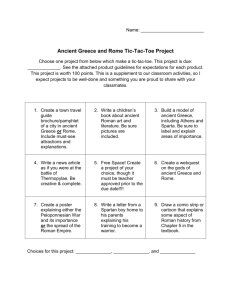
ACNCIENT GREECE
advertisement

ANCIENT GREECE Standard 5 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Greece in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: a. Assessing the influence of geography on Greek economic, social, and political development, including the impact of Greek commerce and colonies • Geography o Physical Features • Balkan, Peloponnesus Peninsulas • Europe, Asia Minor • Mediterranean Sea • Black Sea, Dardanelles o City-States • Athens, Sparta, Troy o Macedonia • Economic and Social Development o Agriculture, lack of arable land o Commerce and the spread of Hellenic culture o Shift from barter to money economy (coins) • Political Development o Mountainous terrain led to development of city-states o Greek cities were designed to promote civic and commercial life o Colonization related to overpopulation and search for arable land Standard 5 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Greece in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: b. Describing Greek mythology and religion • Greek Mythology o Polytheistic o Explanations of natural phenomena, human qualities, and life events • Gods and Goddesses o Zeus, Hera, Apollo, Artemis, Athena, and Aphrodite o Symbols and images in Western literature, art, and architecture Standard 5 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Greece in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: c. Identifying the social structure and role of slavery, explaining the significance of citizenship and the development of democracy, and comparing the city-states of Athens and Sparta • Greek Polis o Free males were citizens with political rights and a responsibility to participate in government o Women, foreigners, slaves had no political rights • Athens o Stages in evolution of Athenian government • Monarchy • Aristocracy • Tyranny • Democracy o Tyrants who worked for reform • Draco, Solon o Origin of democratic principles • Direct democracy. Public debate, duties of the citizens • Sparta o Oligarchy o Rigid social structure o Militaristic and aggressive society Standard 5 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Greece in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: d. Evaluating the significance of the Persian and Peloponnesian Wars • Peloponnesian War 431-404 B.C.E. • Persian Wars 499- 449 B.C.E. o United Athens and Sparta against the Persian Empire o Athenian victories left Greeks in control of Aegean Sea • Battle of Marathon • Battle of Salamis o Athens preserved its independence and continued innovations in government and culture o Caused in part by competition for control of the Greek world • Delian League- Athens • Peloponnesian LeagueSparta o Resulted in slowing of cultural advance and the weakening of political power o Sparta “wins” Standard 5 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Greece in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: e. Characterizing Athens during the Golden Age of Pericles • Extension of democracy o Most adult males had an equal voice • Pericles rebuilt Athens after destruction of Persian Wars o Parthenon f. Citing contributions • The Arts o Drama: Aeschylus, Sophocles o Poetry: Homer • The Iliad and The Odyssey o History: Herodotus, Thucydides o Sculpture: Phidias o Architecture: Columns • Doric, Ionic, Corinthian o Science: Archimedes, Hippocrates o Math: Euclid, Pythagoras o Philosophy: Socrates, Plato, Aristotle Parthenon Greek Columns Standard 5 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Greece in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: e. Characterizing Athens during the Golden Age of Pericles • Extension of democracy o Most adult males had an equal voice • Pericles rebuilt Athens after destruction of Persian Wars o Parthenon f. Citing contributions • The Arts o Drama: Aeschylus, Sophocles o Poetry: Homer • The Iliad and The Odyssey o History: Herodotus, Thucydides o Sculpture: Phidias o Architecture: Columns • Doric, Ionic, Corinthian o Science: Archimedes, Hippocrates o Math: Euclid, Pythagoras o Philosophy: Socrates, Plato, Aristotle Standard 5 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Greece in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: g. Explaining the conquest of Greece by Macedonia • Phillip II o King of Macedonia o Conquered most of Greece • Left weak from Peloponnesian wars • Alexander the Great o Established an empire from Greece to Egypt and the margins of India o Extended Greek cultural influences g. And the formation and spread of Hellenistic culture by Alexander the Great • Hellenistic Age o Blend of Greek, Persian, and Indian elements o Spread of Hellenistic culture through trade Ancient Rome 700 B.C.E- 500 C.E. Standard 6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: a. Assessing the influence of geography on Roman economic, political, and social development • Location o Centrally located in the Mediterranean basin o distant from eastern Mediterranean powers • Physical Features o Italian Peninsula o Alps mountains • Offered protection o Mediterranean Sea • Offered protection • Sea-borne commerce b. Describing Roman mythology and religion • Mythology o Based on Greek polytheistic religion o Explanation of natural phenomena, human qualities, and life events • Gods and Goddesses o Jupiter, Juno, Apollo, Diana, Minerva, and Venus o Symbols and images in literature, art, and architecture Standard 6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: c. Explaining the social structure and the role of slavery, significance of citizenship, and the development of democratic features in the government of the Roman Republic • Social Structure o Patricians • Powerful nobility o Plebeians • Majority of the population o Slaves • Not based on race • Citizenship o Patrician and plebian men o Selected foreigners o Rights and responsibilities of citizenship • Taxes • Military service • Features of Democracy o o o o o Representative Democracy Assemblies The Senate Consuls Twelve Tables (Codified laws) Standard 6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: d. Sequencing events leading to Roman military domination of Mediterranean basin and Western Europe and the spread of Roman culture in these areas • Punic Wars o Rome vs. Carthage 264- 146 B.C.E. • In competition for trade • Hannibal invaded Italian Peninsula • Three wars = Roman victory o Destruction of Carthage o Expanded wealth and trade for Rome • Evolution of the Roman Empire and spread of Roman Culture o Mediterranean basin • Africa, Asia, Europe, including Hellenistic world of the Eastern Mediterranean o Western Europe • Gaul, British Isles Standard 6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: e. Assessing the impact of military conquests on the army, economy, and social structure of Rome • Decline of the Roman Republic o Spread of slavery • Causes farmers to go into debt o Migration of small farmers into cities and unemployment o Civil war over the power of Julius Caesar o Devaluation of Roman currency • inflation f. Assessing the roles of Julius and Augustus Caesar in the collapse of the Roman Republic and the rise of the imperial monarchs • First Triumvirate • o Julius Caesar • Seizure of power • assassination 2nd Triumvirate o Augustus Caesar • Civil War with Marc Antony • Rome’s 1st Emperor • Empire o Unified and enlarged using imperial authority and the military o Failure to provide for peaceful succession of Emperors Standard 6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: g. Explaining the economic, social, and political impact of the Pax Romana • The Pax Romana o Two centuries of peace and prosperity under imperial rule o Expansion and solidification of Roman Empire • Particularly in the Near East • Economic impact o Established uniform system of money • Which helped to expand trade o Guaranteed safe travel and trade on Roman roads o Promoted prosperity and stability • Social impact o Returned stability to social classes o Increased emphasis on the family • Political o Created a civil service o Developed a uniform rule of law Standard 6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: h. Describing the origin, beliefs, traditions, customs, and spread of Christianity • Origins o Roots in Judaism o Led by Jesus of Nazareth • Proclaimed Messiah o Conflicted with Roman polytheistic beliefs • Beliefs, traditions, and customs and Christianity o Beliefs • Monotheism • Jesus o Son and incarnation of God • Life after death o Holy Book • New Testament o Christian doctrine established by early church councils • Spread of Christianity o Popularity of the message o Early martyrs o Carried by apostles throughout Roman Empire Standard 6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: i. Explaining the development and significance of the Church in the late Roman Empire • Impact of the Church of Rome in the late Roman Empire o Emperor Constantine converted to Christianity o Christianity later became the state religion o The Church became a source of moral authority o Loyalty to the Church became more important than loyalty to the emperor o The Church became the main unifying force of Western Europe Standard 6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: j. Listing contributions • Art/Architecture o Pantheon, Coliseum, Forum • Technology o Roads, Aqueducts, Roman arches • Science o Ptolemy • Medicine o Emphasis on public health • Pubic baths, public water system, medical schools • Language o Latin, Roman languages • Literature o Virgil The Aeneid • Religion o Roman mythology o Adoption of Christianity • Law o Principle of innocent until proven guilt • Twelve Tables Rome Standard 6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by: k. Citing the reasons for the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire • Causes o Geographic Size • Difficulty of defense and administration o Economy • Cost of defense and devaluation of Roman currency o Military • Inclusion of mercenaries o Moral decay • People’s loss of faith in Rome and the family o Political • Civil conflict, weak administration o Invasion • Attacks on the borders, barbarians • Division of the Roman Empire o Move of capital by Constantine from Rome to Byzantium • Renamed Constaninople o Survival of Western Roman Empire until 476 C.E. • Last Roman emperor o Eastern Roman Empire continued • Byzantine Empire Review Games! • Greece- Battleship Flashcards • Rome- Flashcards • SOL Questions #32- 78