Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
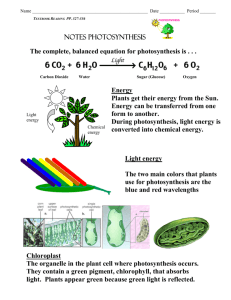
Photosynthesis: ability of plant to capture light energy and turn it into the chemical energy of organic food molecules. (i.e. how plants make their food )
‘photo’ = light; ‘synthesis’ = to make ( to make with light )
Occurs in plant chloroplasts
Chloroplast review
Stroma
Lamellae
Granum
(stacks of thylakoids)
Thylakoids
Thylakoid membrane contains chlorophylls
Chlorophyll = green pigment in chloroplasts that absorbs light
Starch granules are present in the stroma of the chloroplast
Photosynthesis
(continued)
Produce glucose and ATP
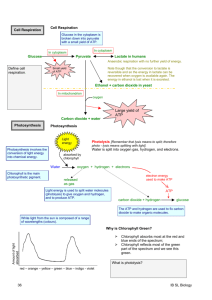
Involves a series of enzyme-controlled reactions, and can be summarized as:
CO
2
+ water Glucose + oxygen + water
The phases
Photosynthesis consists of 2 phases:
1.
The Light dependent phase: need light
2.
The Light independent Phase/Dark
Phase: Does not need light
The Light reaction/ Light Phase
Occurs in the grana of the chloroplast
Light energy (trapped by chloroplast) is used in two ways:
1. Make ATP :
Light + ADP + P ATP
ATP produced directly from light captured by chlorophyll (light energizes e in chlorophyll molecule and the e gets passed down an electron transport chain)
2. Split water into hydrogen and oxygen
Light + water + NADP NADPH
2
+ Oxygen
NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) = hydrogen carrier molecule
Oxygen produced diffuses out of cell (waste)
_____________________________________
LIGHT REACTIONS:
- Convert light energy chemical energy
(NADPH
2 and ATP)
- These energy-rich compounds are used in the Dark Reactions…
The phases
Photosynthesis consists of 2 phases:
1.
The Light dependent phase: need light
2.
The Light independent Phase/Dark Phase:
Does not need light
(OK, I kinda lied…the H from the light phase is needed here…)
The Light independent
Phase/ Dark Phase
Also called Calvin cycle/ Carbon fixation stage
Occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast
Uses the ATP and Hydrogen produced in the
Light Phase (ATP and H travels from the grana to the stroma)
CO
2
+ ATP + Hydrogen
G-3-P + water
(G-3-P = Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate)
Dark reaction (continued)
G-3-P is converted into:
- Carbohydrate (glucose or sucrose)
- Amino acid
- lipid
Glucose formed is often turned into insoluble starch (granules in stroma)
Summary
I Need a Little Light
By Ross Durand copyright 2003 http://www.songplanet.com/artists/bands/669/
I need a little light
So I can store energy
I need a little light
So I can make ATP
I need a little light
I’m gonna make some food
It’s outta sight
And I need a little light
Been sittin here in this chloroplast, feeling green the whole day through
Yeah, I’m a little thylakoid, just waitin’ for something to do
I’m gonna move some electrons through a chain and pump some hydrogen in
But it’s been dark all night and you can see the state I’m in
I need a little light
So I can store energy
I need a little light
So I can make ATP
I need a little light
I’m gonna make some food
It’s outta sight
And I need a little light
When the electrons leave that chain they’re gonna join NADP (plus)
And that high concentration of hydrogen’s gonna want outside of me
Gonna go through a special protein that’s gonna kick some ATP out
That’s what movin these electrons is really all about
I need a little light
So I can store energy
I need a little light
So I can make ATP
I need a little light
I’m gonna make some food
It’s outta sight
And I need a little light
The ATP and NADPH are gonna make a cycle go round
At the end of the calvin cycle glucose can be found
You gotta put in 6 pieces of CO2 to make that precious food
And use up the products of the thylakoid, darn this system’s good
I need a little light
So I can store energy
I need a little light
So I can make ATP
I need a little light
I’m gonna make some food
It’s outta sight
And I need a little light
There’s one other thing that I need besides light
It’s good old water
You see that chlorophyll that loses those electrons – needs to get some back
And that’s what the water does
Now the whole reason that electron move was because of the light
I need a little light
So I can store energy
I need a little light
So I can make ATP
I need a little light
I’m gonna make some food
It’s outta sight
And I need a little light
Factors affecting Photosynthesis
1.
Light wavelength : chlorophyll absorbs all wavelengths of light except green (red and blue absorbed the most).
rate of photosynthesis with red and blue light
2.
Light intensity :
light intensity rate of
Photosynthesis
3.
[Carbon dioxide]: photosynthesis limited by rate of CO
2 absorption
4.
Temperature :
temp rate (until 40 ° C) e.g. plants grow faster in glasshouse
Factors affecting
Photosynthesis (continued)
5.
Water:
water rate of photosynthesis
6.
[Chlorophyll]: magnesium needed for a functional chlorophyll. Low Mg soil less chlorophyll. Plants often turn yellow from lack of chlorophyll (growth rate very slow in these plants)
http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/ animations/content/harvestinglight.html
Mini Quiz
1.
Photosynthesis consists of 2 phases – what are the two phases called?
Light and Dark Phases/ Light dependent phase and Light
2.
independent phase
The light reaction occurs within the ________
3.
CO
2
+ H
2
O _______ + _______ + H
2
O
4.
How is the light energy captured from chlorophyll used? (2 ways)
To make ATP and to split water into hydrogen and oxygen
5.
What is the name of the hydrogen carrier molecule in the light reaction?
NADP
Respiration and
Photosynthesis sheet
Use the resources provided to you (books, laptops, me…) to complete the sheet as a summary/review.
Good sites to go to (for in-depth info)
http://www.biologymad.com/
http://www.scool.co.uk/topic_index.asp?subject_id=3&d=0
http://www.bbc.co.uk/scotland/education/bitesize/hig her/biology/cell_biology/index.shtml