Student Learning Outcomes 101
advertisement

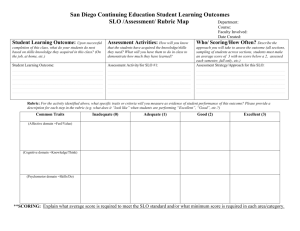
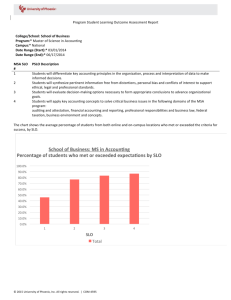
Student Learning Outcomes 101 Foundations of the Student Learning Outcomes Assessment Cycle Presented by Jenny Simon and Lars Kjeseth Reflect... What are some of your concerns about student learning in your program or classroom? What are Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs)? “Robust” student learning outcomes incorporate behavioral objective- what a student should know, value and be able to demonstrate/ perform conditions under which performance will be assessed (simulation, lab, portfolio, writing task) Criteria/ performance standards/ primary traits for assessing student performance Rubric for scoring student performance Course Objectives vs SLOs Course objectives versus student learning outcomes: Generally, a course objective states what student will demonstrate, represent or produce at end of course. SLO also incorporates the conditions under which assessment will occur (test, portfolio, demonstration, etc) as well as evidence/criteria. That is an SLO suggests an appropriate assessment (evidence) that the student has learned. Example Course Objective: By the end of the semester, students will be able to write a well-organized, thesis-driven essay. (English) SLO: Given an in-class writing task based on an assigned reading (context), demonstrate appropriate and competent writing which (objective) states a thesis, supports assertions, maintains unity of thought and purpose, is organized, and is technically correct in paragraph composition, sentence structure, grammar, spelling and word use (traits). Example Course Objective: By the end of the semester, students will be able to analyze behavior following the major accepted theories. (Psychology) SLO: Given a particular behavior and its context (e.g., playing incessantly with one’s hair when under pressure in the presence of the opposite sex) (context), describe how the perspectives of behaviorism, humanistic, psychoanalytic, and biological psychology would interpret that behavior and what methods might each use to alter that behavior (objective). The answer includes theoretical basis, description of causality, and treatment program (traits). Example Course Objective: By the end of the semester, students will be able to understand and apply the scientific method (Biology). SLO: Given a hypothesis (context), design experiments and interpret data according to the scientific method in order to evaluate the hypothesis (objective). Include the ability to approach the scientific method in a variety of ways, formulate questions, design experiments that answer the questions; and manipulate and evaluate the experimental data to reach conclusions (traits). Example Course Objective: Compare and contrast the text and film versions of a literary work. (Film) SLO: After viewing an assigned film based on a literary text (context), write a review of the film (objective). Include an appraisal of the director’s selection and effective translation of content from the literary text and the dominant tone othe director seems to be trying to achieve, supporting each statement with detail from the text and film and the student’s personal reaction to the cited scenes. Pop Quiz Course objective or SLO? Students will understand that individuals (and their families) must be regarded as being unique due to multicultural issues and other variables. (Sociology course) If you answered “objective,” you’re right! Pop Quiz Course objective or SLO? In a written research report, students will critically review the scientific literature, synthesize the findings across studies, and make appropriate ecological recommendations based on current knowledge. (Ecology Course) If you answered “SLO,” you’re right! Pop Quiz Course objective or SLO? Functioning as a member of a team, the student will design and present a concrete structure which complies with engineering standards. (Engineering Course). If you answered “SLO,” you’re right! At What Levels Do We Assess SLOs? Lesson/ unit of study Course Program Occupational certificate Major Department/ Division Associate degree (A.A./A.S./A.A.S) Institutional Practice Writing SLOs Turn to Appendix 1 Read the example SLO Work on the example SLO Write your own SLO with a group of colleagues from the same or similar discipline Material in Appendices 2 & 3 will also help you write your SLO Your SLO should contain: Performance Context Measurable Objective Primary traits Once we’ve written an SLO, what’s next? Writing an SLO is only the first step in the process The next steps include assessing the SLO, analyzing the data, and reflecting on the findings to suggest improvements Identify Assess Reflect Reflect... How could you and your program solve your concerns about student learning through SLOs and assessing SLOs? What other questions do you have?