Nervous System
advertisement
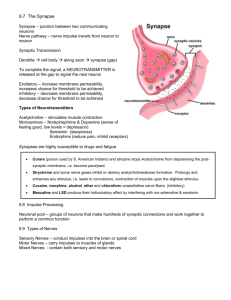
Nervous System Anatomy 2/Musculoskeletal Anatomy Mini Quiz (M.S Anatomy) • Label the different lobes of the brain: (see next page) 1. Orange 2. Pink 3. Green 4. Blue 5. The homunculous and sensory stimulus is apart of what lobe? 6. If you got hit in the back of the head what lobe and function may be affected? 7. ________________associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving 8. Hearing and speech are controlled within this lobe Brain labeling A: Parietal lobe B: Cerebral cortex/cerebrum C: Corpus callosum D: Frontal lobe E: Thalamus F: Hypothalamus G: Amygdala H: Midbrain I: Pituitary gland (anterior) J: Pons K: Medulla oblongata L: Cerebellum M: Hippocampus N: Occipital lobe O: Pineal gland (posterior) P: Brainstem/Spinal cord Q: RAS Brain FUNCTIONS • Brocca's area: control of speech • Wernicke's area: comprehension of language • Motor strip: Controls sending and receives messages of movement from the body • Sensory strip: Controls sending and receives messages of feeling from the body • Cerebrum: the largest part of the brain Coordinates all voluntary muscle activities and interprets sensory impulses Controls higher mental functions: memory, reasoning, intelligence, learning, judgment and emotions • Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving • Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli • Occipital Lobe- associated with visual processing • Temporal Lobe- associated with perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech Functions of the BRAIN • Pons: Controls sleep, posture, respiration, swallowing and bladder • Medulla: lowest part of brainstem • Regulates heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, coughing, sneezing and vomiting • Cerebellum: Controls movements of skeletal muscles • Controls coordination of voluntary muscle movements and balance • Thalamus: Sensory perception and regulation of motor functions • Hypothalamus: Maintains homeostasis: Maintaining stabilization of all the systems of the body • Controls body temperature, pulse and respiration Brain Functions Cont. • Pineal gland: Produces melatonin, which helps maintain circadian rhythm and regulate reproductive hormones • Pituitary gland: Controls endocrine system, producing hormones • Hippocampus: Memory, especially long term • Corpus callosum: Integrate motor, sensory, and cognitive performances between the cerebral cortex (communication between the two brain hemispheres) • RAS: Filters the incoming information • Amygdala: Responsible for emotions, survival instincts, and memory Homunculous “little man” Identify the following • Frontal • Parietal • Occipital • Thalamus • Pineal gland • Pituitary gland • Corpus callosum • Pons • Medulla • Brain stem • Cerebellum • Grey matter • White matter • Lateral ventricle Sheep Brain Dissection… The Size of the Human Brain • The average adult human brain weighs in at 1300 to 1400 grams, or around 3 pounds. • In terms of length, the average brain is around 15 centimeters long (5 inches). • For comparison… A newborn human baby's brain weighs approximately 350 to 400 grams, or three-quarters of a pound. NERVES of the Body COMMON NERVES Lower body nerves • Sciatic • Femoral • Common peroneal • Tibial • Superficial peroneal Sciatic nerve • Connects at lower back • Goes through the back of pelvis down the medial femur • Continues to run down behind middle of the knee all the way down to the base of the heel Femoral nerve • Attach to L3 & L4 • Run nerve anterior down the lateral femur to mid thigh Common peroneal & Tibial • Both nerves branch off of sciatic nerve behind the knee • Tibial goes down middle of calf to behind the Lateral malleolus • Common peroneal wraps around to the side of the Leg, anterior to fibular head Superficial peroneal nerve • Branches off from the common peroneal and goes behind the lateral malleolus The NERVE Functions of the NEURON • Dendrite: Receives other neural impulses • Nucleus: Development of the impulse occurs here • Soma body: Cell body • Axon: Conducts electrical impulse away from cell body • Myelin Sheath: Fatty coding increasing nerve impulse transmission • Schwann Cell: Supports the PNS • Nodes of Ranvier: Help conduction of neuron impulse • Synapse: Passes electrical impulse to another neuron Cranial nerves • I OLFACTORY: Smell • II OPTIC Sensory: Vision (eye movement) • III OCULOMOTOR: Movement of eye, pupil reaction • IV TROCHLEAR: Eye movement • V TRIGEMINAL: Facial sensation • VI ABDUCENS: Lateral movement of eyes • VII FACIAL: Taste & facial expression (smile, frown, surprise) • VIII VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR: Hearing and balance • IX GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL: Swallowing • X VAGUS: Speech and voice: Say ahhh, listen to sound of voice • XI ACCESSORY: Neck ROM and Shoulder shrug • XII HYPOGLOSSAL: Tongue movement (stick it out, move around) Concussion: On the field assessment: Head/Neck injury • Important things to know: • • • • • Coup Counter coup Retrograde amnesia Anterograde amnesia Axial loading Dermatome and Myotome • Dermatome: A skin area innervated by the sensory fibers of a single nerve root • Myotome: A group of muscles primarily innervated by the motor fibers of a single nerve root • http://www.apparelyzed.com/dermatome.html Myotomes (manual muscle testing): Commonly injured • • • • • • • • • C5 – The deltoid muscle (abduction of the arm at the shoulder). C6 – The biceps (flexion of the arm at the elbow). C7 – The triceps (extension of the arm at the elbow). C8 – The small muscles of the hand. (finger ab/adduction, wrist flexion/extension/radial & ulnar deviation) L2 – Hip adductors (hip internal rotation/hip adduction) L3 – The quadriceps (extension of the leg at the knee). L4 – The tibialis anterior (dorsiflexion of the foot at the ankle). L5 – Hamstring (flexion of the knee). S1 – The gastrocnemius muscle (plantarflexion of the foot at the ankle). Reflexes: A response to a stimulus and without conscious thought • Upper body: • Bicep • Tricep • Brachioradialis • Lower body: • Patellar tendon • Achilles • To see more about reflexes: • https://meded.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/neuro3.htm