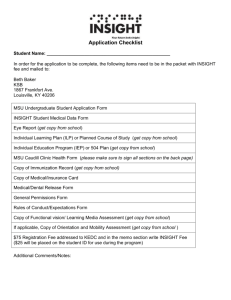
Insight Through Computing
advertisement

15. Strings
Operations
Subscripting
Concatenation
Search
Numeric-String Conversions
Built-Ins: int2str,num2str,
str2double
Insight Through Computing
Previous Dealings
N = input(‘Enter Degree: ’)
title(‘The Sine Function’)
disp( sprintf(‘N = %2d’,N) )
Insight Through Computing
A String is an Array of
Characters
‘Aa7*>@ x!’
A
a
7
*
>
@
x
This string has length 9.
Insight Through Computing
!
Why are Stirngs Important?
1. Numerical Data often encoded as
strings
2. Genomic calculation/search
Insight Through Computing
Numerical Data is Often Encoded in
Strings
For example, a file containing
Ithaca weather data begins with the string
W07629N4226
Longitude:
Latitude:
Insight Through Computing
76o 29’ West
42o 26’ North
What We Would Like to Do
W07629N4226
Get hold of the substring ‘07629’
Convert it to floating format so that
it can be involved in numerical calculations.
Insight Through Computing
Format Issues
9 as an IEEE floating point number:
0100000blablahblah01001111000100010010
9 as a character:
01000otherblabla
Insight Through Computing
Different
Representation
Genomic Computations
Looking for patterns in a DNA sequence:
‘ATTCTGACCTCGATC’
ACCT
Insight Through Computing
Genomic Computations
Quantifying Differences:
ATTCTGACCTCGATC
ATTGCTGACCTCGAT
Remove?
Insight Through Computing
Working With Strings
Insight Through Computing
Strings Can Be Assigned
to Variables
S = ‘N = 2’
‘N = 2’
S
N = 2;
S = sprintf(‘N = %1d’,N)
sprintf produces a formatted string using fprintf rules
Insight Through Computing
Strings Have a Length
s = ‘abc’;
n = length(s);
% n = 3
s = ‘’;
n = length(s)
% the empty string
% n = 0
s = ‘ ‘;
n = length(s)
% single blank
% n = 1
Insight Through Computing
Concatenation
This:
S = ‘abc’;
T = ‘xy’
R = [S T]
is the same as this:
R = ‘abcxy’
Insight Through Computing
Repeated Concatenation
This:
s = ‘’;
for k=1:5
s = [s ‘z’];
end
is the same as this:
z = ‘zzzzz’
Insight Through Computing
Replacing and Appending
Characters
s = ‘abc’;
s(2) = ‘x’
%
s = ‘axc’
t = ‘abc’
t(4) = ‘d’
%
t = ‘abcd’
v = ‘’
v(5) = ‘x’
%
v = ‘
Insight Through Computing
x’
Extracting Substrings
s = ‘abcdef’;
x
x
x
= s(3)
= s(2:4)
= s(length(s))
Insight Through Computing
%
%
%
x = ‘c’
x = ‘bcd’
x = ‘f’
Colon Notation
s(
Starting
Location
Insight Through Computing
:
)
Ending
Location
Replacing Substrings
s = ‘abcde’;
s(2:4) = ‘xyz’
% s = ‘axyze’
s = ‘abcde’
s(2:4) = ‘wxyz’
% Error
Insight Through Computing
Question Time
s = ‘abcde’;
for k=1:3
s = [ s(4:5) s(1:3)];
end
What is the final value of s ?
A abcde B. bcdea
Insight Through Computing
C. eabcd D. deabc
Problem: DNA Strand
x is a string made up of the characters
‘A’, ‘C’, ‘T’, and ‘G’.
Construct a string Y obtained from x by
replacinig each A by T, each T by A,
each C by G, and each G by C
x: ACGTTGCAGTTCCATATG
y: TGCAACGTCAAGGTATAC
Insight Through Computing
function y = Strand(x)
% x is a string consisting of
% the characters A, C, T, and G.
% y is a string obtained by
% replacing A by T, T by A,
% C by G and G by C.
Insight Through Computing
Comparing Strings
Built-in function strcmp
strcmp(s1,s2) is true if the strings s1
and s2 are identical.
Insight Through Computing
How y is Built Up
x: ACGTTGCAGTTCCATATG
y: TGCAACGTCAAGGTATAC
Start:
After 1 pass:
After 2 passes:
After 3 passes:
Insight Through Computing
y:
y:
y:
y:
‘’
T
TG
TGC
for k=1:length(x)
if strcmp(x(k),'A')
y = [y 'T'];
elseif strcmp(x(k),'T')
y = [y 'A'];
elseif strcmp(x(k),'C')
y = [y 'G'];
else
y = [y 'C'];
end
end
Insight Through Computing
A DNA Search Problem
Suppose S and T are strings, e.g.,
S: ‘ACCT’
T: ‘ATGACCTGA’
We’d like to know if S is a substring of T
and if so, where is the first occurrance?
Insight Through Computing
function k = FindCopy(S,T)
% S and T are strings.
% If S is not a substring of T,
%
then k=0.
% Otherwise, k is the smallest
% integer so that S is identical
% to T(k:k+length(S)-1).
Insight Through Computing
A DNA Search Problem
S: ‘ACCT’
T: ‘ATGACCTGA’
strcmp(S,T(1:4))
Insight Through Computing
False
A DNA Search Problem
S: ‘ACCT’
T: ‘ATGACCTGA’
strcmp(S,T(2:5))
Insight Through Computing
False
A DNA Search Problem
S: ‘ACCT’
T: ‘ATGACCTGA’
strcmp(S,T(3:6))
Insight Through Computing
False
A DNA Search Problem
S: ‘ACCT’
T: ‘ATGACCTGA’
strcmp(S,T(4:7)))
Insight Through Computing
True
Pseudocode
First = 1; Last = length(S);
while S is not identical to T(First:Last)
First = First + 1;
Last = Last + 1;
end
Insight Through Computing
Subscript Error
S: ‘ACCT’
T: ‘ATGACTGA’
strcmp(S,T(6:9))
There’s a problem if S is not a substring of T.
Insight Through Computing
Pseudocode
First = 1; Last = length(s);
while Last<=length(T) && ...
~strcmp(S,T(First:Last))
First = First + 1;
Last = Last + 1;
end
Insight Through Computing
Post-Loop Processing
Loop ends when this is false:
Last<=length(T) && ...
~strcmp(S,T(First:Last))
Insight Through Computing
Post-Loop Processing
if Last>length(T)
% No Match found
k=0;
else
% There was a match
k=First;
end
The loop ends for one of two reasons.
Insight Through Computing
Numeric/String
Conversion
Insight Through Computing
String-to-Numeric Conversion
An example…
Convention:
W07629N4226
Longitude:
Latitude:
Insight Through Computing
76o 29’ West
42o 26’ North
String-to-Numeric Conversion
S = ‘W07629N4226’
s1 = s(2:4);
x1 = str2double(s1);
s2 = s(5:6);
x2 = str2double(s2);
Longitude = x1 + x2/60
There are 60 minutes in a degree.
Insight Through Computing
Numeric-to-String Conversion
x = 1234;
s = int2str(x);
% s = ‘1234’
x = pi;
s = num2str(x,’%5.3f’); % s =‘3.142’
Insight Through Computing
Problem
Given a date in the format
‘mm/dd’
specify the next day in the same format
Insight Through Computing
y = Tomorrow(x)
x
02/28
07/13
12/31
Insight Through Computing
y
03/01
07/14
01/01
Get the Day and Month
month = str2double(x(1:2));
day
= str2double(x(4:5));
Thus, if x = ’02/28’ then month is assigned
the numerical value of 2 and day is
assigned the numerical value of 28.
Insight Through Computing
L = [31 28 31 30 31 30 31 31 30 31 30 31];
if day+1<=L(month)
% Tomorrow is in the same month
newDay = day+1;
newMonth = month;
Insight Through Computing
L = [31 28 31 30 31 30 31 31 30 31 30 31];
else
% Tomorrow is in the next month
newDay = 1;
if month <12
newMonth = month+1;
else
newMonth = 1;
end
Insight Through Computing
The New Day String
Compute newDay (numerical) and
convert…
d = int2str(newDay);
if length(d)==1
d = ['0' d];
end
Insight Through Computing
The New Month String
Compute newMonth (numerical) and
convert…
m = int2str(newMonth);
if length(m)==1;
m = ['0' m];
end
Insight Through Computing
The Final Concatenation
y = [m '/' d];
Insight Through Computing
Some other useful string functions
str= ‘Cs 1112’;
length(str)
isletter(str)
isspace(str)
lower(str)
upper(str)
%
%
%
%
%
7
[1 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 1 0 0 0 0]
‘cs 1112’
‘CS 1112’
ischar(str)
% Is str a char array? True (1)
strcmp(str(1:2),‘cs’)
% Compare strings str(1:2) & ‘cs’. False (0)
strcmp(str(1:3),‘CS’)
% False (0)
Insight Through Computing
ASCII characters
(American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
ascii code
:
:
65
66
67
:
90
:
Insight Through Computing
Character
:
:
‘A’
‘B’
‘C’
:
‘Z’
:
ascii code
:
:
48
49
50
:
57
:
Character
:
:
‘0’
‘1’
‘2’
:
‘9’
:
Character vs ASCII code
str= ‘Age 19’
%a 1-d array of characters
code= double(str)
%convert chars to ascii values
str1= char(code)
%convert ascii values to chars
Insight Through Computing
Arithmetic and relational ops on characters
•
•
•
•
‘c’-‘a’ gives 2
‘6’-‘5’ gives 1
letter1=‘e’; letter2=‘f’;
letter1-letter2 gives -1
• ‘c’>’a’ gives true
• letter1==letter2 gives false
• ‘A’ + 2
gives 67
• char(‘A’+2) gives ‘C’
Insight Through Computing
Example: toUpper
Write a function toUpper(cha) to convert
character cha to upper case if cha is a lower case
letter. Return the converted letter. If cha is not
a lower case letter, simply return the character
cha.
Hint: Think about the distance between a letter
and the base letter ‘a’ (or ‘A’). E.g.,
a b c d e f g h …
distance = ‘g’-‘a’ = 6 = ‘G’-‘A’
A B C D E F G H …
Of course, do not use Matlab function upper!
Insight Through Computing
function up = toUpper(cha)
% up is the upper case of character cha.
% If cha is not a letter then up is just cha.
up= cha;
cha is lower case if it is between ‘a’ and ‘z’
Insight Through Computing
function up = toUpper(cha)
% up is the upper case of character cha.
% If cha is not a letter then up is just cha.
up= cha;
if ( cha >= 'a' && cha <= 'z' )
% Find distance of cha from ‘a’
end
Insight Through Computing
function up = toUpper(cha)
% up is the upper case of character cha.
% If cha is not a letter then up is just cha.
up= cha;
if ( cha >= 'a' && cha <= 'z' )
% Find distance of cha from ‘a’
offset= cha - 'a';
% Go same distance from ‘A’
end
Insight Through Computing
function up = toUpper(cha)
% up is the upper case of character cha.
% If cha is not a letter then up is just cha.
up= cha;
if ( cha >= 'a' && cha <= 'z' )
% Find distance of cha from ‘a’
offset= cha - 'a';
% Go same distance from ‘A’
up= char('A' + offset);
end
Insight Through Computing