Atoms - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

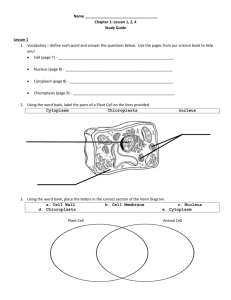
Unit 3 Why is it important for environmentalists to understand how organisms are organized? Every organism is a chemical factory that captures matter & energy from its environment and transforms them into structures & processes that make life possible… We are learning Atoms …… Biosphere Levels of Organization All elements are composed of one type of atom: I. Atoms (the smallest particles that exhibit the characteristics of the element) are made of subatomic particles: a. Protons (+) in the nucleus b. Neutrons (0) in the nucleus Give atoms their weight c. Electrons (-) outside the nucleus in electron cloud Dot diagram - shows valence electrons Bohr Model of nitrogen Levels of Organization II. Compounds: substances composed of different kinds of atoms Levels of Organization II. The Four Organic Compounds that make up bio- compound in cells: 1. Lipids: fats & oils Store energy & make up cell membrane Carbohydrates: sugars, starches, & cellulose 2. Store energy & provide cell structure Proteins: amino acids 3. Structure, enzyme, immunity Nucleic acids: DNA & RNA (made of sugar, phosphate group, & nitrogen base) 4. Store & express genetic information Create a graphic organizer for the four macromolecules. Be sure to include: 1. Name of Macromolecule 2. Function of Macromolecule 3. What are they made up of? (nucleotides, sugars, etc) 4. Examples! (eggs, cell membrane, fruit, etc) 3. Bacteria To Be Turned In: Draw, color, and label the three cell types & their internal structures/ organelles I. Atoms II. Compounds III. Cells Types of Cells Prokaryotic cells: have no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Seen in bacteria Types of Cells Eukaryotic cells: have a nucleus & organelles bound by membrane Seen in plants, animals, fungi, and protists Organelles = tiny organs inside cell Nucleus: house for DNA Mitochondria: “power house”; performs respiration (makes energy from sugar) Chloroplast: in plants only; performs photosynthesis (make sugar from sunlight) Ribosomes: make protein And more… Levels of Organization 6 Kingdoms Prokaryotes/ Bacteria: (have no nucleus or membranebound organelles): 1. Archaebacteria Kingdom: “extreme” prokaryotes Found in hot springs, deep sea, sulfur springs 2. Eubacteria Kingdom: general prokaryotes Found everywhere! Important Note: Bacteria act as decomposers Levels of Organization Eukaryotes: (have nucleus & membrane-bound organelles): 3. Fungi Kingdom: eukaryotic multicellular absorptive *heterotrophs (eat others for food) 4. Protist Kingdom: eukaryotic single- and multi-celled *autotrophs (make own food) & heterotrophs 5. Plant Kingdom: Eukaryotic multicellular autotrophs 4 Types: Mosses Ferns Gymnosperms (i.e. conifers): seeds are not in flowers/fruits Angiosperms : flowering plants that produce seeds in flower/fruit 6. Animal Kingdom: Eukaryotic multicellular heterotrophs 2 Types: Invertebrates: animals without spines Examples: Jellyfish, coral, sponges, insects, worms Vertebrates: animals with spines; 5 main types: Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals organized into higher levels. Organisms can be Levels of Organization Levels of Organization Population: same species living in an area Species = group of similar organisms that can interbreed Example: all the Giant pandas in a forest Community: group of different populations living in same area Example: All the different plants & animals in a forest Levels of Organization Ecosystems: area where living (biotic) & nonliving (abiotic) things interact Where plants & animals interact with each other & the water, soil, wind, sunlight Levels of Organization Biome: Ecosystems with similar climates and communities Example: forest, desert, grassland Biosphere: (Ecosphere)- all ecosystems of the earth Hydrosphere: water portion of Earth Lithosphere: rock/ ground portion of Earth Atmosphere: air portion of Earth Ecosystem Pyramid Choose an organism and illustrate a pyramid about the organism Include biosphere, biome, ecosystem, community, population, and species. Provide a definition/description of each level See example for assistance Classifying Organisms Classification: The process of putting similar things into groups Taxonomy: the science of classifying organisms Organisms are classified into Domains Species Classifying Organisms Three Domains: 1. Archaea Archaebacteria Kingdom 2. Bacteria Eubacteria Kingdom 3. Eukaryota Plant Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Protist Kingdom Animal Kingdom Classifying Organisms Domain Kingdom (king) Phylum (phillip) Class (came) Order (over) Family (for) Genus (grape) Species (soda) Binomial nomenclature is used – Genus species All organisms given two names Human Taxonomy Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammals Order Primates Family Hominid Genus Homo Species Sapiens Homo sapiens The Theory of Natural Selection by Evolution Evolution = The change in organisms over time Important: populations change, not individuals Evolution occurs by Natural Selection Theorized by Charles Darwin Natural Selection: The Steps 1. Genetic diversity in pop. Some individuals have traits better suited for the environment. 2. Individuals with advantageous traits survive longer & make more offspring. 3. Advantageous traits get passed on to the next generation (next set of offspring) 4. Over time, more individuals have these advantageous traits (adaptation) evolution ADAPTATION= trait that helps organisms survive in their environment Can be physical, physiological, behavioral, combo. Environmental Science & Evolution Antibiotic resistance = bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics through natural selection. The steps: Environmental Science & Evolution •Widespread use of antibiotics in medicines, household products & farming has lead to resistant bacteria! •Examples include E. coli and MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) Environmental Science & Evolution Pesticide Resistance = pests develop resistance to chemicals through natural selection