported by 7000 citizens verse over 67,000 south African troops) The capital of Windhoek was captured on the 12th of May but fighting continued until the German forces surrendered at Khorab on the 9th of July 1915. Britain would rule this German territory for over 75 years Image 4: 7 Inch naval Gun of South African troops EAST AFRICA CAMPAIGN Colonel Paul Emil von Lettow-Vorbeck was the leading German commander and a military genius Completely outnumbered and out gunned (all supply routes to East Africa were cut after March 1916) he was still able to withstand the enemy forces for the duration of the war. The Germans fought a guerilla war (raids, hit and run attacks and ambushes) British troops started the fighting on the 5th of August 1914 assaulting the coast with multiple naval attacks The battle in East Africa would never see a German defeat even though they had never more than 18 thousand troops and the allies over 5 times that. The British troops could not deal with the harsh conditions of the jungle, (loosing over 50,000 horses to the tsetse fly) and the harsh terrain slowed their progress greatly. They hired over 1 million Africans to carry their supplies, one fifth of them would die due to mall nutrient and disease. Von Lettow had hoped to keep British forces away from the western front and keep them focused in East Africa. However this did not work. Most of the British troops were Indian (India would supply over 1 750 000 troops over the course of the entire war) or South African. The German surrender on the 14th of November 1918 marked the end of the east African Campaign. Von Lettow surrendered on the 25th of November with out a single major defeat and was celebrated as a German war Hero. Image 5: German troops crossing a river in the jungle of East Africa AFTER THE WAR The end of the African campaigns marked the end of German colonialism and Weltpolitik Britain, France and Belgium would split up the African colonies they had taken from the Germans However Allies dependency on their colonies and the devastation of African land brought up cries for independency African nationalism would arise and many colonies would gain their independence after the 2nd world war MIDDLE EAST THEATRE OF WAR 1. Five Main Campaigns 1. Sinai and Palestine Campaign 2. Mesopotamian Campaign 3. Caucasus Campaign 4. Persian Campaign 5. Gallipoli Campaign 2. The Main Belligerents 1. Ottoman Empire, German Empire, Austria- Hungary, Azerbaijan Democratic Republic 2. Russian Empire, British Empire, France, Armenia and Italy Image 6: Map of the Middle East before World War 1 FIRST YEAR OF THE WAR 1914 The Ottoman Empire signed a secret treaty with Germany and entered the war on the side of the Alliance The major Battles were fought between Ottomans and Russians in the Caucasus Ottoman troops advance through the Persian empire but must re organize their troops due to the fighting in the Caucasus. The Battle of Sarikamish (Caucasus) costs over 100,000 lives. Neither army is willing to budge. Image 7: Russian soldiers in the Forest of Sarikam SECOND YEAR OF WAR 1915 British and French troop start the Gallipoli Campaign in order to capture Istanbul and secure a sea route to and from Russia. It last from the 25th of April to the 20th of December 1915. There were over 500,000 casualties. This campaign allowed the Russian Army to regroup and relieve the pressure on the British Western front. In late February of 1915 the Ottoman Empire tries to seize the strategically important Suez canal. Britain however is well prepared and stops the advance. Britain is successful in Mesopotamia, defeating the Ottomans on multiple occasions. However the good new is overshadowed by losses in Gallipoli. Ottoman troops are weak and badly organized in the Caucasus. The Battle of Gallipoli is sucking major resources while the Russians are able to reinforce their troops. Arabian Rebels join forces with the British. They seek a united Arabia with out Turkish influence and a independent Palestine, which Britain promises to both them and British Jews at home. On the 20th of December 1915, British troops started to flee from the Battle of Gallipoli. The Evacuation of the troops had been completed by January 1916. Image 8: Mustafa Kemal, leader of Turkish troops in Gallipoli THIRD YEAR OF WAR 1916 Image 9: Sharif Hussein bin Ali of Mecca The Turkish troops cannot withstand the Russian Offensive. Russians enter Northeastern Turkey in early 1916. Sharif Hussein bin Ali of Mecca (One of the most powerful people in all of Arabia) Is convinced to start a revolt against the Ottoman Empire. T.E. Lawrence (more commonly known as Lawrence of Arabia) assists this revolt. The reports of this solider serve as a great moral boost back at home. The Turkish forces desperately try to attack the Suez canal (objective is either to capture it, or destroy it). This second attempt fails and they are forced to retreat to Palestine. British troops follow and starts two offensives against Gaza both are unsuccessful. Britain sees the need to send in new reinforcements. THE FINAL YEARS OF WAR 1917-1918 After the failed attempt to take Gaza, British troops reorganize and take Baghdad in March. With the help of Arabian rebels the British troops are able to dominate the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. On the 9th of November 1917 they take Gaza in their third attempt The Russians and the Ottoman Empire sign the Armistice of Erzincan on the 16th of December 1917 after the communist revolution in Russia. The British troops capture Jerusalem just before Christmas. This is used as a propaganda tool to keep the population happy. While the British are winning in the Middle east they are in a stale mate on the western front. A final Offensive against the Ottoman empire is delayed. The Spring Offensive of the Germans requires full attention of the British troops. However after reinforcements arrive from India, Britain defeats the Ottoman Empire in the Battle of Megiddo. (September, 1918) Though the Ottomans win multiple battles verse the newly created Armenian state (Battle of Baku) it become clear they can’t win the war. After the loss of Damascus on the 1st of October and the loss of Aleppo on the 26th they sign the Armistice of Mudros on the 30th of October 1918, marking the end of the war in the middle east. Image 10: British troops around Jerusalem AFTER THE WAR Britain looses over 550,000 troops in the Sinai and Palestine campaign alone. (90% percent of which die to battle unrelated causes) Turkish troops lost over 2 million. After the signing of the armistice, British and French troops occupy Istanbul. (13th of November, 1918) The Paris Peace Conference in 1919 split up the old Ottoman Empire. Britain and France take the majority of the land for themselves, creating protectorates and mandates. The Arabian rebels were denied their own free state. The Ottoman empire would wage a further war, for its independence. The four year long war would lead to the establishment of a Independent Turkish republic on the 29th of October, 1923. BIBLIOGRAPHY Image 1: http://4.bp.blogspot.com/__C-FrnvFfFk/SD_420ArzJI/AAAAAAAAAAQ/K_mnfLzYewY/S1600R/KISH_25_578.gif Image 2: http://www.anandarooproy.com/images/portfolio/slide/image/57/31-Africa-1914-v2.jpg?1152870772 Image 3: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/86/Cameroonian_troops_in_World_War_I.jpg Image 4: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/3c/British4.7InchNavalGunPercyScottCarriageSWAfricaSandWW I.jpg Image 5: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c2/Bundesarchiv_Bild_105-DOA3100%2C_DeutschOstafrika%2C_Artillerie.jpg Image 6: http://unimaps.com/mideast1914/mainmap.gif Image 7:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Sarikam.jpg Image 8: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:GMK_Gallipoli.jpg Image 9: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/fb/Sharif_Husayn.jpg Image 10: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Capture_of_Jerusalem_1917d.jpg Online sources: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_Eastern_theatre_of_World_War_I#1918 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_War_I http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/African_theatre_of_World_War_I http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/worldwars/wwone/ BBC documentary “The First World War” (watched on YouTube)