What is Money?
advertisement

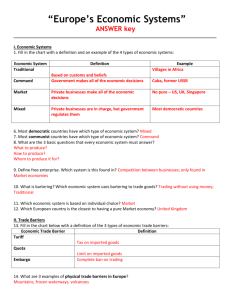
Agenda Bellringer Review Questions Textbook reading: Money Notes: Money HW: Quiz Friday Review What is scarcity? What does a production possibility curve show us? Capitalism, based on consumer wants and needs What is a command economy? Based on tradition, Bartering What is a market economy? Opportunity costs What is a traditional economy? Limited resources for unlimited wants Communism, based on government determined needs What is a mixed economy? Mixture of traditional, command, and market economies Why do we have money? As commerce and trade continued to evolve the process of bartering became much too complicated Consider: If you wanted to sell your iPod and there was no money.You would have to find the person with the right goods (and quantity of them) that satisfied you enough to make the trade. With money, anyone can buy it if they have the cash. Would you trade ipod for a floor waxing machine? 30 various fiction books? Four pizzas? What is money? Can the following items be useful as currency? Textbook reading Read and outline in your notes pages 557-561 Three functions of money Six characteristics of money Three types of money Agenda Bellringer Quiz Finish Money notes Exit ticket Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. What does the term “Land” mean in economics? What does a production possibility curve illustrate? Define Scarcity Provide an example of a trade off Provide an example of physical capital in a landscaping business Provide an example of human capital in a school Define command economy What form of economy did Adam Smith advocate? Define traditional economy What are the three big economic questions? Money as Currency Target: Money Money Is a Federal Reserve Note – meaning a piece of paper backed by the US governments promise it is worth something Three Roles of Money Medium of Exchange Can be anything that is used to determine value during an exchange of goods and services It is the same for everyone so bartering (unless used informally) is now extinct in our country You can buy anything you want, spend a lot or a little, save, etc…. Everyone accepts cash Unit of Account Prices in the US are expressed in the same way in every store – in dollars and cents Everyone knows the value of a dollar People have ‘reasonable expectations’ of costs.You expect a movie will cost around $9, pizza $11, etc… As a unit of account, money lets you compare prices and get the best deal (jacket in store A: $50, in store B: $35) Every country has their own (Japan=Yen, Mexico=Peso) Store of Value You can save your money as long as you want and it will retain its value. I can save the $5 in my pocket and spend it two years from now and it is still $5 Notable exception: Inflation (to be covered later). Simply put: prices rise over time. Six Characteristics of Money Durability Portability They all look the same, count the same, buy the same Limited Supply Able to be divided into smaller denominations on demand Uniformity Easily able to carry around Divisibility Made with cloth and paper to withstand wear and tear Federal Reserve controls amount in circulation Acceptability Everyone in economy is able to use and accept money Sources of Value Commodity money: “stuff” that has value (ie: cattle, gems). Used only in simple, barter based economies Representative money: Objects that only have value because they can be traded for goods with value (silver or gold certificates). Like an IOU but for something very specific. Fiat Money: Money is valuable because our government says it is and only available in limited quantities therefore it is valuable. “Legal tender for all debts, public and private” Circular Flow of Money (Market Economy) Exit Ticket What are the three roles of money? Identify the six characteristics of a good currency What kind of money does the US utilize?