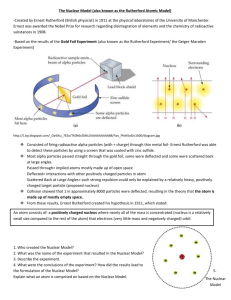
P4 Spaced learning

P4 Spaced learning
Radiation for life
Sparks
Insulating materials
Metals are good conductors, which means that electric charges move easily through them. Materials such as plastic, wood, glass and polythene are insulators. This means they do not allow electric charges to move through them. Some insulators can become electrically charged when they're rubbed together.
Positive and negative charges
Objects can be positively charged, negatively charged or neutral (no charge).
A substance that gains electrons becomes negatively charged, while a substance that loses electrons becomes positively charged. Atoms or molecules that become charged are ions.
Problems with static electricity
Static is a nuisance when:
• Dust and dirt is attracted to insulators such as TV screens and computer monitors
• Clothes made from synthetic materials often cling to each other and to the body, especially just after they've been in a tumble drier.
Static is dangerous when:
• There are flammable gases or vapours or a high concentration of oxygen. A spark could ignite the gases and cause an explosion
• You touch something with a large electric charge on it.
The charge will flow through your body causing an electric shock. This could cause burns or even stop your heart.
When a charged object comes near to another object they will either attract or repel each other
If the charges are the same - they repel
If the charges are opposite - they attract
If one is charged and the other is not - they attract.
Like charges repel, and unlike charges attract.
Safety measures - Higher tier
The chance of receiving an electric shock can also be reduced if:
An object that might become charged is earthed by an earth wire
In a factory, machinery operators stand on insulating mats or wear shoes with insulating soles. Lorries containing flammable gases, liquids and powders are earthed by an earth wire before being unloaded .
Uses of electrostatics
Electrostatic precipitators
The electrostatic precipitator is a device used in chimneys for removing dust.
Higher Tier
The metal grids in the electrostatic precipitator are given a high voltage.
Depending on the design, the grids may be positively charged or negatively charged dust particles lose electrons if the grids are positively charged dust particles gain electrons if the grids are negatively charged.
The charged dust particles then induce a charge on the earthed metal collecting plates and the dust particles are attracted to the plates.
Spraying
Electrostatics can be useful for spraying liquids. For example: spraying paint spraying crops with pesticides and herbicides.
Spraying paint
They work because like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
The spray gun is given a charge. So droplets of point become charged:
They have the same charge, so repel each other producing a fine spray.
The car body part is has the opposite charge.
The paint droplets are attracted to the body part, producing an even coat with little waste.
Higher Tier
• The paint gun loses electrons so that it becomes positively charged
• The paint droplets lose electrons and so also become positively charged
• The object to be painted gains electrons and so becomes negatively charged
• The positively charged paint droplets repel each other and are attracted to the negatively charged surface.
Defibrillators
A defibrillator is a machine that can be used by paramedics to stabilise an irregular heartbeat. They work by discharging electric charge.
Two paddles with insulated handles are charged from a high voltage supply. They are put in good electrical contact with the patient's chest. It is important that only the patient gets a shock:
This is why the paddles have insulating handles
The operator and any one nearby stand clear.
The defibrillator passes charge through the patient to make the heart contract
Current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge. No current can flow if the circuit is broken, for example, when a switch is open
To check for a complete circuit, follow a wire coming out of the battery with your finger. You should be able to go out of the battery, through the lamp and back to the battery.
Resistance = voltage ÷ current
Resistance is measured in ohms, Ω
Voltage (potential difference) is measured in volts, V
Current is measured in amperes
(amps), A
Safe electricals
Resistance
There is a resistance to the flow of an electric current through most conductors. Resistance is measured in ohms, Ω.
The resistance in a wire increases
(and the current decreases) as:
The length of the wire increases
The thickness of the wire decreases
Cables and plugs
Colour
Blue
Brown
Wire
Neutral
Live
Green and yellow
Earth stripes
Resistors are added into a circuit to reduce the amount of current flowing.
The greater the resistance, the lower the current.
A variable resistor or rheostat is a device whose resistance can be changed. It can be used to vary the amount of current in a circuit.
Fuses
The fuse breaks the circuit if a fault in an appliance causes too much current flow.
Double insulation
Some appliances do not have an earth wire as they have plastic casings
Calculating power: Higher Tier
You can work out power using this equation:
Power = voltage × current
Power is measured in watts, W
Voltage (potential difference) is measured in volts,
V
Current is measured in amperes (amps), A
Function
Completes the circuit
Carries the high voltage
A safety wire to stop the appliance becoming live
Ultrasound
Waves
Longitudinal waves
All sound is produced by vibrating particles that form longitudinal waves. In this kind of wave the vibrations of the particles are in the same direction as the wave
Terms you need to know are:
Amplitude - The maximum distance the particles move from their normal position.
The louder a sound is, the more energy it carries and the bigger its amplitude.
Wavelength - The distance between one high pressure region (compression) and the next.
Frequency The number of waves produced in one second, measured in hertz, Hz. A higher pitched sound has a higher frequency than a lower pitched sound.
Compression - A region of higher pressure where particles are squashed together.
Rarefaction - A region of lower pressure where particles are spread out.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is the name given to sound waves that have frequencies greater than 20,000Hz. It's too high pitched for human hearing, but many animals, such as dogs, cats and bats can hear ultrasound.
Ultrasound has many applications in medicine.
These include:
• Looking inside people by scanning the body
• Breaking down kidney stones and stones elsewhere in the body
• Measuring the speed of blood flow in the body
Ultrasound - Higher tier
Ultrasound may be used instead of x-rays for certain scans, such as scan of unborn babies. Compared to x-ray photographs, ultrasound scans:
Do not damage living cells
Produce images of soft tissue
Medical images from ultrasound
Ultrasound is sent into the patient's body. Some of the ultrasound is reflected at each boundary between different tissues or organs.
Breaking down kidney stones
A high powered ultrasound wave is used to break down kidney stones and other stones in the body. The stones vibrate until they shake themselves apart and are then easily passed out of the body via the urethra
What is radioisotopes
There are three main types of radiation, called alpha, beta and gamma radiation, which all have different properties.
Half-life
This is how long it takes for half the nuclei of a piece of radioactive material to decay.
This is called the half-life of the radioactive isotope.
There are two definitions of half-life, but they mean essentially the same thing.
Half-life is the time taken for:
• The number of nuclei of the radioactive isotope in a sample to halve
• The count rate from a sample containing the radioactive isotope to fall to half its starting level
Type of radiation
Alpha particle
Beta particle
Ionisation
Nuclear radiation ionises materials.
Ionisation happens when:
• Particles lose electrons and become positively charged
• Particles gain electrons and become negatively charged
What is it?
Two protons and two neutrons
– the same as a helium nucleus
Fast-moving electron
Higher tier - Ionsation
Ionisation can be harmful to living cells. Alpha particles are particularly good ionisers. They have a much larger mass, and a greater charge, than beta particles.
Higher Tier - Decay
Alpha decay
Two protons and two neutrons are lost from a nucleus when it emits an alpha particle:
The atomic mass number decreases by 4 and the atomic number decreases by 2
A new element is formed that is two places lower in the periodic table than the original element.
Beta decay
In beta decay a neutron changes into a proton plus an electron. The proton stays in the nucleus, the electron leaves the atom with high energy as a beta particle.
The nucleus has one more proton and one less neutron when it emits a beta particle:
The atomic mass number stays the same but the atomic number increases by one
A new element is formed that is one place higher in the periodic table than the original element.
Background radiation
Background radiation is all around us. Some of it comes from natural sources and some comes from artificial sources.
Natural sources
• Cosmic rays – radiation from space
• Rocks and soil – some rocks are radioactive and give off radioactive radon gas
• Living things – plants absorb radioactive materials from the soil and these pass up the food chain
Artificial sources human activity has added to background radiation by creating and using artificial sources of radiation. These include
• radioactive waste from nuclear power stations,
• radioactive fallout from nuclear weapons testing
• medical x-rays.
Use of radioisotope
Tracers
Radioisotopes are used as tracers in industry. These are used for tracking substances.:
• Find leaks or blockages in underground pipes
• Find the route of underground pipes
• Track the dispersal of waste
Smoke detectors
Smoke detectors alert people to fires. Smoke from the fire is detected by the device, which then gives off an alarm. One type of smoke detector uses americium-241, a source of alpha radiation, to detect smoke
Dating rocks
Radioactivity can be used to date rocks. Rocks often contain traces of uranium. This is unstable and eventually decays to lead, which is stable. The age of a rock can be calculated if its ratio of uranium to lead is known. The older the rock, the lower its uranium to lead ratio:
• Young rocks have a high uranium to lead ratio
• Very old rocks have a low uranium to lead ratio
Higher tier
Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope. It is found in the air in carbon dioxide molecules. The amount of carbon-14 in the air has stayed the same for thousands of years. There is a small amount of radioactive carbon-14 in all living organisms because it enters the food chain.
Once an organism dies, it stops taking in carbon-14. The carbon-14 it contained at the time of death decays over a long period of time, and the radioactivity of the material decreases.
Treatment
X-rays, gamma rays and beta particles are all used in medicine to treat internal organs. X-rays are produced by firing electrons at a metal target and gamma rays are emitted by the nucleus of radioactive atoms.
Gamma rays are used to kill cancer cells, to sterilise medical equipment and in radioactive tracers.
Uses of radiation in medicine
Sterilising equipment
Gamma rays are high energy electromagnetic waves which are only stopped by thick lead. This means they can easily pass through medical equipment, such as syringes.
Tracers
Radioactive tracers are used to investigate a patient's body without the need for surgery.
Gamma emitters beta emitters are used because gamma rays and beta particles can pass through skin, whereas alpha particles cannot.
A small amount of radioactive material is put into the patient's body. The radiographer puts a detector around the body to detect any gamma rays or beta particles that pass out of the patient's body.
Tracers and treating cancer - Higher tier
Tracers
Radioisotopes with short half-lives are chosen to make sure that the tracer does not stay radioactive in the body for long periods.
The radioactive tracer is put into the body by one of the following ways:
• By an injection
• By ingestion
Treating Cancer
Gamma rays damage cells whether they are normal or cancerous, so gamma rays must be focused on the tumour. One way of doing this is to use a wide beam of gamma rays, but to rotate the beam around the patient, keeping the tumour at the centre. This concentrates the gamma rays on the cells that need to be killed.
Fission and Fusion
Nuclear fission is the splitting of atomic nuclei. Nuclear power stations use the fission of uranium-235 to heat water.
Fusion is the joining of atomic nuclei.
Chain Reaction
The fission of uranium can set up a chain reaction that will keep on releasing energy as long as there are uranium nuclei present. If this chain reaction is allowed to get out of control, energy is released very quickly and the result is a nuclear bomb. Nuclear power stations are designed to keep chain reactions under control
1. Fuel produces heat, which is used to boil water to make steam.
2. Steam spins a turbine.
3. Turbine drives a generator and the generator makes electricity.
4. Electricity goes to the transformers to produce the correct voltage.
Uranium is a non-renewable energy resource and, like the fossil fuels, it cannot be replaced once it has all been used up.
Higher Tier - Nuclear Fission
For fission to happen, the uranium nucleus must be hit by a neutron. When this happens:
The nucleus splits into smaller nuclei, Energy is released and Two or three neutrons are released.
Nuclear fusion
Nuclear fission is the splitting of large nuclei into smaller ones, while nuclear fusion is the joining of smaller nuclei to make larger ones. Nuclear fusion happens in stars and fusion bombs
Higher Tier – Nuclear Fusion
The Sun and other stars use nuclear fusion to release energy. The sequence of nuclear fusion reactions in a star is complex but overall hydrogen nuclei join to form helium nuclei.
Cold fusion
A group of scientists have claimed that they have achieved ‘cold fusion’ – nuclear fusion at ordinary temperatures and pressures. If it happens, cold fusion could be developed to provide almost limitless and cheap electricity. It would also make the international project to develop a fusion power station using high temperatures and pressures pointless.
Sparks
Insulating materials
Metals are good conductors , which means that electric charges move easily through them. Materials such as plastic, wood, glass and polythene are insulators.
This means they do not allow electric charges to move through them. Some insulators can become electrically charged when they're rubbed together.
Positive and negative charges
Objects can be positively charged, negatively charged or neutral (no charge).
A substance that gains electrons becomes charged, while a substance that loses electrons becomes charged. Atoms or molecules that become charged are .
Problems with static electricity
Static is a nuisance when:
When a charged object comes near to another object they will either attract or repel each other
If the charges are the same –
If the charges are opposite –
If one is charged and the other is not –
Like charges.
Static is dangerous when:
Safety measures - Higher tier
The chance of receiving an electric shock can also be reduced if:
Sparks
Insulating materials
Metals are good conductors, which means that electric charges move easily through them. Materials such as plastic, wood, glass and polythene are insulators. This means they do not allow electric charges to move through them. Some insulators can become electrically charged when they're rubbed together.
Positive and negative charges
Objects can be positively charged, negatively charged or neutral (no charge).
A substance that gains electrons becomes negatively charged, while a substance that loses electrons becomes positively charged. Atoms or molecules that become charged are ions.
Problems with static electricity
Static is a nuisance when:
• Dust and dirt is attracted to insulators such as TV screens and computer monitors
• Clothes made from synthetic materials often cling to each other and to the body, especially just after they've been in a tumble drier.
Static is dangerous when:
• There are flammable gases or vapours or a high concentration of oxygen. A spark could ignite the gases and cause an explosion
• You touch something with a large electric charge on it.
The charge will flow through your body causing an electric shock. This could cause burns or even stop your heart.
When a charged object comes near to another object they will either attract or repel each other
If the charges are the same - they repel
If the charges are opposite - they attract
If one is charged and the other is not - they attract.
Like charges repel, and unlike charges attract.
Safety measures - Higher tier
The chance of receiving an electric shock can also be reduced if:
An object that might become charged is earthed by an earth wire
In a factory, machinery operators stand on insulating mats or wear shoes with insulating soles. Lorries containing flammable gases, liquids and powders are earthed by an earth wire before being unloaded .
Uses of electrostatics
Electrostatic precipitators
The electrostatic precipitator is a device used in chimneys for removing dust.
Higher Tier
The metal grids in the electrostatic precipitator are given a high voltage.
Depending on the design, the grids may be positively charged or negatively charged dust particles lose electrons if the grids are positively charged dust particles gain electrons if the grids are negatively charged.
The charged dust particles then induce a charge on the earthed metal collecting plates and the dust particles are attracted to the plates.
Spraying
Electrostatics can be useful for spraying liquids. For example: spraying paint spraying crops with pesticides and herbicides.
Spraying paint
They work because like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
The spray gun is given a charge. So droplets of point become charged:
They have the same charge, so repel each other producing a fine spray.
The car body part is has the opposite charge.
The paint droplets are attracted to the body part, producing an even coat with little waste.
Higher Tier
• The paint gun loses electrons so that it becomes positively charged
• The paint droplets lose electrons and so also become positively charged
• The object to be painted gains electrons and so becomes negatively charged
• The positively charged paint droplets repel each other and are attracted to the negatively charged surface.
Defibrillators
A defibrillator is a machine that can be used by paramedics to stabilise an irregular heartbeat. They work by discharging electric charge.
Two paddles with insulated handles are charged from a high voltage supply. They are put in good electrical contact with the patient's chest. It is important that only the patient gets a shock:
This is why the paddles have insulating handles
The operator and any one nearby stand clear.
The defibrillator passes charge through the patient to make the heart contract
Uses of electrostatics
Electrostatic precipitators
The electrostatic precipitator is
Spraying
Electrostatics can be useful for spraying liquids. For example:
Defibrillators
A defibrillator is a machine that can be used by paramedics to stabilise an irregular heartbeat. They work by discharging electric charge.
Spraying paint
They work because like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
Higher Tier
Higher Tier
Current
Electric current is
To check for a complete circuit, follow.
Resistance =
voltage
÷
current
Resistance is measured in
Voltage (potential difference) is measured in
Current is measured in
Safe electricals
Resistance
There is a resistance to the flow of an electric current through most conductors. Resistance is measured in ohms, Ω.
Cables and plugs
Colour Wire
Blue Neutral
Brown Live
Green and yellow
Earth stripes
Resistors are added into a circuit
.
to
.
Fuses
Double insulation
Calculating power: Higher Tier
You can work out power using this equation:
Power = X
Power is measured in watts, W
Voltage (potential difference) is measured in volts,
V
Current is measured in amperes (amps), A
Function
Completes the circuit
Carries the high voltage
A safety wire to stop the appliance becoming live
Current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge. No current can flow if the circuit is broken, for example, when a switch is open
To check for a complete circuit, follow a wire coming out of the battery with your finger. You should be able to go out of the battery, through the lamp and back to the battery.
Resistance = voltage ÷ current
Resistance is measured in ohms, Ω
Voltage (potential difference) is measured in volts, V
Current is measured in amperes
(amps), A
Safe electricals
Resistance
There is a resistance to the flow of an electric current through most conductors. Resistance is measured in ohms, Ω.
The resistance in a wire increases
(and the current decreases) as:
The length of the wire increases
The thickness of the wire decreases
Cables and plugs
Colour
Blue
Brown
Wire
Neutral
Live
Green and yellow
Earth stripes
Resistors are added into a circuit to reduce the amount of current flowing.
The greater the resistance, the lower the current.
A variable resistor or rheostat is a device whose resistance can be changed. It can be used to vary the amount of current in a circuit.
Fuses
The fuse breaks the circuit if a fault in an appliance causes too much current flow.
Double insulation
Some appliances do not have an earth wire as they have plastic casings
Calculating power: Higher Tier
You can work out power using this equation:
Power = voltage × current
Power is measured in watts, W
Voltage (potential difference) is measured in volts,
V
Current is measured in amperes (amps), A
Function
Completes the circuit
Carries the high voltage
A safety wire to stop the appliance becoming live
Waves
Longitudinal waves
All sound is produced by vibrating particles that form longitudinal waves. In this kind of wave the vibrations of the particles are in the same direction as the wave
Terms you need to know are:
Amplitude –
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is the name given to sound waves that have frequencies greater than 20,000Hz. It's too high pitched for human hearing, but many animals, such as dogs, cats and bats can hear ultrasound.
Ultrasound has many applications in medicine.
These include:
Ultrasound - Higher tier
Wavelength –
Medical images from ultrasound
Frequency –
Compression –
Breaking down kidney stones
Rarefaction -
Ultrasound
Waves
Longitudinal waves
All sound is produced by vibrating particles that form longitudinal waves. In this kind of wave the vibrations of the particles are in the same direction as the wave
Terms you need to know are:
Amplitude - The maximum distance the particles move from their normal position.
The louder a sound is, the more energy it carries and the bigger its amplitude.
Wavelength - The distance between one high pressure region (compression) and the next.
Frequency The number of waves produced in one second, measured in hertz, Hz. A higher pitched sound has a higher frequency than a lower pitched sound.
Compression - A region of higher pressure where particles are squashed together.
Rarefaction - A region of lower pressure where particles are spread out.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is the name given to sound waves that have frequencies greater than 20,000Hz. It's too high pitched for human hearing, but many animals, such as dogs, cats and bats can hear ultrasound.
Ultrasound has many applications in medicine.
These include:
• Looking inside people by scanning the body
• Breaking down kidney stones and stones elsewhere in the body
• Measuring the speed of blood flow in the body
Ultrasound - Higher tier
Ultrasound may be used instead of x-rays for certain scans, such as scan of unborn babies. Compared to x-ray photographs, ultrasound scans:
Do not damage living cells
Produce images of soft tissue
Medical images from ultrasound
Ultrasound is sent into the patient's body. Some of the ultrasound is reflected at each boundary between different tissues or organs.
Breaking down kidney stones
A high powered ultrasound wave is used to break down kidney stones and other stones in the body. The stones vibrate until they shake themselves apart and are then easily passed out of the body via the urethra
What is radioisotopes
There are three main types of radiation, called alpha, beta and gamma radiation, which all have different properties.
There are two definitions of half-life, but they mean essentially the same thing.
Half-life is the time taken for:
Type of radiation
Alpha particle
Beta particle
Ionisation
Nuclear radiation ionises materials.
Ionisation happens when:
What is it?
Two protons and two neutrons
– the same as a helium nucleus
Fast-moving electron
Higher tier – Ionsation
Alpha decay
Higher Tier - Decay
Beta decay
What is radioisotopes
There are three main types of radiation, called alpha, beta and gamma radiation, which all have different properties.
Half-life
This is how long it takes for half the nuclei of a piece of radioactive material to decay.
This is called the half-life of the radioactive isotope.
There are two definitions of half-life, but they mean essentially the same thing.
Half-life is the time taken for:
• The number of nuclei of the radioactive isotope in a sample to halve
• The count rate from a sample containing the radioactive isotope to fall to half its starting level
Type of radiation
Alpha particle
Beta particle
Ionisation
Nuclear radiation ionises materials.
Ionisation happens when:
• Particles lose electrons and become positively charged
• Particles gain electrons and become negatively charged
What is it?
Two protons and two neutrons
– the same as a helium nucleus
Fast-moving electron
Higher tier - Ionsation
Ionisation can be harmful to living cells. Alpha particles are particularly good ionisers. They have a much larger mass, and a greater charge, than beta particles.
Higher Tier - Decay
Alpha decay
Two protons and two neutrons are lost from a nucleus when it emits an alpha particle:
The atomic mass number decreases by 4 and the atomic number decreases by 2
A new element is formed that is two places lower in the periodic table than the original element.
Beta decay
In beta decay a neutron changes into a proton plus an electron. The proton stays in the nucleus, the electron leaves the atom with high energy as a beta particle.
The nucleus has one more proton and one less neutron when it emits a beta particle:
The atomic mass number stays the same but the atomic number increases by one
A new element is formed that is one place higher in the periodic table than the original element.
Background radiation
Background radiation is all around us. Some of it comes from natural sources and some comes from artificial sources.
Natural sources
Use of radioisotope
Tracers
Smoke detectors
Dating rocks
Artificial sources human activity has added to background radiation by creating and using artificial sources of radiation. These include
Higher tier
Background radiation
Background radiation is all around us. Some of it comes from natural sources and some comes from artificial sources.
Natural sources
• Cosmic rays – radiation from space
• Rocks and soil – some rocks are radioactive and give off radioactive radon gas
• Living things – plants absorb radioactive materials from the soil and these pass up the food chain
Artificial sources human activity has added to background radiation by creating and using artificial sources of radiation. These include
• radioactive waste from nuclear power stations,
• radioactive fallout from nuclear weapons testing
• medical x-rays.
Use of radioisotope
Tracers
Radioisotopes are used as tracers in industry. These are used for tracking substances.:
• Find leaks or blockages in underground pipes
• Find the route of underground pipes
• Track the dispersal of waste
Smoke detectors
Smoke detectors alert people to fires. Smoke from the fire is detected by the device, which then gives off an alarm. One type of smoke detector uses americium-241, a source of alpha radiation, to detect smoke
Dating rocks
Radioactivity can be used to date rocks. Rocks often contain traces of uranium. This is unstable and eventually decays to lead, which is stable. The age of a rock can be calculated if its ratio of uranium to lead is known. The older the rock, the lower its uranium to lead ratio:
• Young rocks have a high uranium to lead ratio
• Very old rocks have a low uranium to lead ratio
Higher tier
Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope. It is found in the air in carbon dioxide molecules. The amount of carbon-14 in the air has stayed the same for thousands of years. There is a small amount of radioactive carbon-14 in all living organisms because it enters the food chain.
Once an organism dies, it stops taking in carbon-14. The carbon-14 it contained at the time of death decays over a long period of time, and the radioactivity of the material decreases.
Treatment
X-rays, gamma rays and beta particles are all used in medicine to treat internal organs. X-rays are produced by firing electrons at a metal target and gamma rays are emitted by the nucleus of radioactive atoms.
Gamma rays are used to kill cancer cells, to sterilise medical equipment and in radioactive tracers.
Uses of radiation in medicine
.
Sterilising equipment
Tracers
Tracers and treating cancer - Higher tier
Tracers
Treating Cancer
Treatment
X-rays, gamma rays and beta particles are all used in medicine to treat internal organs. X-rays are produced by firing electrons at a metal target and gamma rays are emitted by the nucleus of radioactive atoms.
Gamma rays are used to kill cancer cells, to sterilise medical equipment and in radioactive tracers.
Uses of radiation in medicine
Sterilising equipment
Gamma rays are high energy electromagnetic waves which are only stopped by thick lead. This means they can easily pass through medical equipment, such as syringes.
Tracers
Radioactive tracers are used to investigate a patient's body without the need for surgery.
Gamma emitters beta emitters are used because gamma rays and beta particles can pass through skin, whereas alpha particles cannot.
A small amount of radioactive material is put into the patient's body. The radiographer puts a detector around the body to detect any gamma rays or beta particles that pass out of the patient's body.
Tracers and treating cancer - Higher tier
Tracers
Radioisotopes with short half-lives are chosen to make sure that the tracer does not stay radioactive in the body for long periods.
The radioactive tracer is put into the body by one of the following ways:
• By an injection
• By ingestion
Treating Cancer
Gamma rays damage cells whether they are normal or cancerous, so gamma rays must be focused on the tumour. One way of doing this is to use a wide beam of gamma rays, but to rotate the beam around the patient, keeping the tumour at the centre. This concentrates the gamma rays on the cells that need to be killed.
Fission and Fusion
Nuclear fission is the splitting of atomic nuclei. Nuclear power stations use the fission of uranium-235 to heat water.
Fusion is the joining of atomic nuclei.
Chain Reaction
Higher Tier - Nuclear Fission
3.
4.
1.
2.
Nuclear fusion
Higher Tier – Nuclear Fusion
Uranium is a energy resource and, like the fossil fuels, it cannot be replaced once it has all been used up.
Cold fusion
A group of scientists have claimed that they have achieved ‘cold fusion’ – nuclear fusion at ordinary temperatures and pressures. If it happens, cold fusion could be developed to provide almost limitless and cheap electricity. It would also make the international project to develop a fusion power station using high temperatures and pressures pointless.
Fission and Fusion
Nuclear fission is the splitting of atomic nuclei. Nuclear power stations use the fission of uranium-235 to heat water.
Fusion is the joining of atomic nuclei.
Chain Reaction
The fission of uranium can set up a chain reaction that will keep on releasing energy as long as there are uranium nuclei present. If this chain reaction is allowed to get out of control, energy is released very quickly and the result is a nuclear bomb. Nuclear power stations are designed to keep chain reactions under control
1. Fuel produces heat, which is used to boil water to make steam.
2. Steam spins a turbine.
3. Turbine drives a generator and the generator makes electricity.
4. Electricity goes to the transformers to produce the correct voltage.
Uranium is a non-renewable energy resource and, like the fossil fuels, it cannot be replaced once it has all been used up.
Higher Tier - Nuclear Fission
For fission to happen, the uranium nucleus must be hit by a neutron. When this happens:
The nucleus splits into smaller nuclei, Energy is released and Two or three neutrons are released.
Nuclear fusion
Nuclear fission is the splitting of large nuclei into smaller ones, while nuclear fusion is the joining of smaller nuclei to make larger ones. Nuclear fusion happens in stars and fusion bombs
Higher Tier – Nuclear Fusion
The Sun and other stars use nuclear fusion to release energy. The sequence of nuclear fusion reactions in a star is complex but overall hydrogen nuclei join to form helium nuclei.
Cold fusion
A group of scientists have claimed that they have achieved ‘cold fusion’ – nuclear fusion at ordinary temperatures and pressures. If it happens, cold fusion could be developed to provide almost limitless and cheap electricity. It would also make the international project to develop a fusion power station using high temperatures and pressures pointless.



![tutorial #14 [nuclear physics and radioactivity] .quiz](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008407305_1-1884988a9e5162a6b7a2b0d0cf8c83c5-300x300.png)