Essential_Biology_11.2_
advertisement

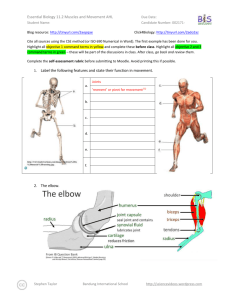
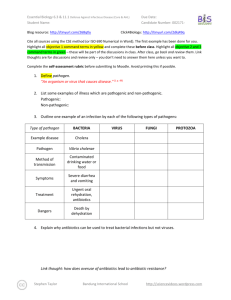
Essential Biology 11.2: Muscles and Movement (AHL) Muscles and Movement When a nerve impulse reaches the terminal end of a motor neuron, it intitiates muscle contraction, causing movement in the body. 1. What are the roles of the following components in movement in the body? Nerves Muscles Bones Joints Tendons Ligaments Synovial fluid Cartilage 2. In the space below, draw and label a simple diagram of a human elbow joint. Include the radius, ulna, humerus, biceps and triceps. Label and state the functions of the joint capsule, synovial fluid and cartilage. 3. Outline how the biceps and triceps work antagonisticallyto ‘bend’ and ‘extend’ the arm. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 11.2: Muscles and Movement (AHL) 4. Compare these types of joints: Elbow Type of joint Range of movement Knee Shoulder/ Hip hinge Hinge movement with some pivoting possible 5. Label this section of a striated muscle cell with the names and functions of each structure. 6. Which part of the muscle cell is depolarized when an action potential reaches the neuromuscular junction? 7. Why are there so many mitochondria in a muscle cell? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 11.2: Muscles and Movement (AHL) 8. The electron micrograph below shows a section of a myofibril. a. Label the dark and light bands and z-lines. b. How many full sarcomeres are shown in this image? c. Draw a simple diagram of the corresponding sarcomeres, showing the actin and myosin fibres (with myosin heads) 9. Annotate the diagrams below to show how muscle contraction occurs in a sarcomere. Include the roles of sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum, Ca2+, actin binding sites, cross bridges, myosin heads, ATP. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 11.2: Muscles and Movement (AHL) 10. Compare these two electron micrographs of a skeletal muscle sarcomere. Contracted or relaxed? Sarcomere length Shorter Z-bands Closer H-bands No change Light bands Dark bands No change 11. What can be deduced from this in terms of relative roles of actin and myosin fibres? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com