pptx - SIU School of Medicine
advertisement

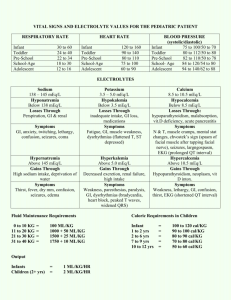
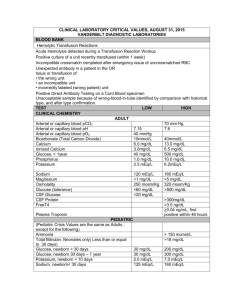
Channeling a Clinician: Design and Construction of Clinical Scenarios for Teaching and Assessment Eric Niederhoffer SIU-SOM Outline • • • • USMLE style scenario template Resources for clinical information Single or multiple disciplines Discuss example designs USMLE Style Scenario Template • A n-year-old (Age) boy/girl/man/woman (Gender) comes/is brought to the physician/emergency department (Site of Care) for evaluation of/with a problem (Presenting Complaint including Duration and Patient/Family History). • Physical examination shows some combination of pertinent findings (Height/Weight/BMI/Percentile, Temperature/Heart Rate/Breathing Rate/Blood Pressure). • Laboratory studies show some combination of test results (Reference Ranges provided for non-adult age groups/special tests). • Which drug, toxic exposure, diet; predict physical findings, lab findings, sequelae; identify underlying cause/mechanism/diagnosis, cause of drug response, drug to administer (Questions) Resources for Clinical Information • Height/weight for children (growth charts)/adults http://www.babycenter.com/average-fetal-length-weight-chart http://pediatrics.about.com/cs/growthcharts2/l/bl_ibw_rslts.htm http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/charts.htm https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/resources/heart/latino-weight-html/need • Heart/respiration rate, blood pressure for children http://www.emedicinehealth.com/pediatric_vital_signs/article_em.htm • Physical exam/heart/lung sounds http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/meded/medicine/pulmonar/pd/contents.htm http://www.med.umich.edu/lrc/psb_open/repo/primer_heartsound/primer_heartsound.html Reference Ranges K+ ClHCO3Ca2+ Urea nitrogen Glucose, fasting Creatinine Phosphorus Total CO2 Total protein Albumin Osmolality Uric acid Serum 135-147 mEq/L 3.5-5.0 mEq/L 95-105 mEq/L 22-28 mEq/L 8.4-10.2 mg/dL 7-18 mg/dL 70-110 mg/dL 0.6-1.2 mg/dL 3-4.5 mg/dL 24-30 mEq/L 6-7.8 g/dL 3.5-5.5 g/dL 275-295 mOsm/kg water 3-7 mg/dL Total cholesterol LDL HDL Triglycerides Lipids <200 mg/dL <130 mg/dL >40 mg/dL <160 mg/dL Na+ Arterial Blood Gases pH 7.35-7.45 Pa.CO2 (PCO2) 33-44 mm Hg Pa.O2 (PO2) 75-105 mm Hg HCO3 22-28 mEq/L O2 saturation 96-100% + Anion gap (no K ) 8-16 mEq/L + with K 12-20 mEq/L Bicarbonate gap -6-+6 mEq/L Blood Hemoglobin, male 13-16 g/dL female 12-15 g/dL Hematocrit, male 42-50% female 40-48% O2 binding capacity 1.34 mL O2/g Hb Creatinine clearance Osmolality Specific gravity Protein Urine 90-140 mL/min 50-1400 mOsm/kg water 1.003-1.030 <150 mg/24 h Potential Diseases Disease Anemia Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Diabetes Down syndrome Gout Lactase deficiency Marfan syndrome 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency Minimal change disease Mixed acid-base disorders Muscular dystrophy Parkinson disease Potential Concepts Concept Protein/enzyme structure/function in health/disease DNA structure/function, transcription/translation in health/disease Signal transduction mediated cellular responses Protein/enzyme small molecule interactions in health/disease Regulation of metabolic flux Serum chemistries (anion/bicarbonate gap) as marker for organ function/disease Example of Single Discipline Question A 3430 g (7 lb 9 oz) infant delivered at 42 weeks gestation to a primigravida woman shows a positive result for newborn screening of hemoglobin disorders. A complete blood count shows: Hemoglobin 17.0 g/dL Hematocrit 49% Mean corpuscular volume 72 fL Hemoglobin electrophoresis shows 80% HbA, 5% HbA2 and 15% HbF. A defect in which of the following globin genes is most likely in this patient? A. Alpha B. Beta C. Gamma D. Delta E. Epsilon F. Zeta Example of Multiple Discipline Question A 51-year-old woman with a history of diarrhea poorly controlled with medication comes to the physician for evaluation of food intolerance. She is 170 cm (5 ft 7 in) tall and weighs 69 kg (152 lb); BMI is 24 kg/m2. Her temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 72/min, respirations are 22/min and blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. A complete blood count, serum studies, and hemoglobin electrophoresis show: Hemoglobin 12.4 g/dL Albumin 2.8 g/dL HbA 93% Hematocrit 37% CO2 content 22 mmol/L HbA2 5% Mean corpuscular volume 72 fL HbF 2% Serum iron concentration is within the reference range. All other values are within the reference ranges. A peripheral blood smear shows microcytosis. Additional laboratory studies show increased concentrations of tissue transglutaminase–immunoglobulin A and tissue transglutaminase–immunoglobulin G. Which of the following changes in globin expression is most likely in this patient? A. Decreased post-translational modification of zeta globin gene product B. Decreased transcription of alpha globin gene C. Decreased translation of beta globin gene D. Increased post-translational modification of zeta globin gene product E. Increased transcription of alpha globin gene F. Increased translation of beta globin gene Let’s Discuss What We Have Designed • Is the presenting complaint/situation clearly defined? • Dpes the physical examination data make sense? • Do the laboratory testing results allow students to exclude differentials and/or focus on the primary concern (how bad is the condition)? • Can students understand the problem by using the information or is it recall? • How can the scenarios be improved or altered to fit the educational need (ask for a clinician’s assistance)?