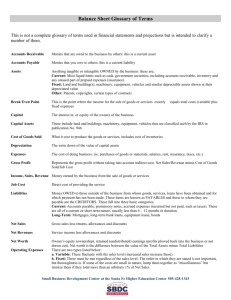
Click to
advertisement

CHAPTER NO. 5
WORKING CAPITAL
MANAGEMENT &
FINANCE
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Capital required for a business can be classified under two
categories VIZ.,
(1) Fixed capital
(2) Working capital
Investments in the long term assets represent that part of
firm’s capital which is blocked on a permanent of fixed
basis is called fixed capital
Funds also needed for short term purposes for the purchase of
raw materials, payments of wages etc are known as
working capital.
“ Working capital is the amount of funds necessary to cover the
cost of operating the enterprises”
SHUBIN
CONCEPTS OF WORKING CAPITAL
BALANCE SHEET
CONCEPT
GROSS WORKING
CAPITAL- it refers to
that amount of capital
which is invested only in
current assets of the
firm.
NET WORKING
CAPITAL
= Current assets –
current assets
NWC may be negative or
positive.
OPERATING CYCLE OR
CIRCULAR FLOW
CONCEPT
Investment in current
assets keep revolving
fast & are being
constantly converted
in to cash & this cash
flows out again in
exchange for other
current assets known
as revolving or
circulating capital.
GROSS WORKING CAPITAL
Total Current assets
Where Current assets are the assets that can be
converted into cash with in an accounting year &
include cash , debtors etc.
Referred as “Economics Concept” since assets are
employed to derive a rate of return.
FEARTURES OF CURREN ASSETS
Short Life Span
cash balances may be held idle for a week or two , thus
a/c may have a life span of 30-60 days etc.
Swift Transformation into other Asset forms
each CA is swiftly transformed into other asset forms like cash is
used for acquiring raw materials , raw materials are transformed
into finished goods and these sold on credit are convertible into
cash
NET WORKING CAPITAL
Current Assets – Current Liabilities
Referred as ‘point of view of an Accountant’.
It indicates liquidity position of a firm &
suggests the extent to which working
capital needs may be financed by
permanent sources of funds.
It indicates the margin of protection
available to the short term creditors
It indicates the financial soundness of the
firm
CONSTITUENTS OF CURRENT
ASSETS & LIABLITIES
CURRENT ASSETS
CASH IN HAND
BILLS RECEIVABLE
SUNDRY DEBTORS
SHORT TERM LOANS &
ADVANCES
TEMPORARY INVESTMENTS
OF SURPLUS FUNDS
PREPAID EXPENSES
ACCRUED INCOMES
INVENTORIES OF STOCK
(1) RAW MATERIAL
(2) WORK-IN-PROCESS
(3) STORES & SPARES
(4) FINISHED GOODS
CURRENT LIABLITIES
BILLS PAYABLE
SUNDRY CREDITORS
OUTSTANDING
EXPENSES
SHORT TERM LOANS
,ADVANCES& DEPOSISTS
DIVIDEND PAYABLE
BANK OVERDRAFT
PROVISION FOR
TAXATION
OPERATING CYCLE OR CIRCULAR FLOW CONCEPT
1. Cash
received
from debtors
& paid to
suppliers of
raw material
4. Sale of
finished
goods
Operating
cycle
3. Finished
goods
produced
2. Raw
material
introduced
in to process
OPERATING CYCLE OR CIRCULAR FLOW CONCEPT
1. Gross operating cycle
2. Net operating cycle
Raw
material
conversion
period
Receivable
conversion
period
Gross
operating
cycle is the
sum total of
these 4
Finished
goods
conversion
period
Work in
process
conversion
period
Net
operating
cycle
period =
Gross
operating
cycle
period -
Payable
deferral
period
OPERATING CYCLE
Purchase Resources
Pay
Sell on Credit
Receive Cash
Inventory Conversion
Receivables Conversion
Payables Period
Cash Conversion Cycle
Operating Cycle
9
FORMULA TO DETERMINE NET OPERATING CYCLE PERIOD
1.
CLASSIFIACATION OR KINDS OF WORKING CAPITAL
GROSS WORKING
CAPITAL
ON THE BASIS OF
CONCEPT
NET WORKING
CAPITAL
KINDS OF
WORKING
CAPITAL
PERMANENT OR
FIXED WORKING
CAPITAL
ON THE BASIS OF
TIME
TEMPORARY OR
VARIABLE
WORKING
CAPITAL
REGULAR
WORKING
CAPITAL
RESERVE
WORKING
CAPITAL
SEASONAL
WORKING
CAPITAL
SPECIAL
WORKING
CAPITAL
THE NEEDS OR OBJECTS OF
WORKING CAPITAL
For the purchase of raw materials, components & spares
To pay wages & salaries
To incur day to day expenses & overheads costs
To meet selling costs
To provide credit facilities to the customers
To maintain the inventories of raw material, work-in-process, stores
and spares & finished goods.
As profits earned depend upon magnitude of sales and they do not
convert into cash instantly, thus there is a need for working capital in
the form of CA so as to deal with the problem arising from lack of
immediate realization of cash against goods sold.
This is referred to as “Operating or Cash Cycle” .
It is defined as “The continuing flow from cash to suppliers, to
inventory , to accounts receivable & back into cash
ADEQUATE WORKING CAPITAL
ADVANTAGES OF
ADEQUATE WORKING
CAPITAL
o
SOLVENCY OF THE
BUSINESS
ADVANTAGES OF
DISADVANTAGES OF
INADEQUATE /EXCESSIVE
WORKING CAPITAL
•
•
o
GOODWILL
o
EASY LOANS
•
o
CASH DISCOUNTS
•
o
o
o
REGULAR SUPPLY OF RAW
MATERIALS
REGULAR PAYMENTS OF
SALARIES,WAGES,&
OTHER DAY TO DAY
COMMITMENTS
EXPLOITATION OF
FAVOURABLE MARKET
CONDITIONS
•
•
•
•
IDLE FUNDS
LEADS TO UNNECESSARY
BUYING HABITS
DEFECTIVE CREDIT POLICY
CREATES OVERALL
INEFFICIENCY
RISE IN SPECULATIVE
TRANSACTION
DIFFICULTY IN PAYING SHORT
TERM LIABLITIES
DIFFICULTY IN AVAILING
DISCOUNT
RATE OF RETURN FALLS
FACTORS DETERMINING THE WORKING CAPITAL
REQUIREMENTS
1. Nature & character of business
2. Size of business/ scale of operation
3. Production policy
4. Manufacturing process/ length of production cycle
5. Seasonal variations
6. Working capital cycle
7. Rate of stock turnover
8. Credit policy
9. Business cycle
10. Rate of growth of business
11. Earning capacity & dividend policy
12. Price level changes
13. Other factors
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Management of working capital is concerned with the problems
that arise in attempting to manage the current assets, the
current liabilities & the inter-relationship that exists between
them or we can say it refers to all the aspects of
administration of both current assets & current liabilities.
Working capital management policies of a
firm have a great effect on its profitability, liquidity &
structural health of the organization. In this context, working
capital management is three dimensional in nature ;
1.
PROFITABILITY
,RISK,
LIQUDITY
2.
COMPOSITION
& LEVEL OF
CURRENT
ASSETS
3.
COMPOSITION
& LEVEL OF
CURRENT
LIABLITIES
3 DIMENSION
OF WORKING
CAPITAL
MANAGEMENT
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Decisions relating to working capital and short term financing
are referred to as working capital management. Short term
financial management concerned with decisions regarding to CA
and CL.
Management of Working capital refers to management of CA as
well as CL.
If current assets are less than current liabilities, an entity has a
working capital deficiency, also called a working capital deficit.
These involve managing the relationship between a firm's shortterm assets and its short-term liabilities.
Active working capital management is an extremely effective way to
increase enterprise value. Optimizing working capital results in a
rapid release of liquid resources and contributes to an improvement
in free cash flow and to a permanent reduction in inventory and
capital costs, thereby increasing liquidity for strategic investment
and debt reduction. Process optimization then helps increase
profitability.
GOALS OF WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
The goal of working capital management is to ensure that
the firm is able to continue its operations and that it has
sufficient cash flow to satisfy both maturing short-term
debt and upcoming operational expenses.
Businesses face ever increasing
pressure on costs and financing requirements as a result
of intensified competition on globalised markets. When
trying to attain greater efficiency, it is important not to
focus exclusively on income and expense items, but to also
take into account the capital structure, whose
improvement can free up valuable financial resources
Investment in CA represents a
substantial portion of total investment.
Investment in CA and level of CL have
to be geared quickly to changes in sales.
PRINCIPLES OF
WORKING CAPITAL
MANAGEMENT POLICY
PRINCIPLE OF
RISK VARIATION
PRINCIPLE OF
COST OF CAPITAL
PRINCIPLE OF
EQUITY POSITION
PRINCIPLE OF
MATURITY OF
PAYMENTS
METHODS OF
ESTIMATING WORKING
CAPITAL
REQUIREMENTS
PERCENTAGE OF
SALES METHOD
REGGRESSION
ANALYSIS METHOD
CASH FORECASTING
METHOD
OPERATING CYCLE
METHOD
PROJECTED
BALANCE SHEET
METHOD
FACTORS REQUIRING CONSIDERATION
WHILE ESTIMATING WORKING CAPITAL
1. Total cost incurred
on material, wages, &
overheads
2. The length of time
for which raw
materials are to
remain in stores
before they are issued
3. The length of the
production cycle or
work in process
4. The length of sales
cycle during which
finished goods are to
be kept waiting for
sales
5. The average period
of credit allowed to
customers.
6. The amount of cash
required to pay day to
day expenses of the
business
7. The average
amount of cash
required to make
advance payments
8. The average cerdit
period expected to be
allowed by suppliers.
9. Time lag in the
payments of wages &
other expenses.
INVESTMENT DECISION PROCESS
Monitor cash flow forecasts
annually / quarterly / monthly / weekly / daily
Identify surpluses
Determine:
{
{
Now and at
period end
20
Amount / currency
Duration / location
Internal policy covering
Investment types
Risk
Ratings
Time frames
Liquidity
Performance objectives
Funding subsidiaries
Tax
External Factors:
INVESTMENT
DECISION
Investment action
Confirmation
Recording / monitoring / reporting
Liquidation
Interest rates / trends
Currency exchange rates
Economic factors
Availability
FINANCING OF WORKING CAPITAL
a.
Financing of
permanent/fixed
/long term
working capital
b.
Financing of
temporary, variable
or short term
working capital
1. Commercial
. SHARES
2.
1
2.
3. PUBLIC
DEPOSITS
Indigenous bankers
3. Trade
DEBENTURES
4.
banks
creditors
Installment credits
Accounts
receivable
5.
4. Ploughing back of
profits
6.
5. Loans from
financial institutions
Accrued expenses
7. Commercial papers
8. advances
9. Commercial banks
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
DETERMINING THE
WORKING CAPITAL
FINANCING MIX/
APPROACHES TO
FINANCING MIX
NEW TRENDS IN
FINANCING WORKING
CAPITAL BY BANKS
1. DEHEJIA
COMMITTEE
THE
HEDGING
OR
MATCHING
APPROACH
THE
CONSERVATIVE
APPROACH
THE
AGGRESSIVE
APPROACH
4.
MARATHE
COMMITT
EE
WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS OR
NEASURING THE WORKING CAPITAL
(A) RATIO ANALYSIS
1. CURRENT RATIO
2. ACID TEST RATIO
3. ABSOLUTE LIQUID
RATIO
4. INVENTORY
TURNOVER RATIO
5. RECEIVABLE
TURNOVER RATIO
6. PAYABLES TURNOVER
RATIO
7. WORKING CAPITAL
TURN OVER RATIO
8. RATIO OF CURRENT
LIABLITIES TO
TANGIBLE NET WORTH
(B) FUNDS FLOW
ANALYSIS
1. CASH FLOW
ANALYSIS
2, FUND FLOW
ANALYSIS
(C) WORKING CAPITAL
BUDGET
1. LONG TERM WORKING
CAPITAL BUDGET
2. SHOT TERM WORKING
CAPITAL BUDGET
THE FINANCING DECISION PROCESS
Monitor cash flow forecasts
annually / quarterly / monthly / weekly / daily
Identify deficits
Determine:
Amount / currency
Duration / location
Internal policy covering
Borrowing internally
Instruments
Financing policy
Existing limits
Performance objectives
Existing facilities
Balance sheet/ratio impact
Tax
External Factors:
FINANCING DECISION
Financing action
Documentation
Recording / monitoring / reporting
Liquidation
Interest rates / trends
Currency exchange rates
Economic factors
Liquidity of market
ZERO WORKING CAPITAL
APPROACH
When, total of current assets = total of current
liabilities then working capital requirement will be
equal to zero . such a situation maybe called as zero
working capital situation.
Total of current assets – total of current liabilities = zero
ZWC approach, which aims at saving in opportunity cost
of funds invested in current assets & ensuring a smooth
& uninterrupted working capital cycle, is a recent
technique of working capital management.
THANK YOU