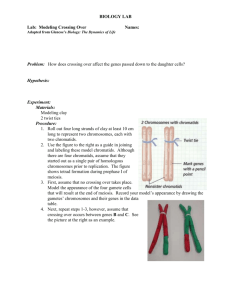
Crossing Over

Jack Cassidy, Jessica Matthews, Keith Murphy, Mike Nickelsburg
Crossing Over
Genetic Recombination http://library.thinkquest.org/19037/genome3.html
Overview
• Who, What, When, Where, Why
• Basics
• Example
• Summary
21 Apr 2002 2
Who Does Crossing-Over
Effect?
Eukaryotes
Limited in Prokaryotes
What is Crossing Over?
The exchange of chromosomal segments between two nonsister chromatids
Crossing Over
21 Apr 2002
Ref: http://gnn.tigr.org/whats_a_genome/Chp3_2.shtml
5
When Does it Happen?
During Prophase I of Meiosis
Remember the differences between
Mitosis and Meiosis?
Meiosis increases genetic diversity in a species
Mitosis creates genetically identical daughter cells
Where does Crossing Over
Occur?
Genetic swapping occurs between paired homologous chromosomes in our sex cells—
The Egg and Sperm
Egg and Sperm
• Chromosomes pair
• Chromosomes may swap genetic material
• New genetic material has been acquired from the other homologue
• NOTE : Genes that have a tendency to remain together during crossing over are said to be linked —we will talk about this concept during Crossing Over Basics
21 Apr 2002 8
Homologous Chromosomes Exchanging DNA by Crossing Over
21 Apr 2002
From: http://www.ultranet.com/~jkimball/BiologyPages/M/Meiosis.html#crossing_over
9
Why Does Crossing Over
Occur?
To provide genetic variation during meiosis
BOTTOM LINE
Its Why You and I Don’t
Look Alike
Crossing Over ensures a combination of the maternal and paternal genes we inherited
The History of Crossing
Over
Linkage
• Gregor Mendel, 1823-1884
– Patterns of Inheritance
• Carl Correns, 1900s
– Gene Linkage
• Alfred Sturtevant http://zygote.swarthmore.edu/cleave1.html
http://www.library.villanova.edu/html2/blueprints/feb01index.html
http://www.oeaw.ac.at/biblio/Archiv/Mendel/mendel.html
21 Apr 2002 13
Crossing Over Basics
Crossing Over Basics
• Occurs at One or More Points Along
Adjacent Homologues during Synapsis
• Points contact each other
• DNA is Exchanged http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/cross3.jpg
21 Apr 2002 15
Ref: Access Excellence http://www.accessexcellence.org/AB/GG/crossing.html
21 Apr 2002 16
Crossing Over Basics
• Gene Mapping
– Tracking crossing over helps determine where genes are located on the chromosome
– Genes that are far apart have a GREATER chance of crossing over
– Genes that are closer have a LESS LIKELY chance of crossing over
• Genes that stay together are said to be LINKED
• One gene can be identified as a MARKER that can infer the presence of the other gene
– This can be used in identifying disease predisposition
21 Apr 2002 17
Crossing Over Basics
• Gene Mapping
– Tracking crossing over helps determine where genes are located on the chromosome
– Genes that are far apart have a
GREATER chance of crossing over
– Genes that are closer have a LESS
LIKELY chance of crossing over
21 Apr 2002 18
Genes get shuffled when chromosomes exchange pieces
Watch an animation of crossing over with an explanation of how the concept was discovered at http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/11/concept/index.html
This web site was produced by the
Dolan DNA Learning Center, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
21 Apr 2002 19
Summary
• Who, What, When, Where, Why
• History
• Basics
• Example
• Summary
From: http://www.ultranet.com/~jkimball/BiologyPages/M/Meiosis.html#crossing_over
20 21 Apr 2002