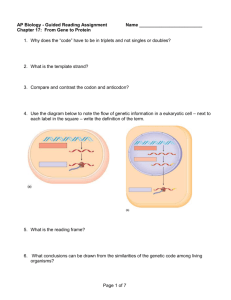
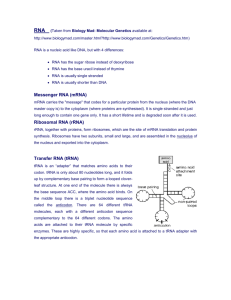
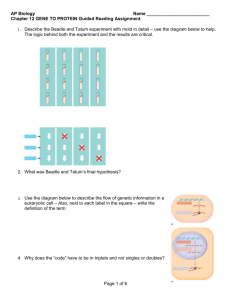
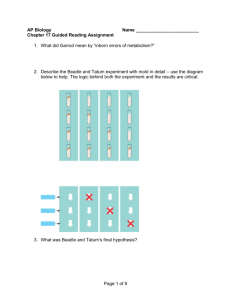
Transcription 11/3/05
advertisement

Transcription 11/3/05 Stable RNA rRNA -Structural component of ribosomes tRNA-Adaptors, carry aa to ribosome Synthesis Promoter and terminator Post-transcriptional modification (RNA processing) Evidence Both have 5’ monophospates Both much smaller than primary transcript tRNA has unusual bases. EX pseudouridine tRNA and rRNA Processing Both are excised from large primary transcripts 1º transcript may contain several tRNA molecules, tRNA and rRNA rRNAs simply excised from larger transcript tRNAs modified extensively 5. Base modifications Examples of Covalent Modification of Nucleotides in tRNA CH3 H H CH3 N N 6 N H N N 6 N N N C C CH3 CH2 O N N N6-Methyladenylate N6-Isopentenyladenylate (m6A) (i6A) O H H H H NH HN 3 4 N O Dihydrouridylate (D) 2 1 5 C H2C NH O N O Uridylate 5-oxyacetic acid (cmo5U) Pseudouridylate (Ψ) (ribose at C-5) N N 3 N CH3 6 CH2 5 NH NH 5 NH2 7-Methylguanylate (m7G) O O N N O 3-Methylcytidylate (m3C) O NH2 H3C N N O C NH 7 Inosinate (I) HO O N NH N N O CH3 O 5-Methylcytidylate (m5C) Base O H H O H O CH3 H 1' 2' 2’-O-Methylated nucleotide (Nm) Modifications are shown in blue. Eukaryotic Transcription Regulation very complex Three different pols Distinguished by -amanitin sensitivity Pol I—rRNA, least sensitive Pol II– mRNA, most sensitive Pol III– tRNA and 5R RNA moderately sensitive Each polymerase recognizes a distinct promoter Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases RNA Pol. Location Products I Nucleolus Large rRNAs (28S, 18S, 5.8S) -Amanitin Promoter Sensitivity Insensitive II Nucleus Pre-mRNA, some snRNAs Highly sensitive III Nucleus tRNA, small rRNA (5S), snRNA Intermediate sensitivity bipartite promoter Upstream Internal promoter and terminator Eukaryotic Polymerase I Promoters RNA Polymerase I Transcribes rRNA Sequence not well conserved Two elements Core element- surrounds the transcription start site (-45 to + 20) Upstream control element- between -156 and -107 upstream Spacing affects strength of transcription Eukaryotic Polymerase II Promoters Much more complicated Two parts Core promoter Core promoter Upstream element TATA box at ~-30 bases Initiator—on the transcription start site Downstream element-further downstream Many natural promoters lack recognizable versions of one or more of these sequences TATA-less Promoters Some genes transcribed by RNA pol II lack the TATA box Two types: Housekeeping genes ( expressed constitutively). EX Nucleotide synthesis genes Developmentally regulated genes. EX Homeotic genes that control fruit fly development. Specialized (luxury) genes that encode cell-type specific proteins usually have a TATA-box mRNA Processing in Eukaryotes Primary transcript much larger than finished product Precursor and partially processed RNA called heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) Processing occurs in nucleus Capping mRNA 5’ cap is a reversed guanosine residue so there is a 5’-5’ linkage between the cap and the first sugar in the mRNA. Guanosine cap is methylated. First and second nucleosides in mRNA may be methylated BACK Polyadenylation Polyadenylation occurs on the 3’ end of virtually all eukaryotic mRNAs. Occurs after capping Catalyzed by polyadenylate polymerase Polyadenylation associated with mRNA half-life Histones not polyadenylated Introns and Exons Introns--Untranslated intervening sequences in mRNA Exons– Translated sequences Process-RNA splicing Heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA)-Transcript before splicing is complete Splicing Overview Occurs in the nucleus hnRNAs complexed with specific proteins, form a ribonucleoprotein particle (RNP) Primary transcripts assembled into hnRNP Splicing occurs on spliceosomes consist of Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (SnRNPs) components of spliceosomes Contain small nuclear RNA (snRNA) Many types of snRNA with different functions in the splicing process Splice Site Recognition Introns contain invariant 5’-GU and 3’-AG sequences at their borders (GU-AG Rule) Internal intron sequences are highly variable even between closely related homologous genes. Alternative splicing allows different proteins from a single original transcript Simplified Splicing Mechanism RNA pol III Precursors to tRNAs,5SrRNA, other small RNAs Promoter Type I Lies completely within the transcribed region 5SrRNA promoter split into 3 parts tRNA promoters split into two parts Polymerase II-like promoters EX. snRNA Lack internal promoter Resembles pol II promoter in both sequence and position DNAse Footprinting Protected region Use: promoter ID End Label template strand Add DNA binding protein Digest with DNAse I Remove protein Separate on gel