AP Lab 7: Genetics of
Drosophila (fruit flies)
Carolina
Purpose
Use fruit flies to do genetic crosses.
Learn to determine the sex of fruit flies
and recognize contrasting phenotypes.
Collect data from F1 and F2 generations
and analyze the results of a
monohybrid, dihybrid, or sex-linked
cross.
Activity A
In part A you will learn to:
observe wild-type flies
recognize male and female flies
compare the mutant phenotypes with the
wild type.
http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_
place/labbench/index.html
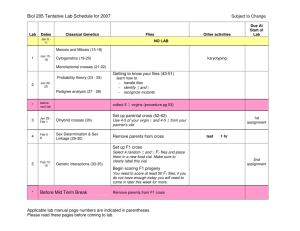
Procedure
Anesthetizing flies will be demonstrated.
Flies will be placed in petri dishes to be
observed.
Draw and document important differences
between phenotypes of:
Males and females
Wild types and mutants
Procedure
After you have observed the flies, return
them to the correctly labeled morgue.
Make sure that if flies begin moving they
are returned to the morgue quickly.
The anesthetizing agent lasts
approximately 50 min.
Activity B
Setting up vials:
Obtain one vial and add 1 level measure
cup of Formula 4-24 to the vial.
Add 1 level measure cup of tap water to
the vial.
After it solidifies, sprinkle 4-7 grains of
yeast to the culture
Procedure
Setting up F1 cross:
Record the code for the cross that you were
given.
Collect 5-6 male/female pairs. (10-12 flies total)
Using Table 2: F1 Data, record sex and
phenotypes for the flies you were given.
Place these flies in your vial and label with
information from the lab.
Return remaining flies to the morgue.
Feedback