Physical Geography of Russia
advertisement

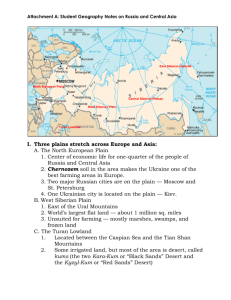
Physical Geography of Russia Lake Baikal Folders/ Composition books Crossword Scissors (if you have them) Key Terms • • • • • • • • North European Plain Siberia Ural Mountains Caucasus Volga River Caspian Sea Black Sea Lake Baikal Key Terms • Ural Mountains mountain range where Europe and Asia meet. • Caspian Sea the world’s largest inland sea, bo • Siberia a vast region in Russia, stretching from the Urals to the Pacific Ocean. Borders the Caucasus Mountains • Volga River the longest river in Europe, located in western Russia • taiga a forest of mainly evergreen trees covering much of Russia Climate • Russia is mainly cold with short summers • Russia’s northern coast is tundra, most of the ground is permafrost (covers 40% of Russia) • Plant life includes small plants in the north and the vast taiga. • Taiga is the largest forest in the World. Natural Resources • Russia has a wealth of natural resources, including rich soils, timber, metals, precious gems, and energy resources. • These resources have been poorly • managed, however, and many remaining resources lie in remote Siberia. North European Plain • Vital to Russia for its crops and industry. • Coalfields stretch throughout the plain. • Wheat, barley, beans, and oats major crops. Siberia • Large part of northern and central Russia that crosses Asia. In the north is the tundra. • Those who do live there fish, hunt seals and walruses, or herd reindeer. • People may use helicopters to travel between villages. Ural Mountains • Mountain range where Europe and Asia meet. • Known for its variety of gems and stones. • Platinum, sapphire, silver Caucasus Mountains • This is a fertile region of valleys where many nonRussian people live. • Thirteen different ethnic groups live in the eight countries, or republics, that border Russia in this region. • Many, like the Armenians, have cultures far older than the Russians. Contains Mount Elbrus, the highest point in Russia at 18,510 feet. Volga River • The longest river in Europe, located in western Russia • An important transportation route. • These transport people and goods from one city to another. Caspian Sea • The Caspian Sea is about the size of California. • It is the largest inland body of water in the world. • The Caspian Sea has salt water, not freshwater. Black Sea • Through this sea, Russia can reach the Mediterranean Sea. • Russia touches many inland bodies of water. In the southwest, it borders on the Black Sea • Few harmful sea animals in the Black sea, other than the Rhizostome jellyfish Lake Baikal • This is the world’s deepest freshwater lake. Lake Baikal holds almost 20 percent of the world’s unfrozen freshwater. It is also the world’s oldest lake, dating back more than 30 million years. • Some of the plant and fish species in the lake can be traced to prehistoric times. • Unfortunately, a large paper mill nearby has polluted the Lake Baikal region. The paper mill is a major source of jobs and wealth. The region struggles to both save the lake and keep the badly needed industry. BAIKAL LAKE MONSTER? Exit Ticket • 1. It is in the _______________________ that the continents of Europe and Asia meet. (Sakhalin islands/Ural Mountains) • 2. The _________________________ provides an important transportation route through Russia. (Lake Baikal/Volga River) • 3. The ________________________’s rich, black soil has made it Russia’s main farming area. (steppe/taiga) • 4. ______________________ is a cold, empty land of barren plains and endless forests. (Siberia/Moscow) • 5. The vast forest of evergreen trees that covers about half of Russia is called the _______________________. (steppe/taiga)