1789-1799 Causes of the French Revolution
advertisement

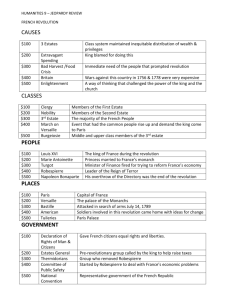
1789-1799 Causes of the French Revolution • Bad Harvests (1780s) • Rising Food Prices • Inadequate transportation network Causes of the French Revolution • Fiscal Crisis *ineffective taxation system *debt from Wars (Seven Years’ War + American Revolutionary War Causes: Ancien Regime Ancien Regime – 3 Estates 1st Estate – Catholic Clergy (130,000) 2nd Estate – French Nobility (300,000) 3rd Estate – The rest of the French Population (Bourgeoisie Urban/rural middle class Urban poor/peasants) Ancien Regime Causes: Ineffectiveness of Louis XVI • Extravagant lifestyle in Versailles *removed and indecisive • Proposed tax reforms (land tax) – refused by the Assembly of Notables • Call for EstatesGeneral (May 1789) – first time since 1614 / weakness of Bourbon monarchy! Causes: Popularity of the Enlightenment Ideas • Natural Rights • Republicanism • Liberalism • Religious Tolerance • Feminism Causes: Social Tensions within French Society • Bourgeoisie vs. Nobility • Peasants vs. Nobles • General resentment toward: - power and influence of the Catholic Church - inequalities of Ancien Regime "This will not long endure." ["Ça ne durera pas toujours"] 1789 – Major Events Leading up to the Storming of Bastille *Assembly of Notables - refused land tax *Meeting of the Estates – General - reps from each estate (old rule: 1 vote per estate) *The Tennis Court Oath (reps from the 3rd estate + some from the first two) - Goal: To write a new constitution - Declared themselves The National Assembly *Soldiers in Paris (mostly foreign mercenaries) Storming of the Bastille (July 14, 1789) 1789 -“The Great Fear” and End of Feudalism • Storming of the Bastille • Sporadic violence and peasant uprisings throughout France • National Assembly abolishes privileges and tithes • Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (statement of revolutionary principles) Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen • Fundamental document of the Revolution • Reflects ideas of the Enlightenment, such as: *Natural rights *Popular sovereignty *Individual freedoms (speech and press) The Women's March on Versailles • Poor harvests of 1789 shortages of grain • Traditional view: “Father of the People” will provide for his flock • Louis XVI and his family – forced to return to Paris and recognize the National Assembly Decline of the Church's Power • Prior to the revolution *1st Estate – 130,000 members *Largest landowner in France *Collected tithes (10% tax) (resented by Protestants and Enlightenment thinkers, like Voltaire) Decline of the Church (cont.) • Reforms under the National Assembly’s Constitution: *All Church property – “disposal of the nation” (nationalized) *Abolishment of tithes, monastic vows, and religious orders *Civil Constitution of the Clergy (1790) – clergy=“employee of the state” (conflict for the clergy over their “loyalty oath”) “The Patriotic De-Fattening Machine” Foreign Threat • Revolution perceived as a threat to European absolutist monarchies • Louis XVI with the moderates – unlikely alliance – different motivations (strengthen the king/army vs. exporting revolution) • France at war with Austria and Prussia (eventually the Dutch and the British join the anti-French alliance) June 1791 – The Royal Flight • Royal family flees Paris – caught at Varennes (5 mi. from the border) • Brought back to Paris • Louis XVI signs a new constitution *Weak constitutional monarchy!!! Legislative Assembly • Conservatives vs. centrists (moderates) vs. radicals • Radicals’ support grows after Louis’ failed escape • Jan.1793 – Louis XVI executed • Continued war = increase in food prices (anger by sansculottes) • The French Republic – 1792- year 1 (Cult of Reason, etc.) The Radical Phase – The Reign of Terror (1793-1794) • Rise of Jacobin radicals (The Mountain – Maximilian Robespierre) • Execution of “Enemies of the Revolution” (Committee of Public Safety) • Counter-reaction (Robespierre loses support – guillotined) The Directory (1795-1799) and the Thermidorian Reaction • New constitution of 1795 (conservative pushback) *Limited (property) suffrage instead of universal suffrage *Establishes the Directory • The Directory – ineffective and corrupt social unrest use of army • Napoleon comes to power - END OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION Napoleon Bonaparte • 1799 – Consulship (first consul of the Republic) • 1804 – Decline of republicanism / declares himself an emperor • Reforms: *The Napoleonic Code *The Concordat *Reforms in tax code, higher education, urban infrastructure *Established Central Bank *Emancipation of Jews *Limits on personal freedoms (freedom of press no more!) • Popular authoritarianism!!! The French Empire – Napoleonic Wars • Successes in Prussia and Austria (early 1800s) • The Continental System – commercial boycott of Britain • Peninsular War – against Spain and Portugal • 1812 –Invasion of Russia (big disaster!) • Exile to Elba • Escape = 100 days • Final defeat – The Battle of Waterloo (1814) • Exile to St.Helena Legacy of the Revolution • “Dawn of the modern era” • Decrease in the power of aristocracy and the Church • Influence of the Enlightenment ideas (republicanism) • Challenge to absolutism • Inspired other revolutions "Liberty leading the People" by Eugène Delacroix, 1830 Timeline of the French Revolution Work Cited: • Slide 1: http://edu.glogster.com/media/4/27/26/97/27269711.jpg • Slide 2: • Slide 3: http://www.twcenter.net/forums/showthread.php?t=125658 • Slide 4: http://memory.loc.gov/service/pnp/cph/3b50000/3b51000/3b51500/3b51557r.jpg http://learnearnandreturn.files.wordpress.com/2011/07/imgsrv.jpeg http://general-history.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/12/ancien-regime.jpg • Slide 5: http://chnm.gmu.edu/revolution/searchimages/165.jpg http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_Ish7688voT0/TLb20E8K2kI/AAAAAAAACu0/btdetXWoP5c/s1600/429px-Ludvig_XVI_av_Frankrike_portr%C3%A4tterad_av_AF_Callet.jpg • Slide 6: http://www.history.ucsb.edu/faculty/marcuse/classes/2c/images/1775GeoffrinSalonIdent$Fr485pxw.jpg • Slide 7: http://www9.georgetown.edu/faculty/spielmag/docs/legrandsiecle/lgs4.htm • Slide 8: http://www.mtholyoke.edu/courses/rschwart/hist151/French%20Revolution%20II/album/slides/old%20regime%20not%20long%20to%20endure.jpg • Slide 9: • Slide 10: http://www.mtholyoke.edu/courses/rschwart/hist151/French%20Revolution%20II/album/index.html http://media-3.web.britannica.com/eb-media/98/90498-004-CEB880DC.jpg http://weissworldhistory.files.wordpress.com/2008/02/tiers-etat.jpg • Slide 11: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Declaration_of_Human_Rights.jpg • Slide 12: http://www.historywiz.com/images/frenchrevolution/womensmarch1.jpg • Slide 13: • http://1.bp.blogspot.com/-YIQJvLNdNK8/TtFYaRYXiRI/AAAAAAAABM8/YCR2t0PlJLA/s1600/three+estates+caricature.jpg http://unamsanctamcatholicam.blogspot.com/2007/09/myth-ofignorant-priests.html • • Slide 15: http://cdn.dipity.com/uploads/events/27567ddb73a00a9dc3846838d17812b9_1M.png and http://www.imperialtometric.com/Edition/batailles/Sections/Battle_of_Valmy.jpg • Slide 16: • Slide 17: • Slide 18: http://bastille-day.com/media/Robespierre.jpg • Slide 21: http://www.rjgeib.com/thoughts/french/robes.jpg and http://www.oocities.org/eurohist1916/eurohistory/APFrenchRevolution.htm