Acute Heart Failure – The road to where?
advertisement

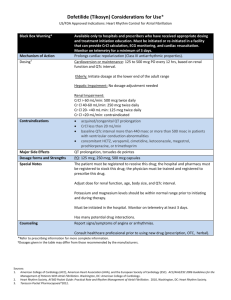
ACUTE HEART FAILURE – THE ROAD TO WHERE? Gad Cotter, Momentum-Research Inc AHF therapy 1970 - 2010 Vasoconstricted (no real criteria) Congestion Renal Impairment Vasodilators Diuresis Renoprotection Low output (No real criteria) Inotrope 10-15% of Patients Nitro-vasodilators Natriuretic peptides Loop Diuretics > 90% of Patients < 5% of patients Levosimendan Dobutamine Milrinone IV Diuretic + Nesiritide IV Diuretic + Inotrope 6% IV Diuretic 72% 4% 4% 9% IV Diuretic + Nitro 1% Nesiritide Alone 1% Inotrope Alone Other AHF Current Treatment Options – this is really sad…. AHF therapy 1970 - 2010 Vasoconstricted (no real criteria) Congestion Renal Impairment Vasodilatation Diuresis Renoprotection Low output (No real criteria) Inotrope 10-15% of Patients Nitro-vasodilators Natriuretic peptides Loop Diuretics > 90% of Patients < 5% of patients Levosimendan Dobutamine Milrinone Critical look: Some improved symptoms, some prevention of in hospital Worsening HF but…. VMAC Nesiritide Critical look – minimal dyspnea improvement With worsening renal function and increased mortality Dyspnea Improvement in VMAC AHF therapy 2010 – Combination Therapy? Vasoconstricted Sys BP > 125 mmHg Vasodilatation Congestion Renal Impairment (eGFR< 80 cc/min) Diuresis Low output Sys BP < 125 mmHg Renoprotection Inotrope # Relaxin ? (phase III) # Direct Soluble GC Activators ? (phase II) #Low dose Loop Diuretics (Phase III)? # Vasopresin Antagonists and low dose Loop diuretics (phase II)? Adenosine A1 Antagonists (Rolofyline)? (phase III - II) Low dose Natriuretic Peptides? (Phase II) # Cardiac Myosin Activators? (Phase II) # SERCA2A Activators? (phase I) AHF therapy Beyond 2010 – Improve diagnosis by non-invasive CO Vasoconstricted Increased SVR Vasodilatation Congestion Renal Impairment (eGFR< 80 cc/min) Diuresis Low output Low Cardiac Power Renoprotection Inotrope # Relaxin ? (phase III) # Direct Soluble GC Activators ? (phase II) #Low dose Loop Diuretics (Phase III)? # Vasopresin Antagonists and low dose Loop diuretics (phase II)? Adenosine A1 Antagonists (Rolofyline)? (phase III - II) Low dose Natriuretic Peptides? (Phase II) # Cardiac Myosin Activators? (Phase II) # SERCA2A Activators? (phase I) Some Supportive information The Lancet - April 15h 2009 Relaxin Mechanisms of Action Relaxin Naturally occurring peptide Up-regulated in pregnancy and HF Vasodilation… Upregulation of ETB Induction of NOS II/III NO, cGMP effectors …but actually an anti-vasocontrictor - Preferential dilates constricted vessels Anti-ischemic effects in animal models Anti-inflammatory Down-modulation of inflammatory cytokines linked to outcome in HF (TNF-a, TGF-b) 11 Global Phase 2 in Acute Heart Failure Study Design Phase 2/3, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, PlaceboControlled, International Study Randomized to placebo, 10, 30, 100, 250 μg/kg of relaxin (3,2,2,2,2) – 48 hr iv infusion, on top of standard of care 234 patients, 54 sites, 8 countries “Acute Vascular Failure” subset of AHF: Patient Population - Dyspnea requiring hospitalization - BNP/NT-pro-BNP > 350/1400 pg/mL - Baseline BP > 125 mmHg - Renal dysfunction (CrCl 30-75 mL/min) Dyspnea (shortness of breath): Serial Likert and VAS to Day 14 Study Endpoints & Objectives Other AHF measures - Signs, symptoms, outcomes through Day 14 - 180 Safety, including renal dysfunction Choose dose, endpoints, sample size, sites 12 for pivotal P3 trials Dyspnea Improvement over Time p=0.06 p=0.05 10000 9000 p=0.16 Dyspnea (AUC; mm*hr) 8000 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 p=0.11 p=0.15 p=0.16 2000 1000 0 Placebo 10 30 100 250 Relaxin (mcg/kg/d) Day 5 Placebo 10 30 100 250 Relaxin (mcg/kg/d) Day 14 13 Kaplan-Meier Event-free Survival (%) CV Death or Heart/Renal Failure Re-hospitalizations to Day 60 Relaxin 30 mcg/kg/d (p<0.05) 1 Cardiovascular Deaths to Day 180 Relaxin 30 mcg/kg/d (p<0.05) 1 Relaxin 10 mcg/kg/d Relaxin 100 mcg/kg/d 0.95 Relaxin 10 mcg/kg/d Relaxin 100 mcg/kg/d 0.95 Relaxin 250 mcg/kg/d 0.9 Placebo 0.85 0.8 0 30 60 90 Days 120 150 180 Relaxin 250 mcg/kg/d 0.9 Placebo 0.85 0.8 0 30 60 90 120 150 Days Critical look – Too good to be true? Lack of clear mechanism of action? 180 soluble Guanylate Cyclase (sGC) Stimulators and sGC Activators NO sGC Stimulator sGC Fe(II) heme sGC Activator sGC Fe(III) heme Oxidative Stress cGMP sGC Activator Stasch/as/3 sGC Stimulator Amplifies protective effects of NO in the cardiovascular system NO-independent mode of action Selective dilation of diseased or oxidative stress impaired blood vessels Proof of Concept Study – Hemodynamic Results Cardiac Output PCWP 7 L/min mmHg 30 24,7 25 6,04 6 5,59 5,04 20,7 20 18,2 15 10 19,0 2h 4h 5 16,9 4,35 4 BAY 58-2667 after BL 5,37 6h FU 2h BAY 58-2667 after BL 3 2h 4h 6h FU 2h Critical look – (1) By bypassing the endothelium, drug also bypases know control pathways? Hence may increase risk of hypotension (2) Will need very careful titration and patient selection, but for some patients especially with endothelial dysfunction – may be very helpful Proof of Concept Study – Hemodynamic Results Cardiac Output PCWP 7 L/min mmHg 30 24,7 25 6,04 6 5,59 5,04 20,7 20 18,2 15 10 19,0 2h 4h 5 16,9 4,35 4 BAY 58-2667 after BL 5,37 6h FU 2h BAY 58-2667 after BL 3 2h 4h 6h FU 2h Rolofylline: Selective Renal Arterial Vasodilator for the Treatment of Acute Heart Failure Thiazides 1. Inhibits sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule enhances diuresis 2. Blocks adenosine-mediated vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole maintains glomerular filtration rate (GFR). 1 Interstitial 2 Na+ Proximal Tubule Adenosine-mediated Vasoconstriction Blocked Adenosine-mediated Vasoconstriction Afferent Arteriole Smooth Muscle Cells MD Cells A1 Receptor Adenosine Distal Tubule Furosemide MK-7418 MD Cells A1 Receptor Adenosine Distal Tubule 20 Mean change in serum creatinine, mg/dL Change in Serum Creatinine 0.35 Placebo (n=78) 0.3 10 mg (n=74) 20 mg (n=75) 0.25 30 mg (n=74) 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 -0.05 Day 2 Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 21 % subjects All-Cause Mortality: 30-Day and 60-Day 18 Placebo (n=78) 16 20 mg (n=75) 14 30 mg (n=74) 10 mg (n=74) 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 30-Day 60-Day Critical look – (1) Effects only patients at risk for renal impairment – many treated for a few to benefit (2) Seizure risk – not globally applicable 22 Myosin Activators - A Novel Mechanism for Heart Failure Therapy • Selectivity for cardiac sarcomere versus other muscle types • No increase in the cardiac myocyte calcium transient • Efficacy in large animal model of heart failure • Lengthens the duration of cardiac contraction rather than the contraction velocity • Improves cardiac function and hemodynamics in dose-dependent fashion • Improves cardiac efficiency without increasing MV02 • High oral bioavailability in preclinical species CK - 1827452 Methods Double blind, placebo controlled phase IIa Study, patients with Chr HF, EF<40%. Dose escalating and time escalating from 2 48 hours of infusion. Results Critical look – shortens diastole while lengthening systole – myocardial perfusion? Calcium Cycling Mediated by SERCA2a is Key to Cardiac Contraction Heart failure => reduced SERCA2a results in reduced contraction & elevated intracellular Ca2+ Contraction Intracellular Ca2+ increased, binds troponin C and starts contractile machinery Relaxation Intracellular Ca2+ declines via reuptake into SR SERCA2a removes 70% of the intracellular calcium from the intracellular space in humans 26 26 XXX Improves Hemodynamics in Myocardial Infarction Model in the Mouse. 27 Vehicle control Hemodynamic Parameters Control XXXXX XXXXX Pmax (mmHg)………………… 51 71 dP/dtmax (mmHg/sec)………. 2716 4237 Contractility Index (sec-1)……. 109 124 Cardiac Output (mL/min)…….. 4536 6102 Ejection Fraction (%)………… 18 28 Stroke Work…………………... 219 660 Stroke Volume (mL)…………. 10 15 Heart Rate (bpm)…………….. 476 410