Marketing Plan
advertisement

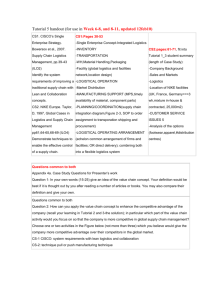
Marketing Plan Marketing Plan • To provide direction and focus for your brand, product, or company. – Nonprofit orgs: to guide their fund-raising and outreach efforts – Gov. agencies: to initiate such as building public awareness of proper nutrition and stimulating area tourism Marketing Plan Components • • • • • • • • Executive Summary Current Marketing Situation SWOT Analysis Objectives and Issues Marketing Strategy Action Programs Budgets Controls Executive Summary • This section summarizes the market offerings, target segments, main goals, recommendations, and points as an overview for senior managers who will read and approve the marketing plan. Current Marketing Situation • In this section, marketing managers discuss the overall market, identify the market segments that they will target, and provide information about company’s current situation. Current Marketing Situation I. Market description: Describing the targeted segments and the benefits and product features in detail provides context for the marketing strategies. II. Product review III. Competitive review IV. Channels and logistics review Current Marketing Situation I. Market description II. Product review: The product review summarizes the main features for all of the company’s products, organized by product line, type of customer, market, or order of product introduction. III. Competitive review IV. Channels and logistics review Current Marketing Situation I. Market description II. Product review III. Competitive review: The purpose of a competitive review is to identify key competitors, describe their market positions, and briefly discuss their strategies. IV. Channels and logistics review Current Marketing Situation I. Market description II. Product review III. Competitive review IV. Channels and logistics review: In this section, marketers list the most important channels, provide an overview of each channels arrangement, and identify developing issues in channels and logistics. SWOT Analysis • Strengths: Internal capabilities that can help the company reach its objectives. • Weaknesses: Internal elements that may interfere with the company’s ability to achieve its objectives. SWOT Analysis • Opportunities External elements that the company may be able to exploit to its advantage. • Threats Current or merging external elements that could potentially challenge the company’s performance. Objectives and Issues • The company’s objectives should be defined in specific terms so management can measure progress and plan corrective action if needed to stay on track. • This section describes any major issues that might affect the company’s marketing strategy and implementation. Marketing Strategy • • • • • Positioning Marketing tools: product strategy Marketing tools: pricing strategy Marketing tools: distribution strategy Marketing tools: marketing communication strategy • Marketing research • Marketing organization Action Programs • Spells out how marketing strategies will be turned into specific action programs that answer the following questions: – – – – What will be done? When will it be done? Who will do it? How much will it cost? • Action programs should be coordinated with the resources and activities of other departments, including production, finance, purchasing, and so on. Budgets • Managers use budgets to protect profitability and plan for each marketing program’s expenditures, scheduling, and operations. Controls • Controls help management assess result after the plan is implemented, identify any problems or performance variations, and initiate corrective action.