Answers - Unit 2
advertisement
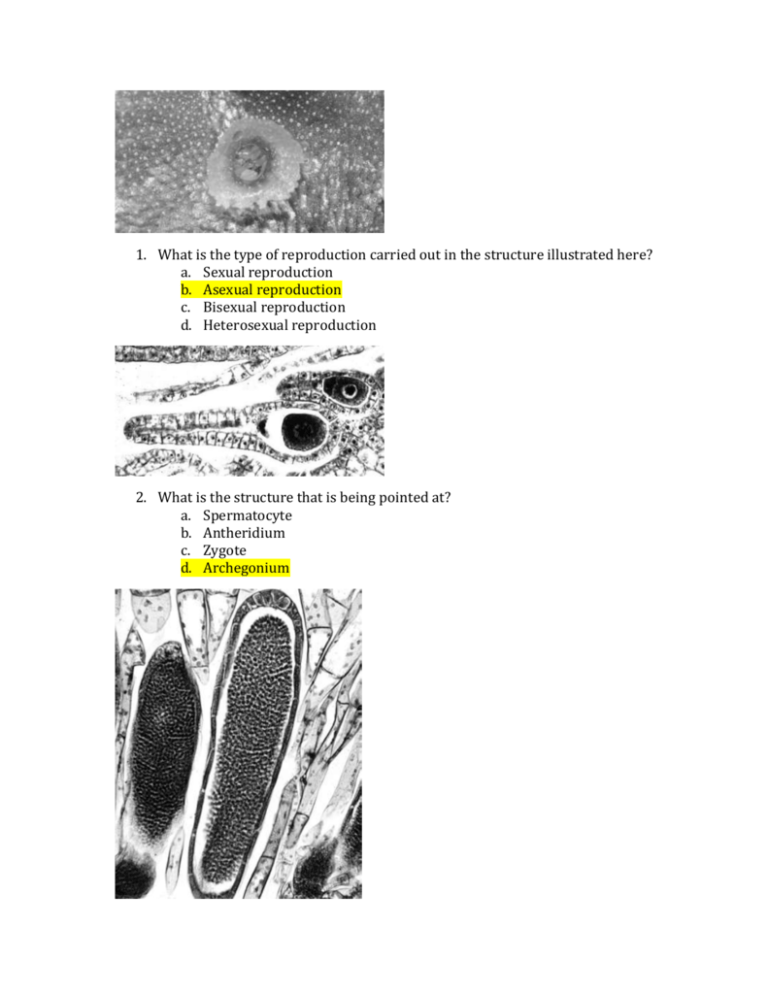
1. What is the type of reproduction carried out in the structure illustrated here? a. Sexual reproduction b. Asexual reproduction c. Bisexual reproduction d. Heterosexual reproduction 2. What is the structure that is being pointed at? a. Spermatocyte b. Antheridium c. Zygote d. Archegonium 3. What is the structure shown here? a. Gametangium b. Gamete c. Sporangium d. Archegonium 4. What is the ploidy level and stage of the structures illustrated? a. 1: haploid, gametophyte; 2: diploid, sporophyte b. 1: diploid, sporophyte; 2: haploid, gametophyte c. 1: Haploid, sporophyte; 2: diploid, gametophyte d. 1: Diploid, gametophyte; 2: haploid, sporophyte 5. What do the megaspores illustrated in this strobilus become? a. Spores b. Female sporophytes c. Male sporophytes d. Female gametophytes 6. The indicated structures are called: a. Antheridia b. Sori c. Archegonia d. Sporangia 7. What does this structure contain? a. Male gametes b. Female gametes c. Both male and female gametes d. Neither male nor female gametes 8. What are the structures indicated? a. Pollen grains b. Female gametes c. Microsporocytes d. Microspores 9. What is the structure indicated? a. Ovary b. Ovule c. Pollen grains d. Female microspore 10. What are pollen grains? a. Mature male sporophytes b. Mature male gametophytes c. Immature male gametophytes d. 2N 11. In moving to land, plants had to overcome which of the following challenges? a. Less available CO2 in the atmosphere than in the oceans b. Desiccation c. Lack of structural support d. Both b and c 12. Plants undergo alternation of generations in which _________. a. The sporophyte generation alternates with the gametophyte generation b. The vascular generation alternates with the nonvascular generation c. Male plants alternate with female plants d. Antheridia alternate with archegonia 13. ____________ protect(s) pollen grains from environmental damage. a. Sporopollenin b. Lignin c. Cuticles d. Stomata 14. The gametophyte state of the plant life cycle is most conspicuous in _______. a. Ferns b. Mosses c. Horsetails d. Seed plants 15. Which of the following produce eggs and sperm? a. Megaphylls b. Fern sporophytes c. Moss gametophytes d. Megaspores e. Moss sporangia 16. Fertilization in moss occurs when sperm swim from a(n) ______ and down the neck of a(n) _______. a. Antheridium; sporangium b. Antheridium; archegonium c. Archegonium; antheridium d. Sporangium; archegonium 17. How are gametes produced in plants? a. By mitosis of gametophyte cells b. By meiosis of gametophyte cells c. By meiosis of sporophyte cells d. By mitosis of spores e. By meiosis of spores 18. Ferns and mosses are limited mostly to most environments because _________. a. They lack cuticles and stomata b. They lack vascular tissue c. They have swimming sperm d. Their seeds do not store water 19. The dots on the underside of a fern frond are spore cases; therefore, what is true of the plant to which the frond belongs? a. It is a spore b. It is a gamete c. It is a sporophyte d. It is a gametophyte 20. Heterosporous plants produce ___________. a. Megaspores that develop into female gametophytes and microspores that develop into male gametophytes b. Megaspores that develop into male gametophytes and microspores that develop into female gametophytes c. Megaspores that bear antheridia and microspores that bear archegonia d. Spores that produce both archegonia and antheridia 21. Sori can be found in which of the following? a. Mosses b. Pterophytes c. Lycophytes d. Charophyceans 22. Which of the following adaptations is common to all seed plants? a. Reduced gametophytes b. Pollen c. Ovules d. All of the above 23. Which one of the following is true of seed plants, but not true of seedless plants? a. The sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte b. The sporophyte is large, and the gametophyte is small and independent c. The gametophyte is reduced and dependent on the sporophyte d. A film of water is necessary for sperm to come in contact with eggs 24. The eggs of seed plants are fertilized within ovules, and the ovules then develop into __________. a. Seeds b. Gametophytes c. Fruit d. Ovaries 25. What gymnosperm phylum is characterized by large cones and fern-like leaves? a. Anthophyta b. Gnetophyta c. Coniferophyta d. Cycadophyta 26. What is located in the scalelike structures packed densely in pollen cones? a. Sporophyte b. Sporangia c. Megasporocytes d. Developing pollen tubes 27. Each pollen grain of a gymnosperm contains a _______. a. Male gametophyte b. Microsporocyte c. Megasporocyte d. Fertilized ovule 28. In ovulate cones megasporocytes undergo _____ and produce _____ megaspores a. Mitosis; diploid b. Meiosis; diploid c. Mitosis; haploid d. Meiosis; haploid 29. Which types of angiosperms would most likely be wind-pollinated rather than animal-pollinated? a. Oak and maple trees b. Roses and tiger lilies c. None of the choices are correct. Plants with flowers are not windpollinated 30. The portion of a flower that receives the pollen is the ________. a. Filament b. Ovary c. Stigma d. Style 31. A pea pod is formed from ________. A pea inside the pod is formed from ________. a. An ovule; a carpel b. An ovary; an ovule c. An ovary; a pollen grain d. Endosperm; an ovary 32. The pollen tube releases two sperm cells into the embryo sac. The result of this is the __________. a. Union of the two sperm nuclei; forming a zygote b. Union of one sperm nucleus with the egg nucleus while the other sperm nucleus unites with two nuclei of another megagametophyte cell, forming a triploid nucleus c. Union of one sperm nucleus with the egg nucleus and the disintegration of the other sperm nuclei. d. Fusion of both sperm nuclei with the egg nucleus and the formation of a triploid zygote 33. The triploid nucleus of the embryo sac develops into the ________. a. Endosperm b. Fruit c. Carpel d. Seed 34. Which of the following characterizes eudicots a. Pollen grains with three openings, floral parts in multiples of three, netlike veins b. Two cotyledons, netlike veins, taproot usually present c. Scattered vascular bundles, netlike veins, floral parts in multiples of five d. Leaves with parallel veins, taproot usually present, vascular bundles arranged in rings.