Physical Patterns and Population (United States)
advertisement

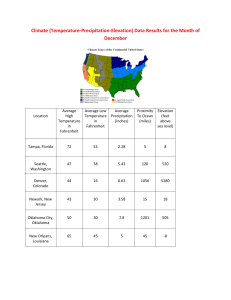
Michigan Grade Level Content Expectations 6 – G1.2.3 Use data to create thematic maps and graphs showing patterns of population, physical terrain, rainfall, and vegetation; analyze the patterns and then propose two generalizations about the location and density of the population. 1 Instructions for Teachers 1. Make copies of slide 3 for each student and provide colored pencils to complete instructions. 2. Have students mark the area of their community. They should note this area on each of the maps in the PowerPoint, especially slides 7 (rainfall), 9 (population density), 12 (land cover), and 15 (elevation). 3. Use the questions on each slide for discussion. 4. Assign the writing activity described on slide 17. (You may print this slide for instructions for students). 5. Project slide 18 for reference during writing activity. 2 (Selected Weather Stations) Instructions Each circle shows average annual precipitation at a weather station. Many weather stations are located at airports 1. Color the weather station circles according to the instructions in the box above. You will see which parts of the U.S. receive the highest and lowest precipitation. 3 (Selected Weather Stations) E D C B A The darkest blue weather stations have highest precipitation. The lightest yellow stations have lowest precipitation. We will use this map to describe how precipitation changes from high to low in the U.S. 4 (Selected Weather Stations) E D C B A 2. Which letters are near stations in the highest precipitation category? ____, ____ 3. Describe where these highest precipitations are in relation to bodies of water. _________________________________________________________________ 5 (Selected Weather Stations) E D C B A 4. Choose the best answer to describe where stations in the lowest category (smallest, light yellow circles) are located. (Use the N-S-E-W compass rose.) _______ a. along the East coast. b. in the middle between Places B and C. c. in the Southwest but not along the coast. 6 E D C B A This map shows regions of precipitation. It was made using hundreds of weather stations. Use the map legend to answer the question. 5. Which place (A, B, C, or D) is located in the 60.1 - 80 category? ______ 7 E D C B A 6. Choose the best answer to describe how precipitation changes between places A, B, C, and D. ______ (Hint: Use the map legend.) a. Precipitation decreases gradually from A to D (moving away from the Gulf). b. Precipitation increases gradually from A to D (moving away from the Gulf). 8 E D Next, we will compare population maps to the precipitation maps. C B A 7. Which place (A, B, C, or D) is located in both the lowest population density category and the lowest precipitation category? ______ (Use the map legend.) Hint: Look at the small precipitation map (inset map in upper right). 9 E D C B NASA and CIESEN (Columbia University) produced this population density map. The darkest red shows highest density, and the lightest orange shows lowest density. A 8. Which place (A, B, C, D) is located in both the lowest population category and the lowest precipitation category? ______ Hint: Look at the small precipitation map (inset map in upper right). 10 E D C Western B Eastern A 9. The black line separates wetter parts of the U.S. from drier parts. Look at the small population map (inset map in upper right) which also has a black line. Which part of the U.S. has lower population densities? _____ a. Higher precipitation regions in East b. Lower precipitation regions in West 11 Amount of precipitation affects what vegetation can grow in a place. 10. NASA created this Landcover Map. Use it along with the Precipitation Map. Which landcovers occur where annual precipitation is more than 20 inches? ____________________ ____________________ _____________________ 12 Amount of precipitation affects what vegetation can grow in a place. 10. NASA created this Landcover Map. Use it along with the Precipitation Map. Which landcovers occur where annual precipitation is less than 20 inches? ____________________ ____________________ _____________________ 13 I J L M K G N H We will use this precipitation map along with a map about elevation to examine how mountains affect precipitation. Places G and H are both near large water bodies and therefore receive middle to high precipitation even though they are at low elevation. 14 I J L M Elevation in meters K G N H 12. Find Places I, K, L, and N on the elevation map. They are all in mountainous areas. Use the elevation legend to see what elevation categories they are in. _________________, __________________ 15 I J L M K G N H 13. Find the mountainous places I, K, L, and N on the precipitation map. They are all in mountainous areas. Winds blow moist air from the Pacific Ocean toward the mountains, and the uplifted air drops rain or snow on mountain tops. 16 Assessment Observe the following population distribution map. Use this map, your precipitation map (showing weather stations), and what you have learned to write: a. A general description of the precipitation pattern in the United States. b. A general description of the population distribution in the United States. c. A generalization about the relationship of population to precipitation, land cover, and elevation in the United States d. An explanation about the population density in your community, using details about precipitation, land cover and elevation. 17 E D C B NASA and CIESEN (Columbia University) produced this population density map. The darkest red shows highest density, and the lightest orange shows lowest density. A 18