5 4 3 2 1
advertisement
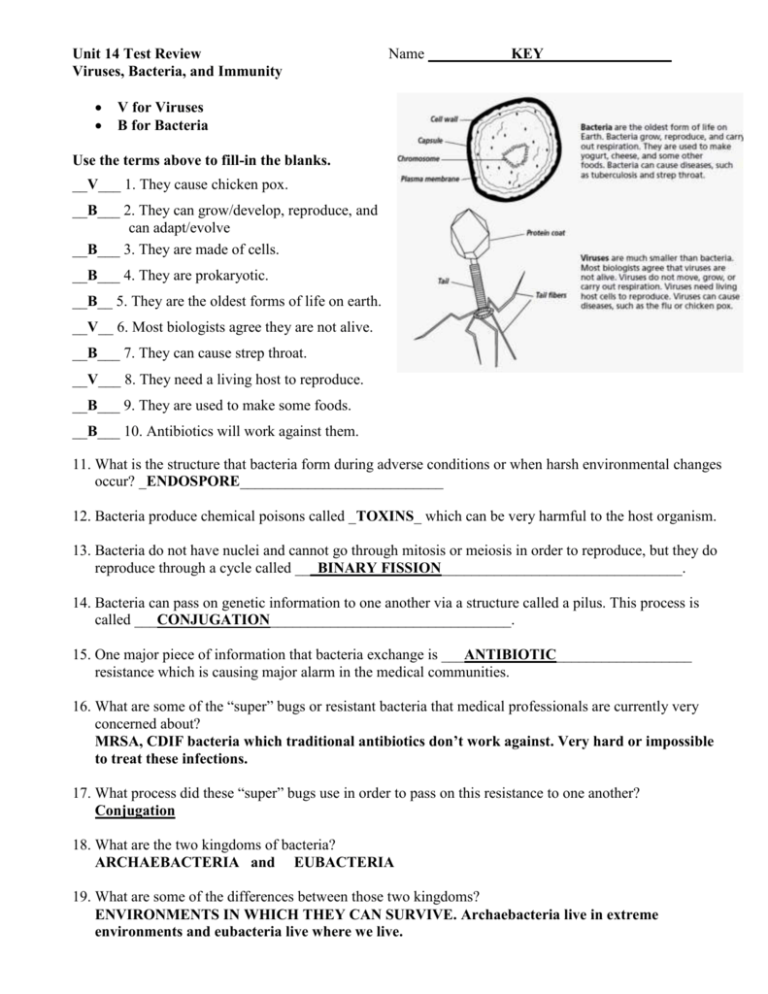
Unit 14 Test Review Viruses, Bacteria, and Immunity Name ___________KEY_________________ V for Viruses B for Bacteria Use the terms above to fill-in the blanks. __V___ 1. They cause chicken pox. __B___ 2. They can grow/develop, reproduce, and can adapt/evolve __B___ 3. They are made of cells. __B___ 4. They are prokaryotic. __B__ 5. They are the oldest forms of life on earth. __V__ 6. Most biologists agree they are not alive. __B___ 7. They can cause strep throat. __V___ 8. They need a living host to reproduce. __B___ 9. They are used to make some foods. __B___ 10. Antibiotics will work against them. 11. What is the structure that bacteria form during adverse conditions or when harsh environmental changes occur? _ENDOSPORE___________________________ 12. Bacteria produce chemical poisons called _TOXINS_ which can be very harmful to the host organism. 13. Bacteria do not have nuclei and cannot go through mitosis or meiosis in order to reproduce, but they do reproduce through a cycle called ___BINARY FISSION________________________________. 14. Bacteria can pass on genetic information to one another via a structure called a pilus. This process is called ___CONJUGATION________________________________. 15. One major piece of information that bacteria exchange is ___ANTIBIOTIC__________________ resistance which is causing major alarm in the medical communities. 16. What are some of the “super” bugs or resistant bacteria that medical professionals are currently very concerned about? MRSA, CDIF bacteria which traditional antibiotics don’t work against. Very hard or impossible to treat these infections. 17. What process did these “super” bugs use in order to pass on this resistance to one another? Conjugation 18. What are the two kingdoms of bacteria? ARCHAEBACTERIA and EUBACTERIA 19. What are some of the differences between those two kingdoms? ENVIRONMENTS IN WHICH THEY CAN SURVIVE. Archaebacteria live in extreme environments and eubacteria live where we live. 20. All bacteria are prokaryotic organisms. What does this mean again?? DO NOT HAVE A NUCLEUS OR MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES; All unicellular 21. What are some of the ways that eubacteria obtain their food? PARASITES – feed on live things SAPROPHYTES – feed on dead things and waste products AUTOTROPHS – make their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis 22. What is the major difference between obligate aerobes and obligate anaerobes? OBLIGATE AEROBE – REQUIRE OXYGEN OBLIGATE ANAEROBE – KILLED BY OXYGEN 23. What is the major difference between gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria? GRAM POSITIVE = TURNS PURPLE b/c thin or no cell walls GRAM NEGATIVE = TURNS PINK b/c thick, resistant cell walls 24. Why would it be important for a physician to know what type of bacteria are present? SO THEY CAN TREAT WITH THE RIGHT ANTIBIOTIC TO BREAK DOWN THE CELL WALL. 25. Fill in the diagram below with the correct bacterial shapes. COCCUS SPIRILLUM BACILLUS 26. What are some of the benefits to having bacteria around? (What good things do they accomplish?) FOOD PRODUCTION (pickles, sauerkraut, yogurt, cheese, etc.) RECYCLING OF NUTRIENTS (decomposers and saprophytes) MEDICINE (insulin production and development of antibiotics) Nitrogen Fixation – (turn forms of nitrogen into forms usable by plants) 27. What is an antibiotic? What organisms will antibiotics work against? An antibiotic is a medicine/chemical designed to kill foreign invaders in the body. ANTIBIOTICS WORK AGAINST BACTERIA BREAKING DOWN THE CELL WALL. 28. What antibiotic was discovered by Fleming in 1928? ___________Penicillin_______________ 29. How do antibiotics work against bacteria? Some antibiotics like penicillin work by keeping a bacterium from building a cell wall. Without support from a cell wall, pressure inside the cell becomes too much and the membrane bursts. Other antibiotics block bacterial ribosomes and prevent them from building proteins. Since proteins do all the cell’s work, a bacterium that cannot build proteins cannot survive. 30. Use the following words for the chart to below. Place the correct word underneath the correct title it aligns with. Lytic Cycle Coccus Binary Fission Conjugation Lysogenic Cycle Nucleic Acids (DNA/RNA) Capsid Alive Obligate anaerobe Made of cells Can cause disease Food production Coccus Binary Fission Conjugation Nucleic Acids (DNA/RNA) Food production Alive Obligate Anaerobe Made of cells Can cause disease Lytic Cycle Lysogenic Cycle Nucleic Acids (DNA/RNA) Capsid Can cause disease 31. Look that the graph below with the different lines on it and answer the following questions. 2 1 Number of Bacteria 3 Time Which line could represent a bacterial colony that has been given an antibiotic? _3_____ Which line could represent bacterial growth in the presence of abundant resources (food and water)? _2___ 32. What is the name of the cell that the virus infects and takes over during its replication cycle? Host cell 33. A virus that infects a bacterium would be called a/an _____bacteriophage_______________________. 34. A virus that uses DNA as its nucleic acid is called a/an ____DNA_____ virus. 35. A virus that uses RNA as its nucleic acid is called a/an ___retrovirus_____________. 36. The infected cell that forms when viral DNA incorporates into the cell’s DNA is called a _provirus___. C E B D A Virus attaches to host cell and injects its nucleic acid into the cell. The viral DNA/RNA is integrated (becomes part of) the host cell chromosome-called a provirus Each time the host cell replicates the provirus is replicated as well. 2 1 5 4 3 37. What are some examples of viruses that go through the lytic cycle? Common Cold, Influenza (FLU) 38. What are some examples of viruses that go through the lysogenic cycle? Herpes, HIV 39. The cell is killed during the ____Lytic___ cycle whereas the cell is not killed during the ____Lysogenic_____ cycle. 40. Symptoms for the ____Lytic____ cycle show up usually in 2-4 days, whereas symptoms for the _____Lysogenic________ cycle can take years to show up. 41. Viruses are (smaller or larger) than bacteria. Immunity 42. Any foreign substance that can cause the immune response in humans would be considered a/an _______Antigen____________. 43. Examples of substances/organisms that cause the immune response would include: Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Allergens (ragweed, dust, cat dander, etc.) 44. What are antibodies? What do they do for humans? Proteins formed by white blood cells that circulate the body and help us recognize foreign invaders to be killed off by our immune system. They fight infection and form after being exposed to an antigen one time prior or through vaccination. 45. What is a pathogen? What are some examples? Any disease causing agent is a pathogen. Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Protozoan are all examples. 46. What is a vaccine? An injection/nasal liquid, etc. that is taken artificially to stimulate the production of antibodies against a certain pathogen. The goal is to stimulate immune memory so that if later infection occurs, the disease does not occur or is significantly less dangerous that it would have been without the vaccine. 47. What can your immune system do if you are infected with a pathogen? Your immune system will first do what it can to kill, engulf foreign pathogen. Later B cells will form antibodies to create memory of disease and will help later prevent infection by this certain type of pathogen. Infectious disease is the chief cause of death in developing countries. More antibiotics would be available in developed countries because they have access to regular medical care. You would then expect numbers of infectious diseases to decrease which is evident in the graph. Developing countries would have higher rates of infectious disease for lack of appropriate medical care. Lack of appropriate medical care, poor nutrition or starvation, and infected water supply. Also highly dense populations where lots of people are in close proximity can lead to fast disease transmission. Doctors advise patients on antibiotics to take yogurt because yogurt contains active cultures (probiotics) of bacteria that are useful for digestion and nutrient absorption. The antibiotics they are taking would kill any existing bacteria, so they would need to be replaced. Yogurt can do that. Two reasons why yes - bacteria have cell walls just like plants do; some bacteria are photosynthesizers like plants Two reasons why not – bacteria are prokaryotes not eukaryotes like plants; some bacteria are heterotrophs








