Chapter_4
advertisement

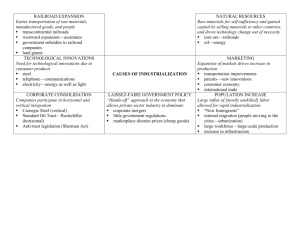
Chapter 4 Railroads Brief History A significant role in the economic development of US from 1850 to 1950. 20世紀後半開始衰落: The rise of alternate transport modes with superior services and/or cost characteristics, primarily motor carriers and pipelines A resurgence in water transportation Changing needs of the US economy. Other modes growing faster, However, may experience a resurgence because of more aggressive marketing and growth in intermodal traffic. History in Taiwan 劉銘傳興建縱貫鐵路 清光緒十三年(西元1887),任命補用知 府<<張士瑜>>為鐵路商務總辦,六月開始由大 稻埕向基隆舖設鐵路西元1891年完工通車,全 長三十二公里,其中穿越獅球嶺的隧道全長五 七三公尺,工程頗為艱巨,完工後在隧道南端 口勒刻「曠宇天開」的碣碑,此碑仍保留在當 地。西元1888年,繼續開築由稻埕往南的鐵路, 至西元1893年完成大稻埕到新竹之間鐵路,不 過此時劉銘傳已經離職, History in Taiwan 十大建設六項交通建 設(鐵路電氣化,中山高速 公路,基隆港,高雄港,中 正國際機場,蘇澳港等. 環島鐵路 高鐵 http://netcity7.web.hi net.net/UserData/tra clubs/ Competition Railroads were the dominant mode of transportation prior to World War II The railways must compete with the other modes of transportation that have either evolved or matured since the 1920s. Taiwan railway need to face the competition after it become a private company. Intermodal Railroad company president said: Our service is not as fast as truck, but we have discovered that customers will accept a slower transit time in exchange for a lower rate, as long as service is consistent and we can usually provide a lower freight rate because our costs are less than truck. Abandonments 1916,the railroad industry owned 254,000 miles of track. Today, more than half of that is gone, enough to circle the Earth three times. The railroads had to abandon significant portions of rail trackage to remain competitive. Does Taiwan railroad need to abandon some trackage to remain competitive? Abandonments In some cases, all or part of the right of way was turned into hiking trails with some bridges left in place. Some became recreational facilities, like Gi-Gi lane up to Ali Mt. The abandonments were either rural branches or duplicate lines left over. General Service Characteristics Commodities Hauled Coal Farm Products Chemicals Transportation Equipment Commodities Hauled 19 century, railroad moved almost every available type of product Today, the railroad system has evolved into a system that ships large quantities of heavy-weight, low-value commodities. Motor carriers concentrate on the handling of small-volume, high-value finished goods, whereas water and pipelines carry the larger volumes of the lowest value types of bulk commodities. Coal 43.8 percent of the total tonnage transported in 1996, the primary haulers of coal. Coal is an alternative energy source that will probably continue to be an important commodity shipped by the railroads. 火力發電及煉鋼 Farm Products Farm products constitute the second largest commodity group hauled by railroads. Chemicals Hazardous materials are transported in specially designed tank cars. The railroads, in comparison with highway movements, safely transport chemicals, and this safety has been steadily increasing for years. This type of long-haul bulk material is ideally suited for rail movement. Transportation Equipment Transportation equipment carloadings, which are linked to the relative health of the domestic automobile industry, have increased to more than five percent of total carloadings, an increase of more than 40 percent since 1982. The railroad are still an ideal mode of transport for many different types of goods, high-value merchandise and raw materials alike. Constraints Railroads are constrained by fixed rights-of-way and therefore provide differing degrees of service completeness. If line-haul mileage continues to decline, the industry will become less service-complete and even more dependent on other modes of transportation for completion of many types of moves. Strengths A large carrying capacity enables the railroads to handle large-volume movements of low-value commodities over long distances. Although pipelines compete directly with the railroads, they are restricted largely to the movements of liquid and gas. Railroad can handle almost any type of commodity by changing the hauling cars. Strengths Liability for loss and damage is usually assumed by the railroads. Steel wheel on steel rail Comparatively high percentage of goods damaged in transit.(~3%) Incidence of loss is usually higher than on other modes because of the high degree of multiple handlings. New Technologies to prevent the cargo damaged – multilevel suspension systes and end-of-car cushioning devices. Equipment Carload is the basic unit of measurement of freight handling by the railroads. 1996-91.9tons/car;1929-46.3tons/car Generalized car types: Boxcar(plain): Standardized roofed freight car with sliding doors on the side used for general commodities. Equipment Boxcar(equipped): Specially modified boxcar used for specialized merchandise, such as automobile parts Hopper car: A freight car with the floor sloping to one or more hinged doors used for discharging bulk materials Covered hopper: A hopper car with a roof designed to transport bulk commodities that need protection from the elements, like rain. Equipment Flatcar: A freight car with no top or sides used, for instance, building materials. Refrigerator car: A freight car to which refrigeration equipment has been added for controlled temperature Gondola: A freight car with no top, a flat bottom, and fixed sides used primarily for hauling bulk commodities Tank car: Specialized car used for the transport of liquids and gases Tank car 35T23000型篷斗車 篷斗車專作為運輸散裝穀類(例如小麥、玉米、黃豆)或散裝 糖類的有篷斗車 Boxcar 守車 供「列車長、車長」與其他列車服務人員乘坐執行公務而的車輛 Flatcar Gondola 煤斗車(Hopper) Service Innovations Piggyback traffic – TOFC & COFC TOFC – Trailer-on-flatcar,on-time deliveries, regularly scheduled departures, and fuel efficiency are the potential. Also simplified their billing procedures and made their computers accessible to customers for service innovations. Service Innovations COFC – container-on-flatcar A container does not have the wheels and must therefore be placed on a flatbed truck for ramp-to-door delivery. 運送貨櫃可吸收小體積貨品,以其與motor carriers 競爭. International commerce: combine with ocean vessels Service Innovations Unit train – specializes in the transport of only one commodity, usually coal or grain, from origin to destination. Many times the shipper owns cars, and the train is, in effect, rented to the shipper for a particular period of time. Cost Structure Fixed Costs Semi-variable Costs Variable Costs Labor Fuel Fixed Costs The railroads, along with the pipelines, are the only modes that own and maintain their own network and terminals. Therefore, there are a large proportion of indirect fixed costs. Mostly operation, maintenance and ownership of rights-of-way, which are not found in other modes(excluding pipelines). Fixed Costs Extensive investment in private terminal facilities Freight yards, which trains are sorted and assembled Terminal areas & sidings, where shippers and connecting railroads are serviced. Freight cars and other equipments. motors can use free of right-of-way, because they don’t need to build roads. Semi-variable Costs Maintenance of Rights-of-way, structures and equipment Variable Costs Labor cost is the largest single element of variable costs for railroads. Fuel and power costs are the next largest group of variable costs. Economies of Scale Very large capital investment because of the cost incurred in buying land, laying tracks, building bridges, providing terminals, and providing right-of-way facilities. Equipment investment is significant. Maintenance of right-of-way structures also results in fixed costs. Technology Computers are playing a large role in every mode of transportation, and the railroads are no exception. Advanced train control systems – can track the flow of trains… Railyard Control – sort and classify as many as 2,500 railcars a day Communications and Signaling – communications between dispatchers, yard workers, field workers and train crews Customer Service High Speed Train Current Issues Alcohol and Drug Abuse Long hours, low supervision, and nights away from home. Energy Railroads are more energy-efficient than any other freight mode except pipelines per tonmile than most of the other modes Railroads cause less damage to the environment than do trucks. Railroad emissions(0.9 grams per net ton-mile) were 75 percent less than truck emissions.