Lab Equipment
advertisement

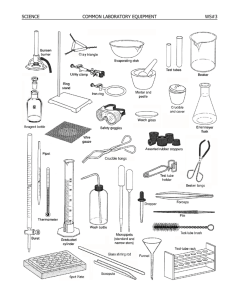
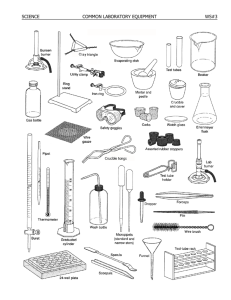
Lab Equipment September 3, 2008 Test Tube Collecting Bottle • Usually for collecting gas, but can collect liquids from an experiment as well. Erlenmeyer Flask • Erlenmeyer flasks hold solids or liquids that may release gases during a reaction or that are likely to splatter if stirred or heated. Florence Flask • Rarely used in first year chemistry, it is used for the mixing of chemicals. Narrow neck prevents splash exposure. Beaker • Beakers hold solids or liquids that will not release gases when reacted or are unlikely to splatter if stirred or heated. Graduated Cylinder • A graduated cylinder is used to measure volumes of liquids. Spring Scale • measures weight by the distance a spring deflects under its load. Triple Beam Balance • used in the laboratory to determine the weight or mass of things Electronic Balance • Measures weight/ mass digitally Thermometer • device that measures temperature Medicine Dropper • Used to transfer a small volume of liquid Thistle Tube • Used to add liquid to an existing system Funnel • A funnel is used to aid in the transfer of liquid from one vessel to another. Delivery Tube • Bent Glass Tubing: gases which evaporate when a liquid is heated can be 'directed' to another part of the apparatus. Rubber Tubing • Transfers liquid or gas from one place to antoher Test Tube Holder • useful for holding a test tube which is too hot to handle. Forceps • used to pick up small objects. Clamp • Utility clamps are used to secure test tubes, distillation columns, and burets to the ringstand. Tongs • Beaker tongs are used to move beakers containing hot liquids • Crucible Tongs for handling hot crucibles Ring clamp • Iron rings connect to a ringstand and provide a stable, elevated platform for the reaction. Clamp Stand • Ringstands are a safe and convenient way to perform reactions that require heating using a Bunsen burner. Test Tube Stand Bunsen Burner • Bunsen burners are used for the heating of nonvolatile liquids and solids. Alcohol Burner • In place of bunsen burner; provides a hot, consistent flame. Wire Gauze • Wire gauze sits on the iron ring to provide a place to stand a beaker Evaporating Dish • The evaporating dish is used for the heating of stable solid compounds and elements. Safety Goggles • Eye protection from chemicals, etc Hot Plate • small electric stove used in laboratory settings to heat glassware Crucible and Cover • Crucibles are used for heating certain solids, particularly metals, to very high temperatures. Clay Triangle • The clay triangle is used as a support for porcelein crucibles when being heated over a Bunsen burner. Mortar and Pestle • used to crush, grind, and mix substances. Stopper • Rubber stoppers are used to close containers to avoid spillage or contamination. • Containers should never be heated when there is a stopper in place. Stirring Rod • A glass rod is used to manually stir solutions. Spatula • Spatulas are used to dispense solid chemicals from their containers. • Chemicals should never be transferred with your bare hands. Scoop Watch Glass • A watch glass is used to hold a small amount of solid, such as the product of a reaction. Hand Lens • Simple microscope Petri Dish and Cover • Used to culture cells/ bacteria Glass Slide with Coverslip • he object to be viewed is typically placed on the middle of the slide with another, much thinner square of glass placed over the specimen…creates even surface for viewing Dissecting Tools • Scalpel: small but extremely sharp knife used for surgery or dissection • Dissecting Needles: helps you cut open the object you are dissecting