- Riverside Preparatory High School
advertisement

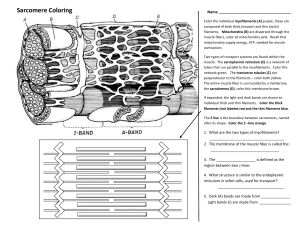
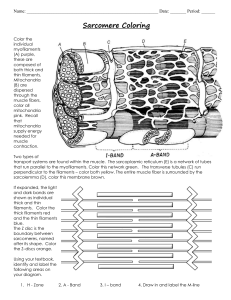
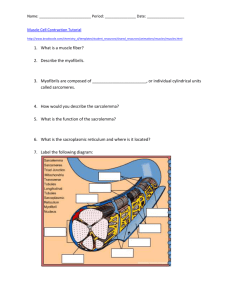
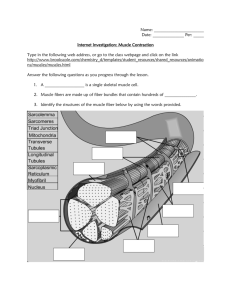
Muscular System Notes Microscopic Muscle Anatomy Myfibrils About 1-2 micrometers in diameter Length of a muscle fiber Composed of multiple myofilaments Contains about 10,000 sarcomeres Myofilaments Actin (thin filaments) Myosin (thick filaments) Microscopic Muscle Anatomy Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Modified version of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum Surrounds each myofibril, forms a tubular network (t tubule) Contains high amounts of Ca2+ ions Sarcomere Repeating units of myofilaments Smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber Z lines: proteins that interconnect thin filaments in muscle fibers M line: proteins that connect thick filaments to each other A band: area of muscle cells that contains thick filaments I band: area of muscle cells that contains thin filaments Thin and Thick Filaments Active site on actin is blocked by tropomyosin Tropomyosin is held in place by troponin Calcium is required to move tropomyosin out of the way (binds to troponin) Action potential from brain stimulates muscle cells, sarcoplasmic reticulum dumps calcium ions into the sarcoplasm. Calcium in sarcoplasm binds to troponin, revealing the active site Sliding Filament Theory During contraction, I band gets smaller, A band stays the same size When myosin binds to actin, it creates a cross bridge Cross bridge pulls (changes shape) thin filament towards the center of the sarcomere Cross bridge detaches, returns to original shape, then reattaches at a new binding site and repeats Activity Draw a muscle fiber Label actin, myosin, troponin, and tropomyosin Explain the role of calcium in muscle contraction Take the information on the sliding filament theory and list out 4 steps to muscle contraction