Introduction: Basic Anatomy of the Heart

Neat Fact – Your heart beats about 100,000 times in one day and about 35 million times in a year. During an average lifetime, the human heart will beat more than 2.5 billion times.
Introduction: Basic
Anatomy of the Heart
Chapter Learning Objectives:
1) Describe the location, approximate size, and function of the heart
2) Describe the protective coverings of the heart
3) Identify the major anatomical structures of the heart and explain how they function
4) Trace the pathway of blood through the heart
5) Describe cardiac muscle
6) Explain the heart’s pacemaker and the electrical conductivity of the heart
7) Explain the waves of an ECG
Developed by Stephanie Lanoue for L.I.T. 5/14/2007
Where is Your Heart Located?
Try this:
1)Stand up.
2)Put your hand on your heart (keep it there).
Neat Fact: The heart pumps about 1 million barrels of blood during an average lifetime--that's enough to fill more than 3 super tankers.
PREDICT
How big is your heart?
Neat Fact: On average, your body has about 5 liters of blood continually traveling through it by way of the circulatory system.
How Would You Describe the Heart? What Do You
Already Know About It?
Class Activity: Appreciating Your Heart as a
Pump.
The Heart’s Protective
Coverings
▪ Do you know that the heart has 2 protective membranes around it?
Heart enclosed in double-walled sac called the ________________ .
Superficial – fibrous pericardium
Deep – serous pericardium
*between the 2 layers is some fluid
Remember the number…
Next, we are going to learn basic heart anatomy:
▪ 4 chambers
▪ 4 valves
▪ 4 main blood vessels coming into/ exiting the heart
Orientation of the Heart in the Body
Left Left
Remember, you are looking at someone else’s chest!
(Speaking of someone else’s chest…heart surgery photos)
Photos from Open Heart Surgery Observations –
Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX
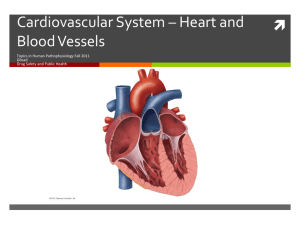
Basic Heart Anatomy
NOTE TO STUDENTS: Label the structures of the heart on your diagram as I explain them.
Heart Chambers
NOTE: Atria = plural form of atrium
Heart Anatomy Continued
Blood Vessels
1
3
2 semilunar valve image
(3 cusps are open)
Valves
Valves, flaps of connective tissue between the atria and ventricles, allow blood to flow one-way mitral valve image
( 2 cusps)
Neat Fact: Heart sounds (“lub, dub”) are caused by the closing of the heart valves. The mitral & tricuspid valves make the 1st sound, and the aortic & pulmonary valves the 2nd.
Valves continued
Chordae tendineae (“heart strings”) attached to ______ and _____ valves.
They anchor valve cusps to the papillary muscles (which play a role in valve function). Papillary muscles protrude from the ventricle walls.
3
2
1
REVIEW
12
11
10
9
8
4
5
6
7
What is a Heart Attack?
http://www.healthscout.com/animation/68/
13/main.html
Additional Important Arteries
Coronary circulation is blood provided by the right and left coronary arteries .
Left coronary
anterior interventricular artery (also known as the left anterior descending which supplies to the interventricular septum and anterior walls of both ventricles)
circumflex artery (supplies left atrium and posterior walls of left ventricle).
Right coronary
marginal artery (supplies myocardium of the lateral right side)
posterior interventricular artery
Cardiac Veins
After passing through capillary beds of the myocardium, the blood flows into the coronary sinus (which empties blood into right atrium). Has 3 tributaries:
______ cardiac vein
______ cardiac vein
_______ cardiac vein
Also, several anterior cardiac veins.
Partner Activity: Blood Flow
Through the Heart
Instructions: Working with a partner, can you describe the flow of blood through the heart? Start with the right atrium.
List all the major structures along the way (chambers, valves, and vessels). Refer to the diagram on page 602.
Example: Rt. atrium > ? valve> ?
(chamber) > ? valve up the pulmonary trunk which divides into the > ? arteries (which send the deoxygenated blood into the ? for
O
2
.) From the lungs back to the heart along the ? Veins > ?
(chamber) through the ? Valve >?
(chamber) > ? Valve > Aorta > Body
> Venae cavae.
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle – _______, short (fat/ _______) cells that are interconnected for quicker communication & conduction of electrical current.
Video footage: http://video.aol.com/video-detail/beating-humanheart-cells-from-embryonic-stem-cells/4230805508
Conduction System
Know Sequence of Excitation:
1. Sinoatrial node (SAN) or __________ >
2. _______ventricular node (AVN) >
3. Atrioventricular bundle ( bundle of ___ ) >
See animation: http://www.jdaross.cwc.
net/cardiac_cycle.htm
4. Right and Left bundle branches >
5. Purkinje fibers (directly supply the papillary muscles)
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
http://www.cardioconnection.org/frameWork.aspx?cnt=cad/diagnosis/ecg#
3 Distinguishable
Waves:
___ – initiation of the heartbeat in the atria
___ – movement of the electrical current through the ventricles
__ – recovery phase; electrical current spreads back over the ventricles in the opposite direction
Electrocardiogram (ECG) continued
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Findings
Healthy heart – _____, ______, and timing of waves tend to be _____________
Unhealthy heart – waves are ______
Examples: an enlarged R wave hints of enlarged ventricles or a prolonged Q-T interval may reveal ventricular arrhythmias
Normal and Abnormal
ECG Readings
(a) _______ – steady sinus rhythm
(b) Non-functional _____
(c) Heart _____ – damage to the AVN (interferes with the ventricles receiving pacing impulses)
(d) __________ fibrillation
(acute heart attack or electrical shock)
Normal and Abnormal ECG Readings continued
Arrhythmias – ________ heartbeats caused by uncoordinated atrial and ventricular contractions
Example: atrial flutter http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3q4TJUmMztY
___________ – rapid and irregular contractions; SAN looses control of setting the pace; fatal condition
Other Heart Abnormalities
Heart ________ – blood back flowing through a heart valve
___________ –abnormally fast heart rate
__________ – heart rate slower than 60 beats per minute
Congestive heart failure – progressively worsening condition in which the heart can no longer pump blood efficiently (heart weakens and enlarges)