Reconstruction Notes
advertisement

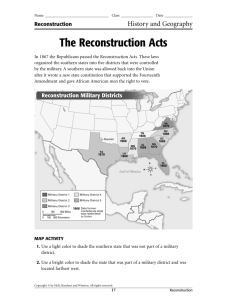
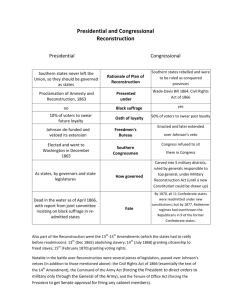
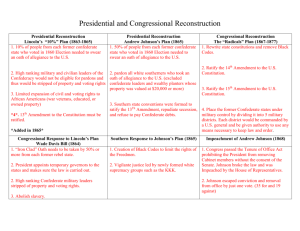
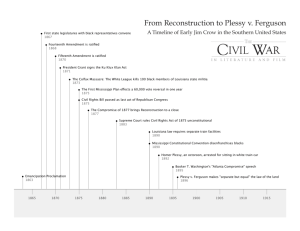
Reconstruction (1865-77) Would be the equivalent of losing 6 million Americans today 35.2 Million (1865) Union Deaths Confederate Deaths 360,000 258,000 Impact of the Civil War Slavery is Abolished What issues are created with the end of slavery? (Group Work) Confederate $$$ is worthless Railroads and infrastructure destroyed Lincoln’s Last Act Wade-Davis Bill Majority of White Men Take an Ironclad Loyalty Oath No Slavery Elect New Government No Former Government Officials or Confederate Military Leaders Lincoln says NO – Pocket Veto President Johnson v. Radical Republicans (Presidential Reconstruction v. Radical Reconstruction) Andrew Johnson Thaddeus Stevens (PA) Charles Sumner (MA) Reconstruction Issues What to do with… Confederate Leaders Confederate Soldiers Confederate Citizens Former Slaves Retribution/Justice v. Rehabilitation Rights of citizenship, land, education, etc. Radical Republican Power Grab? Slaves 13th Amendment (r.1865) Freedmen’s Bureau Family Reunification Education Basic Needs Black Codes (def.) Laws passed by southern state governments designed to limit the rights of African Americans Blacks could not vote, serve on juries, or travel without employment, had to work in unskilled labor Civil Rights Act of 1866 (H.111 to 38) (S.33 to 12) Johnson Vetoes – Congress overrides (How?) th 14 Equal Protection Clause Amendment (r.1868) No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws. 15th Amendment (r.1870) To the tune of “Three Blind Mice”: Free, citizens, vote, 13th, 14th, 15th. It all happened after the Civil War, It all happened after the Civil War. Free, citizens, vote, Military Reconstruction Act of 1867 Registered Texas Voters White: 59,633 Black: 49,479 (Blacks were 30%) Re-admission to representation in Congress Tennessee - July 24, 1866 Arkansas - June 22, 1868 Florida - June 25, 1868 North Carolina - July 4, 1868 South Carolina - July 9, 1868 Louisiana - July 9, 1868 Alabama - July 13, 1868 Virginia - January 26, 1870 Mississippi - February 23, 1870 Texas - March 30, 1870 Georgia - July 15, 1870 Radical Reconstruction Works (ish) African Americans elected to office Republican Legislatures Repealed the Black Codes Johnson Impeached Secretary of War, Edwin M. Stanton Tenure of Office Act Problems Carpetbaggers Scalawags Land Issues Sharecropping Article Racial Tensions Ku Klux Klan Ulysses S. Grant Inexperienced “Whiskey Ring” Panic of 1873 1874, Democrats won seats in Congress Compromise of 1877 Rutherford B. Hayes (R) VS. Samuel Tilden (D) "It is like writing history with Lightning. And my only regret is that it is all so terribly true." -- President Woodrow Wilson