Opportunity Identification
advertisement

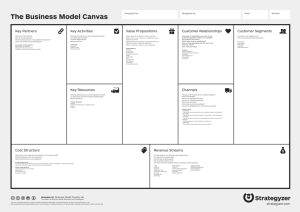
OPPORTUNITY IDENTIFICATION Dr. Dawne Martin MKTG 241 January 29, 2013 LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Review the Opportunity Identification paper • To investigate trends in the external environment that offer new business opportunities • Review “discovery skills” identified in the HBR article “The Innovator’s DNA”, December 2009 • Identify trends in the environment • Determine how the trends justify the business opportunities • For next time: Marketing for Entrepreneurs, Chapters 3 ONE-PAGE OPPORTUNITY IDENTIFICATION • Due: Thursday, January 31, 2013 • Trends: Identify, document and describe trends relevant to the opportunity • Opportunity: Describe the opportunity, including industry, business model and target market • Justification: Expand on trends and how the trends suggest this opportunity THE INNOVATOR’S DNA DYER, GREGERSEN & CHRISTENSEN, HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW, DEC. 2009 • Senior executives in most innovative companies take responsibility for creative work – spend 50% of time in “discovery skills” • Discovery skills • Associating • Questioning • Ask “Why?”, “Why not?”, “What if?” • Imagine opposites • Embrace constraints CHARACTERISTICS OF A GOOD OPPORTUNITY • Creates significant value for customers– solving an important problem, fulfilling a need – willing to pay premium price • Offers significant profit potential – meets risk/reward expectations • Good fit between entrepreneur’s capabilities and expertise • Offers sustainability over time • Can obtain financing INNOVATOR’S DNA (CONTINUED) • Discovery Skills (continued) • Observing: potential customers, suppliers, competitors • Experimenting • Intellectual exploration • Physical tinkering • Engaging new environments • Networking : with diverse individuals GLOBAL TRENDS • Economic Trends • Consumer Trends • Financial Market Trends • Technology Trends • Social Media Trends • Mobile Trends • Demographic Trends • Design & Fashion Trends • Health & Wellness Trends • Travel Trends • http://www.globaltrends.com/features/strategy-a-leadership/67-10-key-trends-to-watch ERNEST & YOUNG GLOBAL TRENDS http://www.ey.com/GL/en/Issues/Business-environment/Six-global-trends-shaping-thebusiness-world FAITH POPCORN:EN-GEN 2011: FAITH POPCORN’S BRAINRESERVE PREDICTIONS • EN-GEN: End of traditional gender roles – neither males nor female, just human • Trends • Women hold 51% of managerial & professional jobs • 4 of 10 mothers are primary breadwinners, bring in close to ½ household income • Single, childless women under 30 earn 8% more than male peers • Number of women with 6 figure salaries increased by 14% in last two years • Women’s health following men – increase in chance of heart attacks, heart surgery GENDER TURNING POINTS: OPPORTUNITIES • Merger of Artistry & Technology – simple, elegant design (Nespresso) • Beyond the Bento Box – men & women experiment with interests and ideas normally associated with other gender • Electric Shock: Electric vehicles combine women’s concerns for environment with men’s love of technology • Recession Lift: Economy has made it difficult for men 45+ to compete – boom in male plastic surgery • Veganomics: More sensitivity to sources of food and consumer products leads to growth in vegan values in all areas (bamboo floors, MooShoes) • Robot Frenzy: Breakthroughs in robot technologies in medicine, manufacturing, prosthetics, military and more BUSINESS MODEL BUILDING BLOCKS • Customer Segments • Segments • Needs require and justify a distinct offer • Reached through different distribution channels • Require different types of relationships • Have substantially different profitability • Are willing to pay for different aspects of the offer • Segmentation approaches • Mass market – don’t distinguish between customer segments • Niche market – specific, specialized customer segments • Segmented – serve multiple segments with different needs • Diversified – serves two unrelated customer segments • Multi-sided Platform (or markets) – two or more interdependent customer segments (Ebay) BUSINESS MODEL BUILDING BLOCKS • Value Proposition: Creates value for a customer segment through a distinct mix of elements catering to segments needs • Newness – meets a new set of needs – cellphones • Performance – improving product or service performance • Customizations – tailoring product and services to specific customer needs – mass customization and co-creation • Get the Job Done– Rolls Royce manufacturers and maintains aircraft engines • Design • Brand/status • Price • Cost Reduction • Risk Reduction • Accessibility • Convenience/Usability BUSINESS MODEL BUILDING BLOCKS • Channels • Channels Types • Direct – sales force, web sites, own stores • Functions: • Building awareness among customers • Helping customers evaluate value proposition/alternatives • Allowing customers to purchase specific products or services • Indirect – Partners stores, wholesalers • Customer Relationships • Personal assistance • Dedicated personal dinner • Self-service • Delivering value proposition to customer • Automated service • Provide post-purchase customer support • Co-creation • Communities Business Model Building Blocks • Revenue Streams • Asset sales • Usage fees • Subscription • Lending/renting/leasing • Licensing • Brokerage fees • Advertising • Key Resources • Physical • Intellectual • Human • Financial • Key Activities • Production • Problem solving • Platform/network BUSINESS MODEL BUILDING BLOCKS • Key Partnerships • Optimization and economies of scale • Reduction of risk and uncertainty • Application of particular resources and activities • Cost Structure • Cost –driven • Value-driven • Cost structure characteristics • • • • Fixed costs Variable costs Economies of scale Economies of scope IN YOUR GROUPS • Work on your Opportunity Analysis • Identify your customer base and your unique value