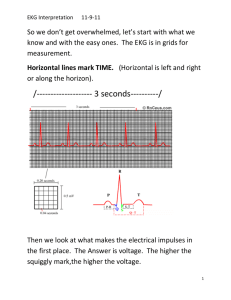
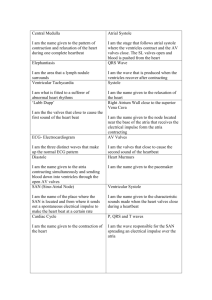
Advanced patient care skills
advertisement

Thomas Forti R.N. The EXAM Certified EKG Technician CET GED and 60 HRs of training 110 Questions (100 Scored) 110 minuets Web exam Score given following the exam Don’t spend too much time on one question Try and figure out the answers before reading the answers Eliminate incorrect answer to try and figure out correct answer HIPAA The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 Patient has right to confidentiality Safeguards to ensure that an individual's health information is used only for purposes related to treatment, payment, or healthcare operations You are responsible for this when at work. HIPAA Medicinal information needs to be sent via secure (encrypted) pathways Best way is to personally deliver the information (Handing the MD the EKG) Not leaving it in a mail box where someone else could view it. Keep work area clear of patient information when you walk away Protected Health information Any information about Health status Health care services Payment Patient identifiers Social security Hone numbers Address Treatment Assessment Test results Diagnoses Medications During Direct contact Phone calls Faxes Emails Anatomy and Physiology 4 Chambers of the Heart Right and Left Atria Right and Left Ventricle Sepal wall separate right from left sides Three layers of the heart Endocardium Myocardium Epicardium Heart is in a sac called Pericardium AKA Pericardial Sac Provided protection and lubrication Anatomy and Physiology Four Valves of the heart Tricuspid and Mitral ○ Between the atria and ventricle Pulmonary and Aortic ○ Blood exits heart Chordae Tendineae ○ Provide support to A-V valves to prevent regurgitation (incompetence) Anatomy and Physiology Coronary Arteries Vessels that supply blood to the myocardium Occur during ventricular diastole Normal perfusion to body occurs during systole RCA ○ Supply right ventricle and inferior wall of left ventricle (bottom) Left Main Splits to ○ Circumflex Supplies blood to posterior (back) and lateral (side) ○ LAD Supplies blood to anterior and Left ventricle Collateral circulation ○ Compensation for loss of O2 in other areas Conduction System Controls the synchronous, rhythmic contraction of the heart muscle SA Node Sinoatrial node 60-100 BPM Primary pacemaker of heart Right Atria Initiates atria contraction Shows as P wave on EKG tracing Internodal Pathways Tracts that the impulse takes from SA-AV node Conduction System AV node Atrioventricular node 40-60 BPM Connects Atria to Ventricle Impulse pulses here before heading to ventricles PR interval Bundle of His Splits impulse to RBBB and LBBB Sits in the Interventricular septum Purkinje Fibers Initiates myocardial contraction 20-40 BPM EKG Theory Measures electrical energy as it travels through the heart Records as energy over time Millivolts and Seconds EKG paper has small squares 1mm x 1mm 5 small boxes = 5mm = 1 large box Tracings are made by a stylus 1mm on y axis = 0.1mv 1mm on x axis = 40ms or 0.04 seconds 1ms = 0.001 seconds EKG Theory EKG paper speed is 25 mm/sec 50mm/sec if rhythm is too fast ○ Only change paper speed if ordered by MD Standard Amplitude Amplitude is change over a period of time 10mm = 1mv Gain is used to increase amplitude (size) Calibration box At beginning of lead ○ Speed and amplitude ○ Standard is 10mm tall and 5mm wide ○ Gain of 1 = 10mm, ½ = 5mm, 2 = 20mm ○ 25mm/sec = 5mm, 50mm/sec = 10mm EKG Theory Refer to user manual and hospital policy For paper type Cleaning (keypad, wires machine) Daily user test Correct power supply Bio-engineer will calibrate machine if needed EKG Theory Einthoven’s triangle Willem Einthoven ○ Discover everything basic of EKGs Bi-Polar Leads I, II, III Unipolar leads V1-V6 Augmented leads ○ avF, avR, avF Calculating Heart Rates 1500 method Atria rate- count the P-P interval ○ Small boxes between the P waves Ventricle rate- count the R-R interval ○ Small boxes between the R waves 1500/boxes Sequence method AKA 300 method ○ Count the large boxes between the R-R waves and 300/boxes ○ 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 Calculating Heart Rates 6 second rule Good for estimating rate if R-R intervals are not regular Count QRS complexes in 6 second strip and multiply by 10 Marks under tracing indicate 3 seconds Artifact Wandering baseline Most common cause is respirations Move electrodes off torso and onto wrists and ankles Have patient relax and breath slowly Seizures Large artifact Seizures must be controlled before EKG can be done Dry Skin Electrodes might now adhere ○ Use Benzoin to promote adhesion ○ Abrade the skin Artifact Wet Skin Dry skin Use Benzoin to promote adhesion Cold patient Warm patient with blanket May have to do EKG with artifact Dry Gel Use new electrodes Cell Phones Turn them off, remove and place aside Can look like p waves often like A-flutter Medical devices Turn off or move away from EKG patient Be careful in the ER or ICU Lead Locations 3 Lead White- Right Shoulder or clavicle area Black- left shoulder or clavicle area Red- Left lower abdomen area Green- Right lower abdomen area 5 Lead White- right sternum/clavicle area Black- Left sternum/clavicle area Red- Left lower thoracic area Green- Right lower thoracic area Brown- Just below and to the right of bottom of sternum Lead Locations Precordial Leads V1- 4th ICS, Right of Sternum V2- 4th ICS, Left of sternum V3- Between V2/V4 V4- 5th ICS, midclavicular V5- 5th ICS, between V4/V6 V6- 5th ICS, midaxillary Right precordial leads Reverse V leads Lead Locations Posterior Leads V7- Left posterior axillary line V8- Left midscapular line V9- left of spine Stress test Limb electrodes go on torso Post EKG Check leads for deflection direction Check leads for artifact Check that patient identifiers are on EKG Name DOB Medical record number Upload EKG Via hospital policy Mount EKG or strip per hospital policy Hole punch, scan or stick onto mounting paper Measuring EKG’s Know how to be able to measure P-P interval ○ Time between Atria contractions R-R interval ○ Time between Ventricle contractions PR interval ○ Time from SA to ventricles ○ 0.12-0.2 seconds QRS ○ Time for ventricles to depolarize ○ 0.06-0.12 seconds Parts of Waves Positive Anything above isoelectric line Negative Anything below isoelectric line PR segment Time impulse travels through AV node End or P to beginning of QRS ST segment Time it take for ventricles to repolarize End of QRS to end of T wave Parts of Waves J Point Point when ventricles depolarize and ventricle repolarize ○ End of QRS QT interval Time it takes ventricles to depolarize and repolarize Sinus Rhythms P wave resent P wave upright and rounded QRS complex narrow 80-120 milliseconds PR 120-200 milliseconds Regular Sinus Rhythm Rate 60-100 Sinus Bradycardia Rate less then 60 Sinus Tachycardia Rate greater then 100 Sinus Arrhythmia Rate around 60-100 Rhythm is irregular Atria Rhythms P waves abnormal shaped or absent QRS complexes narrow Atrial Fibrillations Atrial Fibrillation with Rapid Ventricular P waves = Flutter waves (abnormal P waves) Rate varies Regular Supraventricular SVT No P waves, No PR interval Rate greater then 100 Irregularly irregular Atrial Flutter No P waves, No PR interval Rate 60-100 Irregularly irregular P waves often NOT seen Regular Premature Atrial Complex PAC P wave abnormal QRS follows P wave NSR with PAC Junctional Rhythms Starts at AV node or Bundle of His P wave absent or abnormal (inverted) QRS narrow or above 120 milliseconds Junctional Rhythm P-wave absent or abnormal ○ Rate 40-60 Junctional Bradycardia Rate less then 40 Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Rate 60-100 Junctional Tachycardia Rate above 100 Ventricle Rhythms QRS complex wide Idioventricular Rhythm Wide QRS complexes Rate 20-40 Ventricular tachycardia Monomorphic ○ Wide QRS with rate above 120 ○ Complexes look identical Polymorphic ○ Complexes have different amplitude Ventricular Rhythms Ventricular Fibrillation No identifiable waves Asystole Absence of electrical activity in the heart Premature Ventricular Complex Wide QRS, absent P waves R wave opposite direction of T wave NSR with PVC Multifocal PVCs ○ Different shaped PVCs ○ Patterns – Bigeminy, Trigemity (every other or 3rd) Heart Blocks Impulse is delayed or blocked as it travels to the ventricles 1st degree PR interval greater then 200 milliseconds 2nd degree type 1 PR interval elongates until dropped QRS complex 2nd degree type 2 PR interval normal if present Dropped QRS complex without warning 3rd degree Complete lack of association between the atria and ventricles ○ P waves present at normal rate ○ QRS waves at rate of Junctional rate or idioventricle Could be wide or narrow Injury Ischemia ST segment depression T wave inversion Injury ST elevation ○ 1mm in limb leads ○ 2mm in precordial leads Infarction ST elevation will return to baseline Pathological Q waves develop Pathological Q waves can indicate MI Lead Locations for MI ST segment Morphology Draw line from J point to top of T wave Convex ST segment is above line Can be Ischemia STEMI Concave ST segment is below line Can be ischemia but often benign ST segment sloping T Wave T wave is peaked T wave is Hyperacute Hight is greater then ½ the QRS T wave elongates Cardiac Compromise Tachy or brady Pallor Diaphoresis Decrease in BP Breathing problems Anxiety or confusion Cyanosis Chest pain or tightness Back, arm, jaw pain Nausea and vomiting Lightheadedness Weakness Syncope Left-threating arrhythmias Ventricular tachycardia Check Pulse Ventricular fibrillation Call for help Start CPR Use AED Asystole Check in 2 leads Call for help Start CPR Bradycardia Call for help Check Vitals Prepare patient for pacing Tachycardia Call for help Check vitals Cardioversion Pacemakers Paced Ventricular Paced Atrial-Ventricular Patient Care Responsible for knowing patients Medical History ○ Smoking, alcohol, drugs, stress, exercise, nutrition, work environment, family history, marital status, children ○ Past medical conditions Stroke, MI, Aneurysm, murmurs, PE, DVTs, Heart failure, hypertension, COPD, CHF ○ Current Complains Pain, SOB, Edema, Palpitations, Fainting, Weakness Surgical History ○ What, when, complications (more details if cardiac) Medication List (also allergies) ○ Currently taking and recently stopped (last month or 2) ○ Include OTC medications, birth control, erectile dysfunction Patient Care Explain procedures fully with easy to understand terms Explain purpose, length, steps of procedure Preparation if test isn’t for today Allow them to ask questions Patient Care EKG Allow physician to assess the electrical activity of the heart Non-invasive, Painless Around 10 mins What the electrodes are for Empty pockets, relax, lay flat avoid moring or talking Patient Care Holter Monitors activity for 24-72 hours Instruct patient to bathe rior to appointment ○ Pt can not remove electrodes or get device wet during time Loose fitting clothing to help prevent artifact Notify if irritation occurs from electrodes Normal daily activity ○ Including work exercise and sleep Journal with date time and duration of any symptoms ○ Lightheadedness, palpations, chest pain, SOB ○ Note when medications taken, physical activity and sleeping Patient to call physician office if electrodes fall off ○ Electrodes get replaced by Tech NOT patient ○ Batteries get changed by Tech NOT patient ○ Electrodes get moved by Tech Call 911 for serious symptoms Patient Care Stress Test Used to determine how the heart function under increased workload from exercise Take about 10 mins Electrodes and Blood pressure during test Baseline EKG prior and end of test Test goes until ○ Symptoms occur Lightheadedness, dizziness, SOB, Chest pain ○ Target heart rate reached or physician orders test to end Patient not to eat, drink or smoke 3 hours prior Continue normal medication unless instructed by physician to hold medication Wear clothing and shoes for exercising Patient Care Stress Test Monitor for ○ Vital Sings ○ Arrhythmias ○ Cardiopulmonary compromise ○ Heart rate Complications ○ Most common is hypotension and arrhythmias ○ Stop and let patient rest ○ Lay patient down ○ Report change to physician Patient Care Telemetry Continuous monitoring of electrical system Within hospital Notify staff if symptoms occur Vitals Check Pulse Adult- Radial Child- Brachial Apex use stethoscope ○ 5th ICS midclavicular Pulse oximeter ○ Used to determine amount of oxygen in blood ○ Normal is above 95% ○ Cant read if: cold hands, colored nails, edema, fake nails Vitals Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms Rhythms