Streams and Floods
advertisement

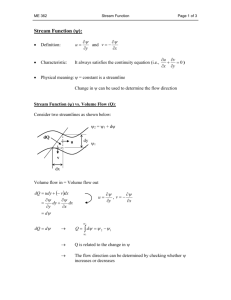
Streams and Floods Prepared by Betsy Conklin for Dr. Isiorho The Hydrologic Cycle • the movement of water and water vapor from the sea to the atmosphere, to the land, and back to the sea and atmosphere The Hydrologic Cycle (cont.) Streams • stream: a body of running water that is confined in a channel and moves downhill under the influence of gravity • can imply size (rivers = large, streams = smaller, creeks = smallest) but geologists use the term when talking about any body of running water • headwaters of stream: upper part of stream near its source in mountains • mouth: place where a stream enters the sea, lake, or larger stream Streams (cont.) • flood plain: a broad strip of land built by sediment on either side of a stream • stream channel: a long narrow depression eroded by the stream into rock or sediment • stream banks: the sides of the channel • stream bed: the bottom of the channel • sheetwash: a thin layer of unchanneled water flowing downhill, common in deserts due to lack of vegetation Streams (cont.) • sheet erosion: when a thin layer of surface material, usually topsoil, is removed by a flowing sheet of water • rills: the tiny streams formed by overland sheetwash that becomes concentrated in small channels • longitudinal profile: shows a typical stream viewed from the side • cross section: a representation of a portion of a stream in a vertical plain Drainage Basins • drainage basin: the total area drained by a stream and its tributaries • can be outlined on a map by drawing a line around the region drained by all the tributaries to a river • tributary: a small stream flowing into a larger one • divide: a ridge or strip of high ground dividing one drainage basin from another Drainage Patterns • drainage pattern: the arrangement of a river and its tributaries • types: – dendritic: resembles the branches of a tree or veins in a leaf Drainage Patterns (cont.) – radial: when the streams diverge outward like spokes of a wheel; formed on high conical mountains Drainage Patterns (cont.) – rectangular: when tributaries have frequent 90o bends and tend to join other streams at right angles; develops on regularly fractured rock Drainage Patterns (cont.) – trellis: consists of parallel main streams with short tributaries meeting them at right angles; forms in a region where tiled layers of resistant rock such as sandstone alternate with nonresistant rock such as shale Drainage Patterns (cont.) Stream Velocity • stream velocity: the distance water travels in a stream per unit time • moderately fast river = 5 km/hr (3 mph) • stream reaches its maximum velocity near the middle of the channel • high velocity generally results in erosion and transportation • low velocity generally results in deposition Stream Velocity (cont.) • factors effecting stream velocity: – shape of the channel – roughness of the channel – human interference (construction of a culvert or bridge can partially block a channel, increasing a stream’s velocity) Stream Gradient • stream gradient: downhill slope of a stream’s bed or the water surface, if the stream is very large • gradient of 5 ft/mile means the river drops 5 ft. vertically for every mile that it travels horizontally • usually decreases downstream Discharge • discharge: the volume of water that flows past a given point in a unit of time • found by multiplying the cross-sectional area of a stream by its velocity (or width X depth X velocity) • reported in cubic feet per second (cfs) in the US, or in cubic meters per second (m3/sec) Discharge (cont.) • increases during a flood, may be up to 50 to 199 times normal flow • stream erosion and transportation generally increase as a result of a flood’s velocity and discharge Stream Erosion • three types of stream erosion: – hydraulic action: refers to the ability of flowing water to pick up and move rock and sediment – solution: usually slow but effective process of weathering and erosion in which rocks are dissolved by water – abrasion: the grinding away of the stream channel by the friction and impact of the sediment load; can cause potholes (usually most effective on a rocky stream bed) Stream Transportation of Sediment • bed load: the large or heavy sediment particles that travel on the stream bed • traction: movement of sediments by rolling, sliding or dragging • saltation: when sediments are carried downstream in a series of short leaps or bounces Transportation of Sediment (cont.) • suspended load: sediment that is light enough to remain lifted indefinitely above the bottom by water turbulence; the muddy appearance of a stream during a flood or after a heavy rain is due to a large suspended load • dissolved load: the portion of the total sediment load in a stream that is carried in solution Bar • bar: a ridge of sediment, usually sand or gravel, deposited in the middle or along the banks of a stream; formed by deposition when a stream’s discharge or velocity decreases; stream deposits heavier boulders first and small particles last Gravel bars along the banks and in the middle of a stream Placer Deposits • when the heavy sediment is concentrated in the stream where the velocity of the water is high enough to carry away lighter materials but not the heavy sediment • found in streams where the running water has mechanically concentrated heavy sediment Braided Streams • a stream that flows in a network of many interconnected rivulets around numerous bars • a stream tends to become braided when it is heavily loaded with sediment and has banks that are easily eroded A braided river Meandering Streams and Point Bars • meanders: a pronounced sinuous curve along a stream’s course • point bar: a stream bar deposited on the inside of a curve in the stream, where the water velocity is low • meander cutoff: a new, shorter channel across the narrow neck of a meander A meandering stream Meandering Streams/Point Bars (cont.) • the simultaneous erosion on the outside of a curve and deposition on the inside can deepen a gentle curve into a hairpin-like meander 1 Deposition Erosion Deposition 3 Erosion 2 Point bars Curve shifts outward and downstream Oxbow Lake • oxbow lake: a crescent-shaped lake occupying the abandoned channel of a stream meander that is isolated from the present channel by a meander cutoff and sedimentation Meander neck becomes narrower Neck cutoff occurs Oxbow lake Flood Plains • flood plain: a broad strip of land built up by sedimentation on either side of a stream channel • natural levees: low ridges of flooddeposited sediment that form on either side of a stream channel and thin away from the channel Flood Plain (cont.) Flood Plains 1 2 Sediment deposited during floods 3 Natural leeves Backswamp Deltas • delta: a body of sediment deposited at the mouth of a river when the river’s velocity decreases • distributaries: small, shifting channels that carry water away from the main river channel and distribute it over the surface of the delta • a delta can be represented by the Greek symbol delta () due to the fact that some deltas are broadly triangular Deltas (cont.) River Land Distributaries Marshy delta surface Topset beds Lake Foreset beds Bottomset beds • foreset beds: form the main body of the delta • topset beds: nearly horizontal beds of varying grain size formed by distributaries shifting across the delta surface • bottomset beds: deposits of the finest silt and clay that are carried out into the lake by the river water flow or by sediments sliding downhill on the lake floor Deltas (cont.) • wave-dominated delta: a delta formed by the reworking of sand by wave action Mediterranean Sea Distributaries Barrier Islands Nile River (Egypt) Deltas (cont.) • tide-dominated delta: a delta formed by the reworking of sand by strong tides Bangladesh Tidal sand bars Deltas (cont.) • stream-dominated delta: a delta with fingerlike distributaries formed by the dominance of stream sedimentation (also called birdfoot delta) Alluvial Fans • alluvial fan: a large, fan- or cone-shaped pile of sediment that usually forms where a stream’s velocity decreases as it emerges from a narrow mountain canyon onto a flat plain Narrow mountain canyon Braided stream Alluvial fan Plain Flooding • recurrence interval: the average time between floods of a given size • flood erosion: caused by the high velocity and large volume of water in a flood • high water: covers streets and agricultural fields and invades buildings, shorting out electrical lines and backing up sewers • flood deposits: usually silt and clay Urban Flooding • urbanization enhances flooding due to paved areas and storm sewers which increase the amount and rate of surface runoff of water, making river levels higher during storms • bridges, docks, and buildings built on flood plains can also constrict the flow of flood waters, increasing the water heigh and velocity and promoting erosion Flash Flooding • flash floods: local, sudden floods of large volume and short duration, often triggered by heavy thunderstorms Controlling Floods • upstream dams: trap water and release it slowly after a storm • artificial leeves: embankments built along the banks of a river channel to contain floodwaters within the channel • protective walls: made of stone (riprap) or concrete constructed along river banks to slow erosion • floodwalls: walls of concrete, may be used to protect cities from flooding Controlling Floods (cont.) • bypasses: reduce the discharge in the main channel by diverting water into designated basins in the flood plain Weir Dam Bypass Leeve Flood wall Reservoir Stream Valley Development • valleys: the most common landforms on the earth’s surface that are usually cut by streams • downcutting: the process of deepening a valley by erosion of the stream bed • base level: the limit of downcutting Graded Stream • graded stream: a stream that exhibits a delicate balance between its transporting capacity and the sediment load available to it • an increase in gradient causes an increase in a stream’s velocity, allowing the stream to erode and carry more sediment • a change in sediment load can cause a change in gradient as well Lateral Erosion • lateral erosion: the erosion and undercutting of a stream’s banks and valley walls as the stream swings from side to side across its valley floor 1 2 3 Undercutting of valley wall Widening flood plain Headward Erosion & Stream Piracy • headward erosion: the slow uphill growth of a valley above its original source through gullying, mass wasting, and sheet erosion • stream piracy: the natural diversion of the headwaters of one stream into the channel of another Stream Terraces • stream terraces: steplike landforms found above a stream and its flood plain 1 Flood plain 3 Terraces 2 Terraces Terraces New flood plain Incised Meanders • incised meanders: meanders that retain their sinuous curves as they cut vertically downward below the level at which they originally formed resulting in a meandering valley Incised meanders of the Colorado River Meandering river Land surface at base level Base level Incised meanders Land surface has been lifted above base level Uplift Base level Superposed Streams • superposed streams: a river let down onto a buried geologic structure by erosion of overlying layers The stream initially cuts through the horizontal sediment Continued erosion removes horizontal strata and stream cuts through underlying rock forming narrow valleys in resistant rock Pictures All pictures used in this power point presentation were taken from the following: Carlson, Diane H., David McGeary and Charles C. Plummer. Physical Geology: Updated Eighth Edition. New York City, McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2001.