Downloading - Association for Pathology Informatics
advertisement

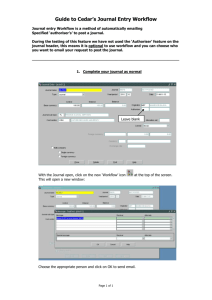
Creating BioMoby Workflows In Taverna Mark Wilkinson Edward (Eddie) Kawas iCAPTURE Centre, St. Paul’s Hospital Vancouver, BC Downloading Taverna • Taverna can be obtained from: http://taverna.sourceforge.net • Once at the site, click on Download • Download the version appropriate for your operating system. • Between releases, the Moby functionality may be updated and you can find instructions on how to acquire those updates from: http://biomoby.open-bio.org/index.php/moby-clients/taverna_plugin Running • For a more comprehensive guide on Running and using Taverna, please refer to http://taverna.sourceforge.net/usermanual/manual.html • Assuming that you have downloaded and unzipped Taverna, you can run it by double-clicking on runme.bat (windows) or executing runme.sh (Unix/Linux/OS X) • Taverna’s splash screen • Once Taverna has loaded, you will see 3 windows: – Advanced Model Explorer – Workflow Diagram – Available Services • The Advanced model explorer is Taverna’s primary editor and allows you to load, save and edit any property of a workflow. • Workflow diagram contains a read only graphical representation of your workflow. • The Available services window lists all of the services available to a workflow designer. • Under the node ‘Biomoby @ …’ Moby services and Moby data types are represented. • The Object ontology is available as children of MOBY Objects node • Services are sorted by service provider authority • If you wish to use registries other than the default one, you can add a new Moby ‘Scavenger’ by choosing to ‘Add new Biomoby scavenger…’ • Enter the registry’s location and click okay. Creating Workflows • I have the workflow saved and would like to offer it for download. • We will start by adding the Object ontology node Object to our workflow. • The Advanced model explorer now shows that we have a processor called Object – Object has 3 input ports: id, namespace and article name – Object has 1 output port: mobyData • The Workflow diagram illustrates our processor • We can discover services that consume our data type, context click on ‘Object’ and choose ‘Moby Object Details’ • A window will pop up that tells you what services Object feeds into and is produced by • Expanding the Feeds into node results in a list of service provider authorities • Expanding an authority, for example, bioinfo.icapture.ubc.ca, reveals a list of services • We will choose to add the service called ‘MOBYSHoundGetGenBankFasta’ to our workflow. • A look at the state of our current workflow. • And graphically. • The service consumes Object, with article name identifier, and produces FASTA, with article name fasta. • To discover more services, context click on the service that outputs the data type that you would like to discover consuming services for and choose Moby Service Details. • The resultant window displays the services inputs and outputs. • There are also tool tips that show up when your mouse hovers over any particular input or output that tells you what namespaces the data type is valid in • Context clicking on an output reveals a menu with 3 options. – A brief search for services that consume our datatype – A semantic search for services that consume our datatype – Adding a parser to the workflow that understands our datatype • The result of choosing to add a parser for FASTA to our workflow. • The parser allows us to extract: – The namespace and id from FASTA – The namespace and id from the child String – The textual content from the child String • The result of choosing to conduct a brief search for services that consume FASTA • We will add the service getDragonBlastText to our workflow by choosing ‘Add service -…’ from the context menu • The current state of our workflow shown graphically. • A more complex view of our workflow • Finding services that consume NCBI_BLAST_Text starts by viewing the details of the service ‘getDragonBlastText’ • Conduct a brief search • Add the service ‘parseBlastText’ to our workflow • Our current workflow • Workflow inputs are added by context clicking on Workflow inputs in the Advanced model explorer and choosing ‘Create New Input…’ • The result from adding 2 inputs: – Id – namespace • The workflow input id will be connected to Object’s input port ‘id’ • Workflow after connecting the workflow input ‘id’ • The workflow input namespace will connect to Object’s input port ‘namespace’ • Workflow after connection the workflow inputs. • Workflow outputs are added by context clicking on Workflow outputs in the Advanced model explorer and choosing ‘Create New Output…’ • The result from adding 2 workflow outputs: – moby_blast_ids – fasta_out • The output moby_blast_ids will be connected to parseBlastText’s output port Object(Collection –’hit_ids’) • The output fasta_out will be connected to Parse_Moby_Data_FASTA’s output port fasta_’content’ • To run the workflow, click on ‘Tools and Workflow Invocation’ • Choose ‘Run workflow’ • A prompt to add values to our 2 workflow inputs • To add a value to the input ‘id’ click on id from the left pane and choose ‘New Input’ • Enter 656461 as the id • Choose namespace from the left and click on ‘New Input’ • Enter NCBI_gi as the value for namespace • Once you are done, click on ‘Run Workflow’ • Our workflow in action • Once the workflow is complete, we can examine the results of our workflow. • A detailed report is available outlining what happened when and in what order. • We can examine the intermediate inputs and output, as well as visualize our workflow. • If we choose the Graph tab, our workflow is illustrated. • Intermediate inputs allow us to examine what a service has accepted as input • Similarly, Intermediate outputs allows us to examine the output from any particular service. • Without the parser, FASTA is represented as a Moby message, fully enclosed in its wrapper. • Non-moby services do not expect this kind of message • Non-moby services expect the just the sequence and using the Parse_Moby_Data processor, we can extract just that • Moby services can interact with the other services in Taverna. • Let’s add a Soaplab service. • We will choose a nucleic_restriction soaplab service called ‘restrict’ • Choose the restrict service and add it to the workflow. • We will connect the output port fasta_’content’ from the service Parse_Moby_Data_FASTA to the input port ‘sequence_direct_data’ from the service restrict • The result of our actions so far. • We will need to add another workflow output to capture the output of restrict. • Create an output called restrict_out • Connect the output port ‘outfile’ from the service restrict to the workflow output restrict_out • Once the connections have been made, run the workflow again using the same inputs. • The workflow on the left has some extra services added to it. – FASTA2HighestGenericSequenceObject from the authority bioinfo.icapture.ubc.ca – runRepeatMasker genome.imim.es from the authority – A Moby parser for the output DNASequence from runRepeatMasker. – A workflow output Masked_Sequence • Add them to your workflow • The service runRepeatMasker is configurable, i.e. it consumes Secondary parameters. • To edit these parameters, context click on the service and choose ‘Configure Moby Service’ • The name of the parameter is on the left and the value is on the right. • Clicking on the Value will bring up a drop down menu, an input text field, or any other appropriate field depending on the parameter. • The parameter species contains an enumerated list of possibilities. • Select human. • When you have made your selection, you may close the window. • Let’s run the workflow • We will run our workflow with a list – Click on id in the left pane and then click on New Input twice • Enter 656461 and 654321 as the ids • Enter NCBI_gi as the value for namespace • Our workflow will now run using each id with the single namespace • Notice how the workflow is running with iterations. This is happening because the Enacter is performing a crossproduct on the input • You can still view intermediate inputs and outputs. • Using the queryIDs, you can track each invocation of a moby service through the whole workflow • • Imagine now that you want to run the workflow using a FASTA sequence that you input yourself (without the gi identifier) To do this, context click on getDragonBlastText and choose Moby Service Details – – • Expand the Inputs node and context click on FASTA(‘sequence’) Choose Add Datatype – FASTA(‘sequence’) to the workflow A FASTA datatype will be added to the workflow and the appropriate links created • Notice the datatype FASTA on the left of the workflow – Since the datatype FASTA hasa String, a String was also added to our workflow and the appropriate connection was made • We will now have to add another workflow input and connect it to the String component of FASTA. • A workflow input ‘sequence’ was added to the workflow and a connection was made from the workflow input to the input port ‘value’ of String. • We also removed the link between MOBYSHoundGetGenBankFasta and getDragonBlastText by context clicking on the link in the Advanced model explorers’ Data links and choosing to remove the link • Now when we choose to run our workflow, we will also have the chance to enter a FASTA sequence • Go ahead an enter any FASTA sequence as the input to the workflow input ‘sequence’ • Run the workflow • Any results can be saved by simply choosing to Save to disk – You will be prompted to enter a directory to save the results. – Each workflow output will be saved in a folder with the same name as a workflow output and the contents of the folder will be the results • You can also choose Excel, which produces an Excel worksheet with columns representing the workflow outputs and with rows that represent the actual data.