Types of Economies
advertisement

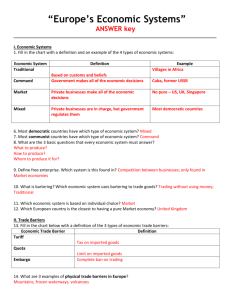
Standard 1: Scarcity and Economic Reasoning Objective: Understand why choices need to be made and things given up Essential Knowledge: Scarcity, Factors of Production, Opportunity Cost, Types of Economies, Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) Warm-up in Notebook Question: How much does a Big Mac cost? Unit 1 Part 3 Types of Economies & Circular Flow Diagram Types of Economies There are four types of Economies in the world: Market Economy Command Economy Traditional Economy Mixed Economy Market Economy If you went to a pawn shop to buy a watch, how would you decide what price to pay for it? Who sets the price of a product in a market economy? The buyers and sellers agree to the price Pros: Competition allows for prices to remain where they should be. Cons: What if only one business was selling the product? Command Economy Some countries in the world have total control of their citizens’ lives. In this type of economy, the government sets the price for all goods and services. Pros: Everyone gets paid the same, prices are the same for everyone. Cons: Why would you work harder in this scenario if you knew there was no incentive for it? Would you work overtime? Traditional Economy Notre Dame football is the best college football team in the country. Even if you don’t believe that, you can’t deny that they some great traditions. One tradition they have is having the players hit the “Play Like a Champion Today” sign when they leave the locker room. They have done it since the first football game ever played there and will continue to do it for decades to come. Traditional Economy A traditional economy is where the price of goods and services stay the same over time. There are a few 3rd world countries still using this system. It usually involves bartering. Bartering: Trading goods and services for other goods and services. In a traditional economy, 1 goat may equal 10 bushels of wheat. 10 years from now what will 1 goat equal? Mixed Economy Simple! An economy that combines two or more of the other economies listed. What type of economy does the United States have? You guessed correct! A mixed economy We have a mixture of market and command economies. Most products are determined by supply/demand (market economy) but some products like milk have a set price determined by the government. Circular Flow Diagram: Definitions Free Enterprise: The government lets business decide what to charge for products. Capitalism: Consumers (you and I) own the factors of production. Circular Flow Diagram: How a Market Econ. Works 1. Consumers sell their factors of production (land, labor, & capital) to entrepreneurs in exchange for money. 2. Entrepreneurs gather the factors of production and create a product. 3. Entrepreneurs sell the finished product to consumers and receive money (hopefully profit). 4. Consumers purchase products 5. Cycle begins again.