Chapter 2: Frequency Distributions
advertisement
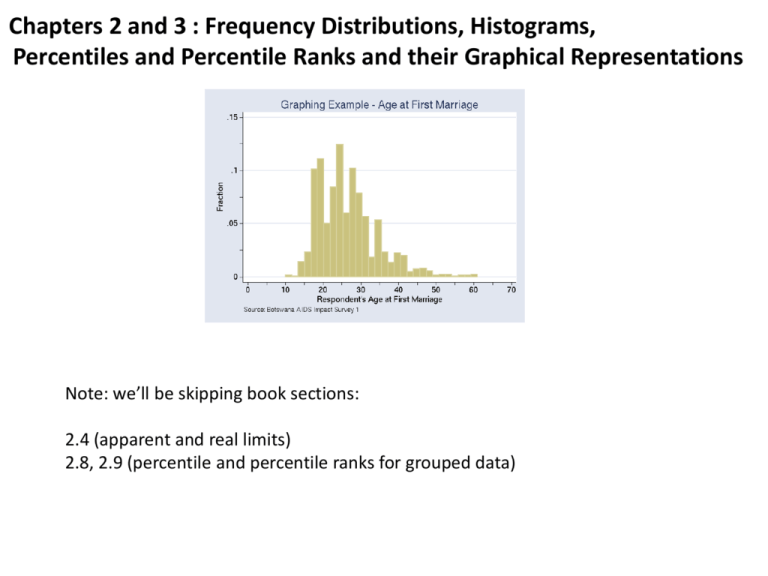
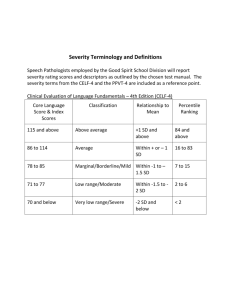
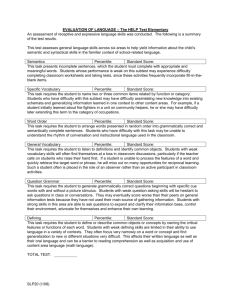
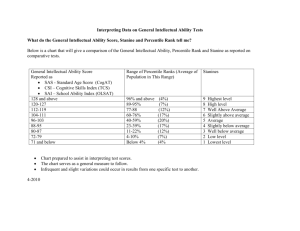
Chapters 2 and 3 : Frequency Distributions, Histograms, Percentiles and Percentile Ranks and their Graphical Representations Note: we’ll be skipping book sections: 2.4 (apparent and real limits) 2.8, 2.9 (percentile and percentile ranks for grouped data) Chapter 2: Frequency Distributions, Histograms, Percentiles and Percentile Ranks How can we represent or summarize a list of values? frequency distribution: shows the number of observations for the possible categories or score values in a set of data. Can be done on any scale (nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio). Often represented as a bar graph (Chapter 3). Example of a frequency distribution for nominal scale data: 2008 Auto sales by country: Japan: 11,563,629 China: 9,345,101 US: 8,705,239 Germany: 6,040,582 South Korea: 3,806,682 Brazil: 3,220,475 Car sales drawn as a histogram 12 Japan: 11,563,629 China: 9,345,101 US: 8,705,239 Germany: 6,040,582 South Korea: 3,806,682 Brazil: 3,220,475 Car Sales in 2008 (millions) 10 8 6 4 2 0 Japan China US Germany South Korea Brazil This histogram shows the proportion of members for each category. Distribution of all M&M's. Ice Dancing , compulsory dance scores, 4 Winter Olympics 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 96.12 92.75 89.62 85.36 84.58 83.89 83.12 80.47 80.3 79.31 76.73 74.25 72.01 68.87 63.73 59.64 Making histograms from interval and ratio data We need to bin the raw scores into a set of class intervals. How do we decide these class intervals? Be sure the intervals don’t overlap, have the same width, and cover the entire range of scores. Use around 10 to 20 intervals. Use a ‘sensible’ width (like 5, and not 2.718285) Make the lower score a multiple of the width (e.g. if the width is 5, a lower score should be 50, not 48) If a score lands on the border, put it in the lower class interval. Ice Dancing , compulsory dance scores, Winter Olympics n=23 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 96.12 92.75 89.62 85.36 84.58 83.89 83.12 80.47 80.3 79.31 76.73 74.25 72.01 68.87 63.73 59.64 Let’s use a class interval width of 5 points, with a lowest score of 55. Class Intervals Frequency (f) 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 1 2 2 3 1 2 5 2 2 1 1 1 Count the number of scores in each bin to get the frequency Histogram of Ice Dancing Scores (frequency) Frequency (f) 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 1 2 2 3 1 2 5 2 2 1 1 1 5 4 Frequency Class Intervals 3 2 1 0 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 Ice Dancing Score Relative frequency n=23 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 96.12 92.75 89.62 85.36 84.58 83.89 83.12 80.47 80.3 79.31 76.73 74.25 72.01 68.87 63.73 59.64 Class Intervals Frequency (f) 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 1 2 2 3 1 2 5 2 2 1 1 1 Relative frequency (prop) .0435 .0870 .0870 .1304 .0435 .0870 .2174 .0870 .0870 .0435 .0435 .0435 Relative frequency (%) 4.35 8.70 8.70 13.04 4.35 8.70 21.74 8.70 8.70 4.35 4.35 4.35 Divide by the total number of scores to get relative frequency in proportion Then multiply by 100 to get relative frequency in percent Relative frequency histogram of Ice Dancing Scores (frequency) 25 Relative Frequency (%) Relative Class Intervals frequency (%) 110-115 4.35 105-110 8.70 100-105 8.70 95-100 13.04 90-95 4.35 85-90 8.70 80-85 21.74 75-80 8.70 70-75 8.70 65-70 4.35 60-65 4.35 55-60 4.35 20 15 10 5 0 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 Ice Dancing Score Choosing your class intervals can have an influence on the way your histogram looks interval width 10 interval width 5 5 Frequency Frequency 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 4 3 2 1 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Ice Dancing Score 0 60 interval width 3 interval width 1 2 Frequency Frequency 3 2 1 0 80 100 Ice Dancing Score 60 80 100 Ice Dancing Score 1 0 60 80 100 Ice Dancing Score These three graphs have the same class intervals on the same scores! 5 5 3 4 2 Frequency Frequency 4 1 Frequency 0 5 4 3 2 1 0 60 70 80 90 100 Ice Dancing Score 110 3 2 1 60 70 80 90 Ice Dancing Score 100 110 0 60 80 100 Ice Dancing Score When possible, include zero on your y-axis. Not like this When possible, include zero on your y-axis. y-axis: Like this Enrollment (Millions) 8 6 4 2 0 As of March 27 March 31 Goal As of March 27 March 31 Goal Not like this Enrollment (Millions) 7 6.8 6.6 6.4 6.2 6 “Fox News Apologizes For Obamacare Graphic, Corrects Its 'Mistake‘” Percentile ranks and percentile point: Percentile Point: A point on the measurement scale below which a specific percentage of scores fall. Percentile Rank: The percentage of cases that fall below a given point on the measurement scale. Percentile ranks are always between zero and 100. Growth charts convert percentile points to percentile ranks At 30 mos. P95 = 36lbs Percentile ranks and percentile point: What is the percentile rank for a percentile point of 100? In other words, What proportion of scores fall below a score of 100? Class interval 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 f 1 2 2 3 1 2 5 2 2 1 1 1 rel f(%) 4.35 8.7 8.7 13.04 4.35 8.7 21.74 8.7 8.7 4.35 4.35 4.35 Cumulative f 23 22 20 18 15 14 12 7 5 3 2 1 Cumulative % 100 95.65 86.96 78.26 65.22 60.87 52.17 30.43 21.74 13.04 8.7 4.35 78.26% of the scores fall below 100 The number 78.26 is the percentile rank The number 100 is the corresponding percentile point We write P78.26 =100 Ice Dancing , compulsory dance scores, Winter Olympics Percentile ranks and percentile point: Class interval 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 f 1 2 2 3 1 2 5 2 2 1 1 1 rel f(%) 4.35 8.7 8.7 13.04 4.35 8.7 21.74 8.7 8.7 4.35 4.35 4.35 Cumulative f 23 22 20 18 15 14 12 7 5 3 2 1 Cumulative % 100 95.65 86.96 78.26 65.22 60.87 52.17 30.43 21.74 13.04 8.7 4.35 21.74% of the scores are below 75 or P21.74 = 75 or 100-21.74=78.26% of the scores are above 75. Ice Dancing , compulsory dance scores, Winter Olympics The Cumulative Percentage Curve Cumulative % 100 95.65 86.96 78.26 65.22 60.87 52.17 30.43 21.74 13.04 8.7 4.35 100 90 Cumulative Percentage Class interval 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 Ice Dancing Score 21.74% of the scores fall below a score of 75 The number 21.74 is the percentile rank The number 75 is the corresponding percentile point We write P21.74 = 75 115 The Cumulative Percentage Curve Cumulative % 100 95.65 86.96 78.26 65.22 60.87 52.17 30.43 21.74 13.04 8.7 4.35 100 90 Cumulative Percentage Class interval 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 Ice Dancing Score 78.26% of the scores fall below a score of 100 The number 78.26is the percentile rank The number 100 is the corresponding percentile point We write P78.26 = 100 115 The Cumulative Percentage Curve Cumulative % 100 95.65 86.96 78.26 65.22 60.87 52.17 30.43 21.74 13.04 8.7 4.35 100 90 Cumulative Percentage Class interval 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 Ice Dancing Score 50% of the scores fall below a score of about 84 The number 50 is the percentile rank The number 84 is an estimate of the percentile point We write P50 = 84 115 Cumulative frequency distribution Class interval 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 f 1 2 2 3 1 2 5 2 2 1 1 1 rel f(%) 4.35 8.7 8.7 13.04 4.35 8.7 21.74 8.7 8.7 4.35 4.35 4.35 Cumulative f 23 22 20 18 15 14 12 7 5 3 2 1 Cumulative % 100 95.65 86.96 78.26 65.22 60.87 52.17 30.43 21.74 13.04 8.7 4.35 What is the percentile point for a percentile rank of 21.74%? Answer: 75 points (21.75% of the scores fall below 75) Ice Dancing , compulsory dance scores, Winter Olympics Cumulative frequency distribution Class Intervals Frequency (f) 110-115 105-110 100-105 95-100 90-95 85-90 80-85 75-80 70-75 65-70 60-65 55-60 1 2 2 3 1 2 5 2 2 1 1 1 Cumulative frequency 23 22 20 18 15 14 12 7 5 3 2 1 Cumulative proportion 1.00 .96 .87 .78 .65 .61 .52 .30 .22 .13 .09 .04 Cumulative percent 100 96 87 78 65 61 52 30 22 13 8 4 What is the percentile point for a percentile rank of 50? (Or what is P50?) We know it’s between 80 and 85, since 52% fall below 85 and 30% fall below 80. Ice Dancing , compulsory dance scores, Winter Olympics Here’s how to calculate the percentile rank for each raw score: note this is different from the book! Score 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 96.12 92.75 89.62 85.36 84.58 83.89 83.12 80.47 80.3 79.31 76.73 74.25 72.01 68.87 63.73 59.64 Rank order 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Subtract 1/2 22.5 21.5 20.5 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 15.5 14.5 13.5 12.5 11.5 10.5 9.5 8.5 7.5 6.5 5.5 4.5 3.5 2.5 1.5 0.5 Divide by n (23) Multiply by 100 0.98 98 0.93 93 0.89 89 0.85 85 0.80 80 0.76 76 0.72 72 0.67 67 0.63 63 0.59 59 0.54 54 0.50 50 0.46 46 0.41 41 0.37 37 0.33 33 0.28 28 0.24 24 0.20 20 0.15 15 0.11 11 0.07 7 0.02 2 The percentile point for a percentile rank of 50 is 84.58 ( P50 = 84.58) Ice Dancing, compulsory dance scores, Winter Olympics Here’s how to calculate the percentile rank for each raw score: Score 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 96.12 92.75 89.62 85.36 84.58 83.89 83.12 80.47 80.3 79.31 76.73 74.25 72.01 68.87 63.73 59.64 Rank order 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Subtract 1/2 22.5 21.5 20.5 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 15.5 14.5 13.5 12.5 11.5 10.5 9.5 8.5 7.5 6.5 5.5 4.5 3.5 2.5 1.5 0.5 Divide by 23 0.98 0.93 0.89 0.85 0.80 0.76 0.72 0.67 0.63 0.59 0.54 0.50 0.46 0.41 0.37 0.33 0.28 0.24 0.20 0.15 0.11 0.07 0.02 Multiply by 100 98 93 89 85 80 76 72 67 63 59 54 50 46 41 37 33 28 24 20 15 11 7 2 The percentile point for a percentile rank of 80 is 100.6 (P80 = 100.6) Ice Dancing , compulsory dance scores, Winter Olympics How do we calculate the percentile point for all the other ranks? Example: What is the percentile point for the percentile rank of 90%? Score 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 Rank order 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 Subtract 1/2 22.5 21.5 20.5 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 Divide by 23 0.98 0.93 0.89 0.85 0.80 0.76 0.72 Multiply by 100 98 93 89 85 80 76 72 We know it’s between 106.6 and 108.55 In fact, it’s ¼ of the way between 106.6 and 108.55 (90-89)/(93-89) = 1/4 That means that P90 = 106.6 + 1/4(108.55-106.6) = 107.09 How do we calculate the percentile point for other ranks? Example, what is the percentile point for the percentile rank of P75? Score 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 Rank order 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 Subtract 1/2 22.5 21.5 20.5 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 Divide by 23 0.98 0.93 0.89 0.85 0.80 0.76 0.72 Multiply by 100 98 93 89 85 80 76 72 We know it’s ¾ of the way between 96.67 and 97.38 96.67 + 3/4(97.38-96.67) = 97.2 How do we calculate the percentile point for other ranks? Example, what is the percentile score for the percentile rank of P25? Score 80.47 80.3 79.31 76.73 74.25 72.01 68.87 63.73 59.64 Rank order 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Subtract 1/2 8.5 7.5 6.5 5.5 4.5 3.5 2.5 1.5 0.5 Divide by 23 0.37 0.33 0.28 0.24 0.20 0.15 0.11 0.07 0.02 Multiply by 100 37 33 28 24 20 15 11 7 2 We know it’s 1/4 of the way between 76.73 and 79.31 76.73 + 1/4(79.31-76.73) = 77.37 General formula for calculating percentile points: Example, what is the percentile point for the percentile rank of 81? Score 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Rank order 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 Subtract 1/2 22.5 21.5 20.5 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 Divide by 23 0.98 0.93 0.89 0.85 0.80 0.76 0.72 Multiply by 100 98 93 89 85 80 76 72 Make a chart like the one above Find the two rows that fall above and below the percentile rank Let PH and PL be the high and low cumulative percentiles (85 and 80 in this example) Let SH and SL be the high and low scores (103.33 and 100.06 in this example) If p is the percentile rank (81 in our example), then the percentile point is: p PL SL ( SH SL) PH PL 81 80 100.06 (103.33 100.06) 100.71 85 80 Going the other way: from percentile ranks to percentile points Example: What is the percentile rank for the percentile point of 103.33? Score 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 Rank order 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 Subtract 1/2 22.5 21.5 20.5 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 Divide by 23 0.98 0.93 0.89 0.85 0.80 0.76 0.72 Multiply by 100 98 93 89 85 80 76 72 This is easy, since 103.33 is one of the scores. The percentile rank is 85%. 85% of the scores fall below 103.33 Going the other way: from percentile ranks to percentile points Example: What is the percentile rank for the percentile point of 100? Score 111.15 108.55 106.6 103.33 100.06 97.38 96.67 Rank order 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 Subtract 1/2 22.5 21.5 20.5 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 Divide by 23 0.98 0.93 0.89 0.85 0.80 0.76 0.72 Multiply by 100 98 93 89 85 80 76 72 This is not as easy, since 100 is not one of the scores. We do know that it is between 76 and 80. In fact, we know it must be really close to 80, since P80 is 100.06 Here’s how to do it. After finding the two rows that bracket the percentile point, if S is the percentile point, then the percentile rank is: S SL PL ( PH PL) SH SL 100 97.38 76 (80 76) 79.91 100.06 97.38 79.91% o the scores fall below 100 Another Example: integer valued data Scores on Professor Flans’ Midterm (n = 20) Raw Test Scores 94 93 92 91 87 86 85 84 84 83 82 81 81 80 80 77 73 73 68 59 We’ll choose a class interval width of 3. An odd number for width is good for integer data because the middle value will be a whole number. Class interval 58-61 61-64 64-67 67-70 70-73 73-76 76-79 79-82 82-85 85-88 88-91 91-94 94-97 97-100 f 1 0 0 1 2 0 1 5 4 2 1 3 0 0 Remember, scores that land on the border are assigned to the lower class interval. So 85 lands in the interval 82-85. Bins labeled by the centers of the class intervals 5 f 1 0 0 1 2 0 1 5 4 2 1 3 0 0 4 Frequency Class interval 58-61 61-64 64-67 67-70 70-73 73-76 76-79 79-82 82-85 85-88 88-91 91-94 94-97 97-100 3 2 1 0 60 63 66 69 72 75 78 81 84 87 90 93 96 99 Test Score You can also show the whole interval on the x-axis labels 5 Frequency 4 3 2 1 0 58-61 61-64 64-67 67-70 70-73 73-76 76-79 79-82 Test Score 82-85 85-88 88-91 91-94 94-97 97-100 The Cumulative Percentage Curve Class Interval 97-100 94-97 91-94 88-91 85-88 82-85 79-82 76-79 73-76 70-73 67-70 64-67 61-64 58-61 Cumulative frequency frequency 0 20 0 20 3 20 1 17 2 16 4 14 5 10 1 5 0 4 2 4 1 2 0 1 0 1 1 1 Relative frequency(%) 0 0 15 5 10 20 25 5 0 10 5 0 0 5 cumulative frequency % 100 100 100 85 80 70 50 25 20 20 10 5 5 5 The Cumulative Percentage Curve for Professor Flans’ Midterm Estimate the percentile point for a percentile rank of 50% Cumulative frequency% 100 100 100 85 80 70 50 25 20 20 10 5 5 5 100 Cumulative Frequency (%) Class Interval 97-100 94-97 91-94 88-91 85-88 82-85 79-82 78-79 73-76 70-73 67-70 64-67 61-64 58-61 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 61 64 67 70 73 76 79 82 85 88 91 94 97 100 Test Score About 50% of the scores fall below 82. (So P50 is about 82) Estimating percentile points and percentile ranks from the cumulative percentage curve Estimate the percentile point for a percentile rank of 90% Cumulative Frequency (%) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 61 64 67 70 73 76 79 82 85 88 91 94 97 100 Test Score 90% of the scores fall below a score of about 92. (P90 is about 92) Calculating percentile points from raw data. What is the percentile point for a percentile rank of 50%? Test score 94 93 92 91 87 86 85 84 84 83 82 81 81 80 80 77 73 73 68 59 Rank order 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Subtract 1/2 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 15.5 14.5 13.5 12.5 11.5 10.5 9.5 8.5 7.5 6.5 5.5 4.5 3.5 2.5 1.5 0.5 Divide by 20 0.975 0.925 0.875 0.825 0.775 0.725 0.675 0.625 0.575 0.525 0.475 0.425 0.375 0.325 0.275 0.225 0.175 0.125 0.075 0.025 Multiply by 100 97.5 92.5 87.5 82.5 77.5 72.5 It’s between 82 and 83 67.5 p PL 62.5 SL ( SH SL ) 57.5 pH pL 52.5 47.5 42.5 82 (83 82) 50 47.5 82.5 37.5 52.5 47.5 32.5 27.5 P50 = 82.5 22.5 17.5 12.5 7.5 2.5 Calculating percentile points from raw data. What is the percentile point for a percentile rank of 90%? Test score 94 93 92 91 87 86 85 84 84 83 82 81 81 80 80 77 73 73 68 59 Rank order 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Subtract 1/2 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 15.5 14.5 13.5 12.5 11.5 10.5 9.5 8.5 7.5 6.5 5.5 4.5 3.5 2.5 1.5 0.5 Divide by 20 0.975 0.925 0.875 0.825 0.775 0.725 0.675 0.625 0.575 0.525 0.475 0.425 0.375 0.325 0.275 0.225 0.175 0.125 0.075 0.025 Multiply by 100 97.5 92.5 87.5 82.5 77.5 72.5 It’s between 92 and 93 67.5 p PL 62.5 SL ( SH SL ) 57.5 pH pL 52.5 47.5 42.5 92 (93 92) 90 87.5 92.5 37.5 92.5 87.5 32.5 27.5 It’s exactly halfway 22.5 between 92 and 93 17.5 12.5 7.5 2.5 Going the other way: from percentile ranks to percentile points Example, what is the percentile rank for the percentile point of 90? Test score 94 93 92 91 87 86 85 84 84 83 82 81 81 80 80 77 73 73 68 59 Rank order 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Subtract 1/2 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5 15.5 14.5 13.5 12.5 11.5 10.5 9.5 8.5 7.5 6.5 5.5 4.5 3.5 2.5 1.5 0.5 Divide by 23 0.975 0.925 0.875 0.825 0.775 0.725 0.675 0.625 0.575 0.525 0.475 0.425 0.375 0.325 0.275 0.225 0.175 0.125 0.075 0.025 Multiply by 100 97.5 92.5 87.5 82.5 77.5 72.5 67.5 62.5 57.5 52.5 47.5 42.5 37.5 32.5 27.5 22.5 17.5 12.5 7.5 2.5 It’s between 77.5 and 82.5 S SL pL ( pH pL) SH SL 90 87 77.5 (82.5 77.5) 81.25 91 87 81.25% of the scores fall below 90 points More stuff about frequency distributions: Frequency polygon 5 5 4 4 Frequency Frequency Frequency histogram 3 2 1 0 3 2 1 60 63 66 69 72 75 78 81 84 87 90 93 96 99 Test Score 0 60 63 66 69 72 75 78 81 84 87 90 93 96 99 Test Score Properties of frequency distributions ‘normal’ or bell-shaped Negatively skewed positively skewed Example of a negatively skewed distribution 40 35 Frequency 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 GRE quant scores 700 750 800 Example of positively skewed distribution: Household annual income Household income distribution as of 2006: •P0-89 (bottom 90%) — income below $104,696 (average income, $30,374*) •P90-100 (top 10%) — income above $104,696 (average income, $269,658*) •P90-95 (next 5%) — income between $104,696 and $148,423 (average income, $122,429*) •P95-99 (next 4%) — income between $148,423 and $382,593 (average income, $210,597*) •P99-100 (top 1%) — income above $382,593 (average income, $1,243,516*) •P99.5-100 (top 0.5%) — income above $597,584 (average income, $2,022,315*) •P99.9-100 (top 0.1%) — income above $1,898,200 (average income, $6,289,800*) •P99.99-100 (top .01%) —income above $10,659,283 (average income, $29,638,027*) So the ‘top 1%’ can be described as: P99 = $382,593 http://www.wealthandwant.com/issues/income/income_distribution.html Two (of many) ways that frequency distributions differ Shift in central tendency 0 20 40 60 Scores 80 100 80 100 Shift in variability 0 20 40 60 Scores