200412ICADLinvited - Edward A. Fox
advertisement

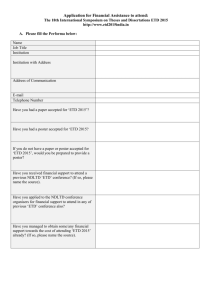
ICADL 2004 Invited Talk Digital Libraries for Education: Case Studies Edward A. Fox, fox@vt.edu Digital Library Research Laboratory, Dept. of CS Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061 USA http://fox.cs.vt.edu/talks/2004/ Acknowledgements (Selected) • Sponsors: ACM, Adobe, AOL, CAPES, CNI, CONACyT, DFG, IBM, Microsoft, NDLTD, NSF (IIS-9986089, 0086227, 0080748, 0325579; ITR-0325579; DUE0121679, 0136690, 0121741, 0333601), OCLC, SOLINET, SUN, SURA, UNESCO, US Dept. Ed. (FIPSE), VTLS Acknowledgements (cont’d) • Faculty, Staff: Lillian Cassel, Debra Dudley, Weiguo Fan, C. Lee Giles, Eberhard Hilf, John Impagliazzo, Filip Jagodzinski, Deborah Knox, Aaron Krowne, Alberto Laender, Gail McMillan, Manuel Perez, Naren Ramakrishnan, … • Students: Pavel Calado, Yuxin Chen, Fernando Das Neves, Shahrooz Feizabadi, Marcos Goncalves, Nithiwat Kampanya, S.H. Kim, Aaron Krowne, Ming Luo, Fernando Das Neves, Ryan Richardson, Rao Shen, Hussein Suleman, Wensi Xi, Baoping Zhang, Qinwei Zhu, … Outline • • • • • 5S Framework for DL Digital Libraries for Education CITIDEL NSDL NDLTD Definition: Digital Libraries are complex systems that • • • • • help satisfy info needs of users (societies) provide info services (scenarios) organize info in usable ways (structures) present info in usable ways (spaces) communicate info with users (streams) • Compare with the Five Elements of Traditional Chinese Medicine … Digital Libraries in Education • • • • • • • Analytical Survey, ed. Leonid Kalinichenko © 2003, www.iite-unesco.org, info@iite.ru Transforming the Way to Learn DLs of Educational Resources & Services Integrated/Virtual Learning Environment Educational Metadata Current DLEs: US (NSDL, DLESE, CITIDEL, NDLTD), Europe (Scholnet, Cyclades), UK (Distributed National Electronic Resource) Digital Libraries in Education - 2 • Advanced Frameworks & Methodologies – Instructional course development with learning module repositories, Learning Object reuse – Community organization around DLEs – Other content for science and research – Cyberinfrastructure, data grids – Curriculum-based interfaces (see Krowne et al.) – Concept-based organization of learning materials and courses (CMs, ontologies) DLEs: Future Vision (p. 6) • Global learning environment of the future: • Student-centered • Interactive and dynamic • Enabling group work on real world problems • Enabling students to determine their own learning routes (styles, personalization) • Supporting lifelong learning DLEs: Objectives (p. 11) • Long-range: lifelong/distance/anytimeanywhere • Intermediate goals: – Support for students, teachers, parents – Enhanced student performance – More students excited about science – More Internet-based science educ. resources • with increased quality and comprehensiveness, • easy to discover and retrieve, • preserved and universally available DLEs: Guiding Principles (p. 12) • • • • • • • • Driven by educational and science needs Facilitating educational innovation Stable, reliable, permanent Accessible to all Leveraging prior research: DL, courseware, … Adaptable to new technologies Supporting decentralized services Resource integration thru tools/organization Outline • • • • • 5S Framework for DL Digital Libraries for Education CITIDEL NSDL NDLTD CS -> CSTC + CRIM • NSF and ACM Education Committee funded a 2 year project “A Computer Science Teaching Center” - CSTC - http://www.cstc.org/ • College of NJ, U. Ill. Springfield, Virginia Tech • Focused initially on labs, visualization, multimedia • Multimedia part was supported by a 2nd grant to Virginia Tech and The George Washington University: http://www.cstc.org/~crim/ (with curricular guidelines also under development) CS Teaching Center (CSTC) • Instead of building large, expensive multimedia packages, that become obsolete and are difficult to re-use, concentrate on small knowledge units. • Learners benefit from having well-crafted modules that have been reviewed and tested. • Use digital libraries to build a powerful base of support for learners, upon which a variety of courses, self-study tutorials & reference resources can be built. • ACM support led to Journal of Educational Resources in Computing (JERIC), accessible from www.cstc.org Browsing (2) Computing and Information Technology Interactive Digital Educational Library (CITIDEL) • Domain: computing / information technology • Genre: one-stop-shopping for teachers & learners: courseware (CSTC, JERIC), leading DLs (ACM, IEEE-CS, DB&LP, CiteSeer), PlanetMath.org, NCSTRL (technical reports), … • Submission & Collection: sub/partner collections www.citidel.org www.CITIDEL.org • Led by Virginia Tech, with co-PIs: – Fox (director, DL systems) – Lee (history) – Perez (user interface, Spanish support) • Partners – College of New Jersey (Knox) – Hofstra (Impagliazzo) – Villanova (Cassel) – Penn State (Giles) Overview of CITIDEL architecture USER PORTALS DIGITAL LIBRARY SERVICES REPOSITORIES Digital library architecture for local and interoperable CITIDEL services EDUCATORS Multilingual Searching LEARNERS Browsing Union Metadata Filtering Filtering Profiles OAI Data Provider Annotating ADMINISTRATORS Revising Administering User Profiles Annotations OAI Data Harvester Remote and Peer Digital Libraries (eg. NSDL -CIS) PORTALS SERVICES REPOSITORIES CITIDEL Technology Features •Component architecture (Open Digital Library) •Re-use and compose re-deployable digital library components. •Built Using Open Standards & Technologies •OAI: Used to collect DL Resources and DL Interoperability •XSL and XML: Interface rendering with multi-lingual community based translation of screens and content (Spanish, …) •Perl: Component Integration •ESSEX: Search Engine Functionality •Very fast, utilizing in-memory processing •Includes snap-shots for persistence •Multi-scheming •Integrates multiple classifications / views through maps, closure PIPE: Personalization by Partial Evaluation • Interactions at existing web sites are predefined by the site designer • Personalization is achieved by the designer’s anticipation of users’ expectations • PIPE allows automatic personalization of a web site without designer anticipation – Recognized with the 2001 New Century Technology Council Innovation award PIPE Provides Mixed-Initiative Interaction • Involves an extra specification window (e.g., a toolbar) • system-initiated + user-initiated modes of interaction Traditional browser: the user merely clicks on available hyperlinks. PIPE window: the user can type in any information out-of-turn CITIDEL + PIPE • Adds Interaction Personalization to CITIDEL •Automatically handles multi-modal conversion to Cell phone, PDA, Etc. •Can be adopted to any digital data set, only requires XML file of content with hierarchy maintained. Cluster Search Results from CITIDEL Cluster NDLTD-Computing CitiViz HomePage http://feathers.dlib.vt.edu/CitiViz/index.html CitiViz Display of Detailed Information for a Selected Document: A Tower of Cylinders (to solve occlusion problem) CitiViz initial interface 1.Show me retrieved results from ACM DL 1. Show me retrieved results from ACM DL 2. “algorithm analysis”, by “Donald Knuth” 2. “algorithm analysis”, by “Donald Knuth” Clustering results 2. “algorithm analysis”, by “Donald Knuth” 3. “data compression” 3. “data compression” Conclusions • Text mining + information visualization • Document clustering provides insights for users. • Overview of document attributes in the 2D scatter plot • Overview of hierarchical concept map displayed as a hyperbolic tree supports “focus+context” navigation. • Integrated the 2D scatter plot space with a network of citations. • Online tutorial and system – also animation. CITIDEL -> NSDL • A collection project in the • National STEM (science, technolgy, engineering, and mathematics) education Digital Library – NSDL • National Science Digital Library • www.nsdl.org • (Next slides courtesy Lee Zia, NSF) NSDL ProgramTracks • Core Integration: coordinate a distributed alliance of resource collection and service providers; and ensure reliable and extensible access to and usability of the resulting network of learning environments and resources • Collections: aggregate and actively manage a subset of the digital library’s content within a coherent theme / specialty • Services: increase the impact, reach, efficiency, and value of the digital library in its fully operational form • Targeted (Applied) Research: have immediate impact on one or more of the other three tracks • Pathways: large efforts across broad ranges of areas or approaches or users NSDL Information Architecture Essentially as developed by the Technical Infrastructure Workgroup Portals & Portals & Clients Portals & Clients Clients User Interfaces Core NSDL “Bus” NSDL NSDL NSDL Collections Collections Collections Collection Building referenced referenced items&& Special items collections Databases collections Core Core Services: Collectionmetadata Building Core gathering CollectionServices protocols Building Services harvesting NSDL NSDL Services Other NSDL Services Services Usage Enhancement Core Services: CI Services information retrieval CI Services browsing CI Services authentication CI Services personalization CI Services discussion annotation Outline • • • • • 5S Framework for DL Digital Libraries for Education CITIDEL NSDL NDLTD A Digital Library Case Study • Domain: graduate education, research • Genre:ETDs=electronic theses & dissertations • Submission: http://etd.vt.edu • Collection: http://www.theses.org Project: Networked Digital Library of Theses & Dissertations (NDLTD) http://www.ndltd.org What are the long term goals? • 400K US students / year getting grad degrees are exposed / involved • 200K/yr rich hypermedia ETDs may turn into electronic portfolios (50M pages, images, video, audio, …) • Dramatic increase in knowledge sharing: literature reviews, bibliographies, … • Services providing lifelong access for students: browse, search, prior searches, citation links • Hundreds/thousands of downloads/year/work Why ETDs? Short Answer • For Students: – Gain knowledge and skills for the Information Age – Richer communication (digital information, multimedia, …) • For Universities: – Easy way to enter the digital library field and benefit thereby • For the World: – Global digital library – large, useful, many services • General: – Save time and money – Increased visibility for all associated with research results Status of the VT Project • Approved by university governance Spring 1996; required starting 1/1/97 • Submission & access software in place • Submission workshops for students (and faculty) occur often: beginner/adv. • Faculty training as part of Faculty Development Initiative • Over 5000 ETDs in collection – some have audio, video, large images, software, … Q uickTim e™ and a Cinepak decom pr essor ar e needed t o see t his pict ur e. http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-2227102539751141/ Access to VT’s ETDs http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/theses/ 5,000,000 4,500,000 4,000,000 3,500,000 3,000,000 2,500,000 2,000,000 1,500,000 1,000,000 500,000 ETD files requested Abstracts requested 1997/98 231,709 165,710 1997/98 483,030 215,493 1999/00 578,152 260,699 2000/01 2,173,420 573,149 2001/02 4,497,199 471,917 What led to today’s discussion? • 1987 mtg in Ann Arbor: UMI, VT, … • 1992 mtg in Washington: CNI, CGS, UMI, VT and 10 universities with 3 reps each • 1993 mtg in Atlanta to start Monticello Electronic Library (regional, US Southeast): SURA, SOLINET • 1994 mtg at VT: std: PDF + SGML + multimedia objects • 1996 funding by SURA, US Dept. of Education (FIPSE) • 1997 meetings in UK, Germany, ... • 1998 – 1st symposium – Memphis (20) • 1999 – 2nd symposium – Blacksburg (70) • 2000 – 3rd symposium – St. Petersburg (225) • 2001 – 4th symposium – Caltech (200) • 2002 – 5th syposium – BYU, Provo, Utah • 2003 – 6th syposium – Berlin (215) • 2004 – 7th syposium – U. Kentucky • 2005 – 8th syposium – Sydney, Australia NDLTD: How can a university get involved? • Select planning/implementation team – – – – Graduate School Library Computing / Information Technology Institutional Research / Educational Technology • Join online, give us contact names – www.ndltd.org/join • Adapt Virginia Tech or other proven approach – Build interest and consensus – Start trial / allow optional submission Convene Local Planning Group ETD Build Local ETD Site ETD Workshop/Training Digital Library Policies Inspection/Approval Student Prepares Thesis/Dissertation NDLTD Literature Computer Resources Research Student Defends & Finalizes ETD My Thesis ETD Student Gets Committee Signatures and Submits ETD Signed Grad School Graduate School Approves ETD, Student is Graduated Ph.D. Library Catalogs ETD, Access is Opened to the New Research WWW NDLTD ETD Union Collection (OAI) VIRTUA ODL (VT) Future: recommender, … Merged Metadata Collection LEGEND OAI Data Provider Virginia Tech ETD Archive OCLC ETD Archive Brazil ETD Archive … OAI Service Provider OAI Harvesting OCLC SRU Interface ETD Union Search Mirror Site in China (CALIS) (http://ndltd.calis.edu.cn – popular site!) Language = German; hits = 137 Full record display NDLTD Incorporation • Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations incorporated May 20, 2003 in Virginia, USA • Charitable and educational purposes (501 c 3) – Can accept donations, collect dues, receive funds • Officers – Executive Director (Ed Fox) – Secretary (Gail McMillan) – Treasurer (Scott Eldredge) Board of Directors • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Suzie Allard (ETD 2004, U. Kentucky) • Denise A. D. Bedford (World Bank) • Julia C. Blixrud (ARL, SPARC) • José Luis Borbinha (National Lib Portugal)• Alex Byrne (ETD 2005, ADT: Australia) • Tony Cargnelutti (ETD 2005, Australia) • Vinod Chachra (VTLS) • Susan Copeland (RGU, UK) • Jude Edminster (Bowling Green St. Univ.) • Scott Eldredge (Treasurer, ETD 2002, BYU) • Edward A. Fox (Exec Director,Virginia Tech) • John H. Hagen (West Virginia U.) Thomas B. Hickey (OCLC) Christine Jewell (U. Waterloo, Canada) • • Delphine Lewis (ProQuest) Joan K. Lippincott (CNI) Mike Looney (Adobe) Gail McMillan (Secretary, Virginia Tech) Joseph Moxley (ETD 2000, USF) Eva Müller (U. Uppsala, Sweden) Ana Pavani (PUC Rio, Brazil) Axel Plathe (UNESCO, Paris) Sharon Reeves (National Library Canada) Peter Schirmbacher (ETD 2003, Humboldt) Hussein Suleman (U.Cape Town, S. Africa) Shalini R. Urs (U. Mysore, India) Eric F. Van de Velde (ETD 2001, Caltech) Some Countries • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Australia Belgium Brazil Canada Chile China, Hong Kong Columbia Finland France Germany Greece India Italy Jamaica Korea Lithuania Malaysia Mexico • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Namibia Netherlands Norway Poland Russia Singapore S. Africa S. Korea Spain Sudan Sweden Switzerland Taiwan Thailand Turkey UK USA Venezuela Yugoslavia Some Institutional Members • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • ADT (Australian Digital Theses) British Library Cinemedia Coalition for Networked Information (CNI) Committee on Institutional Cooperation (CIC) Consorci de Biblioteques Universitàries de Catalunya Dissertationen Online (Germany) ETDweb, a Division of Answer4.com Ibero-American Science & Technology Education Consortium (ISTEC) National Documentation Centre (NDC), Greece National Library of Portugal (for all universities) OCLC Online Computer Library Center OhioLINK Organization of American States (SEDI/OAS) Southeastern Library Network (SOLINET) UNESCO (www.unesco.org/webworld/etd) ETDs and Publishing • Early controversies waning • Faculty: prior publication? – Protective of future academics • Surveys of publishers – No specific policies largely – Consider submissions individually • VT ETD Alumni – None had problems getting published • Authors – Retain some rights, e.g., link to curriculum vitae, online course materials ETD-MS • ETD Metadata Standard – XML-encoded metadata standard (content and encoding) for Electronic Theses and Dissertations (ETDs) – in part conforming to Dublin Core (DC) – using RDF – using UNICODE • Specified relationship with MARC Added Support by NDLTD • Links from NDLTD site – ETD individuals support – submit ETD – ETD discussion (e-prints) – community activities – Conference papers and presentations – community activities • Partnering: Adobe, MERLOT, Scirus, … • Marcel Dekker book now available – Edward A. Fox, Shahrooz Feizbadi, Joseph M. Moxley, and Christian R. Weisser, eds., The ETD Sourcebook: Theses and Dissertations in the Electronic Age, New York: Marcel Dekker, 2004 Spirit of NDLTD • • • • Help make a better (smaller) world Win-win-win (everyone can benefit) Have fun helping others Helpers/teachers learn more than those they work with • Build on standards • ETDs are preservable, popular, expressive, “better” • Doable, feasible, learnable, affordable, sharable • Please join NDLTD! Main Message • Digital libraries can help advance education. • China is invited to engage in NDLTD, as well as CITIDEL, NSDL, and other DL ventures. • UNESCO Analytical Survey on Digital Libraries in Education is recommending DLE in each nation. • Local and national support can – stimulate activities, including collaboration – promote a sharing culture, especially in research and teaching – leverage others’ investments (networking, computing, …) – encourage / facilitate learning Summary • • • • • • 5S Framework for DL Digital Libraries for Education CITIDEL NSDL NDLTD and, for friendship and information … A warm welcome awaits you in Sydney, Australia at the 8th International Symposium on Electronic Theses and Dissertations ETD 2005 evolution through discovery 28 – 30 September 2005 UNSW ETD2005: evolution through discovery The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia Hosted by: The University of New South Wales (UNSW) Library and the The Council of Australian University Librarians (CAUL) in association with the Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations (NDLTD) UNSW ETD2005: evolution through discovery The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia UNSW Library Lead institution - Australian Digital Theses (ADT) Program http://adt.caul.edu.au/ Developer and ongoing management of ADT Program Member of NDLTD with representatives on NDLTD Board and other committees Participated in ETD annually since 1998 Digital submission mandatory from 2005 UNSW ETD2005: evolution through discovery The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia Conference venue The Scientia Multi-award-winning building UNSW ETD2005: evolution through discovery The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia International access Sydney International Airport - 20 minutes from UNSW campus - over 100 international flights per day UNSW ETD2005: evolution through discovery The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia And it’s Springtime in Sydney …. Sydney Sydney Ocean Beaches …within minutes of UNSW Sydney National Parks …within the metropolitan area The Blue Mountains …an ideal day trip ADT special announcement: We are rolling out the ADT Program to other countries in the region, including New Zealand, and we welcome others to join!!! UNSW ETD2005: evolution through discovery The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia Further information UNSW Library: http://info.library.unsw.edu.au/ Australian Digital Theses Program@UNSW: http://adt.caul.edu.au/ Sydney, Australia: Tourism New South Wales: http://www.tourism.nsw.gov.au/home/ Barani: indigenous history of Sydney city: http://www.cityofsydney.nsw.gov.au/barani/ UNSW ETD2005: evolution through discovery The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia