Origins of Mankind and Civilization
advertisement

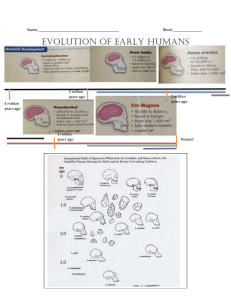
Origins of Mankind and Civilization Pre-history Purpose The purpose of today’s lesson is to identify and understand the important aspects of the lives’ of early humans Objectives – The students will predicted the needs of early humans – The students will determine early human migration routes based on evidence – The students will compose a diary entry from the perspective of an early human Prehistory The story of humankind begins about 5,500 years ago… Prehistory: – The long period of time before people invented systems of writing Prediction Write down three things that you believe you could not live without Discuss with a partner Stone age humans had much simpler needs – Even simple needs were hard to get What simple things did stone age people need to survive? Hominids The first humanlike creatures can be traced back 4.4 million years These are called hominids Anthropology- the study of hominids Scientists Anthropologists – Study bones and fossils and look for change Paleontologists – Study fossils to determine characteristics Archaeologists – Study artifacts left behind (tools, pots, beads, etc.) Dating Early Artifacts Archaeologists and anthropologists have to determine when the fossils or artifacts originated Radio-carbon dating: – Test for carbon decay Prehistoric Finds Oldest human ancestor – Fossils found in Ethiopia – Teeth, bones, skull – 4.4 million years old – These creatures would have weighed about 65 pounds, and stood 4 feet tall Prehistoric Finds Lucy – 3.2 million year old skeleton – Found in 1974 in Africa The First Hominids Australopithecus- – “southern ape” Homo habilis – “person with ability” The First Hominids Homo erectus – “person who walks upright” Homo sapien – “Person who thinks” – All people today! Humans The Ice Ages Four long periods of cold climate During, only the middle latitudes of Earth were warm enough for human and animal life Land bridges allowed for movement Paleolithic Age Old Stone Age Began with Homo habilis making stone tools Lasted until about 12,000 BCE Homo habilis to Homo erectus Appeared in Africa 1.8 million years ago Early Humans were HunterGatherers What does it mean to be a hunter-gatherer? – Mostly hunted for the majority of their food – Captured fish – Gathered nuts, berries, and other easy to find food to add to their diets This lifestyle forced humans to move often in order to find food – Nomads – Constantly tracking herds of animals Used animals for food, clothing, making homes and even tools from their bones Homo erectus Hunter-gatherer society Fire Nomadic Gestures language and grunts… led to crude Homo sapiens Neanderthals – 100,000 years ago – Nomadic, hunter-gatherers – Better tools – Advanced culture Cro-Magnons – Improved technology – Social life Neolithic Revolution Agricultural Revolution- shift from food gathering and hunting to planting crops – Causes: raising temperatures and climate change, high supply of grain, crops provided a steady source of food Neolithic Revolution cont. Farming Methods – Slash and burn farming: cut down trees and burn grasses cleared the field and fertilized the soil – Domestication of animals: horses, goats, pigs, dogs, sheep, goats and camel Locations – Africa wheat and barley – China grain and wild rice – Mexico and Central America corn, beans and squash – Peru tomatoes, sweet potatoes, white potatoes Neolithic Revolution Neolithic Revolution advances lead to the first civilizations! Make Your Own Cave Painting It’s time to crate some cave art of your own! Using a piece of led not in a mechanical pencil use the space provided to draw a beautiful picture or event. – Think of any things in nature that you might have seen that would be simple to draw.