Geologic Time
advertisement

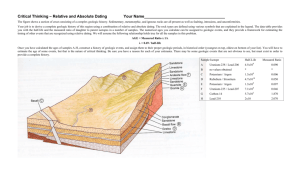
Image source: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stardust/main/index.html Stardust • • • • • First sample return mission in 34 years Traveled ~ 3 billion miles Retrieved samples of comet Wild-2 Flew through the comets tail Collected dust particles in aerogel Image source: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stardust/main/index.html Image source: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stardust/main/index.html Image source: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stardust/main/index.html Image source: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stardust/main/index.html Geologic Time Image source: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stardust/main/index.html Image source: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stardust/main/index.html Geologic Time • • • • • • Fundamental geologic observations Relative vs. absolute dating Economic implications Philosophical dimensions Earth’s place in the Solar System Meteorites Relative dating techniques • Nicolaus Steno (1669) – Observations regarding sedimentary rocks • Principle of Superposition • Principle of Original Horizontality • Principle of cross-cutting relationships – Developed for dating igneous rocks • Law of Faunal succession (~1800) – Allows correlation of rocks of same age Principle of Original Horizontality (Grand Canyon, USA) Principle of Superposition (Grand Canyon, USA) Source: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Doug Sherman, photographer. Schist and Granite Source:Courtesy of Carla W. Montgomery. Uniformitarianism • Still many unanswered questions… – Absolute age, length of geologic processes “The Present is the Key to the Past” James Hutton, late 18th century Source: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Doug Sherman, photographer. Age of the Earth Age of the Earth • How old is the Earth? Bishop Usher (16th century) Bible…..~6,000 years old (4004 BC) Lord Kelvin (19th century) Cooling…20-40 million years old John Joly (1899) Salinity of oceans…100 million Radioactivity Age of the Earth • Radiometric Dating Radioactive isotopes in rocks decay at a known rate U, Rb, K, Th, C, others…. • Counting atoms in the rocks tells time Parent-daughter ratio • Concept of half-life How long it takes for half the parent isotope to decay Parent-daughter ratios become smaller in time Isotope clocks are useful for ~ 7 ½ lives Absolute dating: isotopic clocks • Carbon 14C in the atmosphere, then we eat the carbon 14C isotopic half-life = ~6,000 years 14N • U-Pb 206Pb, and 235U 207Pb 238U isotopic half-life = ~4,500,000,000 years 4.5 billion years old (4.5 byo) 238U • Other ‘old’ isotopic clocks Rb Sr, K Ar, Th Pb A very old Earth… • • • • • • Meteorites ~ 4.57 byo Earth ~ 4.56 byo Oldest rocks on Earth ~ 4.0 byo Oldest minerals ~ 4.4 byo Oldest sediments ~ 3.8 byo Oldest fossils ~ 3.5 byo Billions, not millions! The Oldest Minerals on Earth: Zircon (ZrSiO4) 50 um Geologic time scale • Subdivisions of geologic time – Eon, Era, Period, Epoch – Eons • Precambrian: 4.5 b.y. to ~0.5 b.y. • Phanerozoic: ~0.5 b.y. to today Geologic time scale • Subdivisions of geologic time – Eon, Era, Period, Epoch – Eras • Paleozoic: ~560 m.y. to ~250 m.y. • Mesozoic: ~250 m.y. to ~65 m.y. • Cenozoic: ~65 m.y. to today Geologic time scale • Subdivisions of geologic time – Eon, Era, Period, Epoch – Today (your lifetime) • Eon: Phanerozoic (~550 m.y. now • Era: Cenozoic (65 m.y. now • Period: Quaternary (2 m.y. now • Epoch: Holocene (10 k.y now Image source: http://www.gly.fsu.edu/~salters/GLY1000/12Rock_record_time/Slide27.jpg