Introduction to History
advertisement

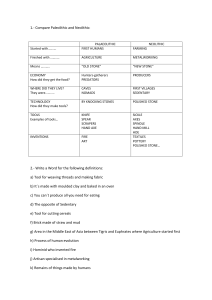
Introduction to History What is history? - A record and explanation of what people have thought, said and done. What do you know about History? On a blank Sheet of paper draw a map of the world. You have 7 minutes How close were you to the actual map? Now fill in as many names of continents, countries, and bodies of water! 7 minutes On the back of the map write down as many people and/or events that you think we might cover this year Now put the events in chronological order. Ways to Analyze Civilizations: Political Economic everyday life, gender, family, social class. Intellectual leaders, practices, traditions, beliefs. Social money, trade, business. Religion government, leaders, law and order, laws. tech. advances, education, new ideas. Artistic music, paintings, architecture, literature. Characteristics of a Civilization CHARACTERISTIC SIGNIFICANCE Makes and enforces laws - Exercises authority over organized state - Standardizes money systems Organized Government - Organized Religion -Offers Division of Labor -Encourages Class Structure -Defines System of Writing -Provides guidance and questions of life, death, nature - Selects clergy trade and development of new technology - Promotes a system of social classes a persons place in society - Reflects the distribution of wealth a way to keep accurate records -Serves as a way to pass on knowledge Human Beginnings Pre-History – the period before writing had been invented; any period before 5,500 years ago. I. II. Most people were nomads – moved constantly in search of food - Had few possessions Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) A. Began 2.5 million years ago and ended – 12,000 B.C. B. Named because they used stone tools C. Were hunter-gatherers (females gathered fruits, nuts, and seeds; males were hunters) D. By 50,000 B.C. developed speech Human Beginnings Cont’d III. IV. Neanderthals (200,000 years ago) A. Nomads B. Used fire for cooking C. Skillful crafting of stone knives, spear heads, bone tools D. Lived in small groups of around 35 - 50 Neolithic Period (New Stone Age) – Neolithic Revolution A. Shift from gathering food to producing food B. Agriculture brought about a more stable environment - grew crops like: wheat, barley, rice, potatoes C. Domesticated animals – cattle, pigs, sheep, chickens, dogs Human Beginnings Cont’d D. People lived longer because they could produce food E. People settled in communities F. Technological advances - Invented the plow - Fertilized their fields - Looms for weaving - Baked clay bricks for construction - Hammered metals to make weapons and jewelry - Created calendars (to measure seasons) - Worshiped deities