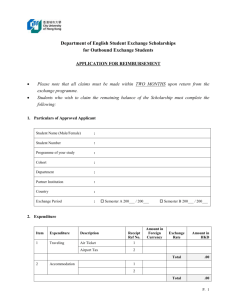
MRCS FIN REG (Final English Version)
advertisement

1 MYANMAR RED CROSS SOCIETY FINANCIAL REGULATIONS CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1 Myanmar Red Cross Society was formed under Myanmar Red Cross Society Act of 1959 with the object to alleviate human sufferings caused by any natural or man-made disaster. 2. As the leading humanitarian organization in Myanmar, the Society is committed to assist vulnerable people and to improve and maintain their health and well-being. Objectives of Financial Regulations 3. The purpose of having Accounting Systems and Control Procedures in place is to promote sound financial management practices, transparency, safeguard the assets and use of financial and other resources in the pursuit of the Society's objectives in an effective and efficient manner. 4. The Financial Regulations shall govern the financial administration of Myanmar Red Cross Society. The Regulations are intended to guide the management, officers and staff of the Society in dealing with day to day financial affairs and recording of financial transactions. 5. These Financial Regulations are intended to be used as a reference book by members of Finance and program staff of Myanmar Red Cross Society and it shall be used in connection with training of all staff members. Scope 6. The Financial Regulations define the accounting policies, financial rules and procedures to bring about transparency and consistency in recording and reporting of financial transactions of Myanmar Red Cross Society as well as to meet the requirements as framed by Myanmar Accountancy Council and International Financial Reporting Standards as may be applicable. 7 The Regulations are a handy official reference and guide to all executives and staff for undertaking and recording the financial transactions of the Society while carrying out activities at its Headquarters or at its Branches in accordance with its constitution. 8. The accounting policies, procedures and rules defined herein are to be complied with by National Society staff employed at Headquarters and Branches, auditors and donor / partner representatives for all financial agreements, commitments and transactions. 9. The Executive Director, with the assistance of Head of Finance, shall be responsible for the financial administration of Myanmar Red Cross Society in accordance with these Financial Regulations and shall establish directives and internal procedures as are necessary. 2 CHAPTER 2 FINANCE DIVISION-ORGANOGRAM AND FUNCTIONAL RESPOSIBILITIES Organization Chart 10. The Finance Division shall be headed by Head of Finance. He will report to the Executive Director. The Head of Finance Division will be supported by a Deputy Head in his work. 11. The Head of Finance will head the Finance Division and render all services and advise the Program Division heads on financial matters. 12. Organogram of Finance Division is as shown below:- Head of Finance Division Deputy Head of Finance Division ( 2 posts ) Finance Officer ( 4 posts ) Finance Assistant ( 5 posts ) Cashier ( 1 post ) Office Helper ( 1 post ) Job Descriptions 13. Job descriptions for each of the above-mentioned positions of the Finance Department shall be determined by the Head of Finance with the approval of the Executive Committee. 3 Functional Responsibilities of Finance Division 14. Under the supervision of the Head of Finance, Finance Division shall be responsible for:(a) Accounting assets, liabilities, income and expenditures of the Society with all relevant supporting vouchers, documents and in line with the accounting policies adopted by Myanmar Red Cross Society. (b) Maintaining all books of account as required under the laws of Myanmar. (c) Ensure that the procedures of the Society are adhered to while releasing the funds. (d) Ensure that all records relating to each of the financial transactions recorded in books of account are kept safely and securely. (e) Ensure that all investment documents, cheque books and cash are kept safely and securely. (f) Ensure submission of yearly budget consolidating all the proposed activities based on the operational plans of Myanmar Red Cross Society and to review the budget from time to time. (g) Provide financial and other relevant information to the management for decision making in running day to day affairs of Myanmar Red Cross Society. (h) Timely financial reporting to donor agencies in coordination with program managers. (i) Presenting yearly financial statements i.e. balance sheet, income and expenditure statement, and cash flow statement to the Executive Committee. (j) To give financial concurrence for MOU / Agreements / Contracts. (k) To ensure timely audit of the yearly statement of the accounts of Myanmar Red Cross Society. 4 CHAPTER 3 ACCOUNTING SYSTEM 15. The Society shall keep the accounts in double entry accrual accounting system and shall follow the accounting standards published by Myanmar Accountancy Council. 16. Every financial transaction must be supported with source documents like purchase invoices, sales invoices, cash payment, receipts, purchase orders, goods received notes (GRN), etc. which shall be kept safely and securely. 17. The financial transactions shall be checked by assistants and before recording in the books of entry it shall be checked and approved by the Head of Finance or Deputy Head of Finance if delegated by the Head of Finance. 18. The Head of Finance shall ensure that accounting policies and principles mentioned hereunder are observed in entirety by the accounting staff. Books of Account 19. The Society shall keep its accounts on computer-based accounting system to produce the following books of account:(a) Cash Book (b) Bank Book (c) General Ledger 20. The other supplementary records to be maintained are:(a) Petty Cash Book (b) Inventory Register (c) Fixed Assets Register (d) Losses Register 21. Petty Cash Book shall be maintained on the basis of imprest system. The respective heads of divisions shall appoint a person other than the Cashier as a petty cash holder. 22. All financial transactions shall be recorded in a way every transaction can be tracked individually. The following voucher forms shall be used as source documents for posting the transaction records in the ledger. (a) Cash Payment Voucher (b) Cash Receipt Voucher (c) Bank Payment Voucher (d) Bank Receipt Voucher (e) Journal Voucher 23. at all time. All vouchers for a period of one month shall be properly filed and placed to be accessible Financial Statements 24. year. The following financial statements shall be drawn on annual basis covering the financial (a) (b) (c) Balance Sheet Income and Expenditure Account Cash Flow Statement 25. Finance Division shall prepare appropriate formats for recording the financial transactions and for preparing the financial statements. 5 Accounting Policies Historical Cost Convention 26 convention. All financial transactions shall be recorded under historical cost (actual incurred cost) Matching Principles 27. All revenues shall be recognized in the accounting period to which they relate. Also all expenditure shall be accounted for in the year to which they relate. Conservatism 28. All the expected expenditure shall be provided but the revenues for which there is any doubt shall not be included. Full Disclosure 29. Any information which is likely to influence the judgment and decision of the readers of the financial reports shall be disclosed by the way of note to the financial statements. Inventory / Stock Valuation 30 At the year end the closing stock of goods and material shall be valued at lower of the cost or the net realizable value. Valuation of gifted Assets / Materials 31. All goods received as donation or gift in-kind valuing more than Kyat 500,000 ( Kyat Five Hundred Thousand Only ) shall be recorded at the value indicated in the shipment documents at the first instance. In case where no shipment documents are available it shall be recorded at a value approved by the Procurement and Disposal Committee. 6 CHAPTER 4 CHART OF ACCOUNT Chart of Account 32. Chart of Account (CAO) is a list of accounts that is used as a primary reference for tracking and categorizing the financial transactions based on its nature. 33. In order to ensure consistency the same Chart of Account as the codes should be used by NHQ and the branches. 34. Standard chart of account is designed to:(a) Classify the type of accounting transactions . (b) Meet the accounting and reporting requirements of generally accepted accounting principles. (c) Provide meaningful reports for internal and external stakeholders. 35. Primarily the accounts shall be classified according to the following groups for the purpose of preparing the financial statements. The classifications mentioned below are only indicative and can be amended as per need. Assets Funds & Liabilities Fixed Assets Owned Funds 1. Land 1. Corpus / Capital 2. Building 2. Reserve 3. Warehouses 3. Surpluses 4. Motor 4. Designated funds Vehicles 5. Earmarked Funds 5. Office Equipments 6. Furniture 7. Computer hardware 8. Software 9. Electrical Fittings 10. Books 11. Other equipments 12. Capital work in progress Investments: Liabilities : 1. Stocks & 1. Advances for Shares projects 2. Fixed 2. Outstanding deposits expenses 3. Treasury 3. Earnest money papers deposits 4. Creditors 5. Other payables Current Assets 1. Cash in hand 2. Balance at bank 3. Short term deposits Income 1. Local Donations 2. International Donations 3. Interest 4. Membership fee 5. Gains on disposal of assets 6. Other income Expenses 1. Relief expenses 2. Human resources - Salary - Benefits - Training 3. Office expenses 4. Depreciation 5. Loss on dis- posal of assets 7 4. Inventory / stock 5. Loans, advances & Prepayments 6. Receivables 36. To record the transactions appropriately, a comprehensive Chart of Account shall be prepared by Finance Division. Account Codes for the computer accounting system 37. The formal code for any revenue & expense account shall have four elements: (a) Account Code : Account Code is the Account number which identify the account as income, expenditure, asset or liability (b) Project Code / Segment Code : Project code is an identification of the various programs. Each program shall have a project code, including the core expenses. (c) Activity Code : Activity code is in principle a code identifying activities for the various programs. (d) Donor Code : The donor code is used where donors require specific reports for their contribution. General donor code can be used to identify the general funds. Responsibility for indicating Account Codes 38. Primarily the department requesting the disbursal of funds or receiving the earmarked funds shall indicate all codes on the source documents. In case any clarification is needed the Head of Finance shall be the final authority to record the transaction in line with the accounting policy of Myanmar Red Cross Society. 8 CHAPTER 5 DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY 39. The Executive Committee may delegate to the Executive Committee members and other senior officials of the Society financial powers as follows for the effective implementation of these regulations. SN 1 Particulars Pay & Allowances ▲ Executive Director Honorary Secretary President Executive Committee Full - Full - Full - Full - 2 Local Travel (including air travel) ▲ 3 Foreign Travel - - Full - 4 Plans/Budget for Programmes, World RC Day, Central Council Meeting, Outstanding RCV Meeting, etc. - - - Full 5 Disbursement approval for World RC Day, outstanding RCV Meeting, CC Meeting, etc Up to K 2,000,000 Up to K 4,000,000 Full - 6 Disbursements for Emergency Expenses for health and disaster Up to K 2,000,000 Up to K 4,000,000 Full - 7 Programme Expenses Disbursements (Excluding emergency relief) Up to K 2,000,000 Up to K 4,000,000 Full Full 8 Office Expenses Full - Full - 9 Expenses paid in Foreign Currency from MRCS fund Up to USD 1,000 Up to USD 2,000 Full - 10 Investment (Including Generation Activities) - - Full Full 11 Capital Expenditure Procurement of relief and other goods (As defined in Procurement Procedure) USD 1,000 USD 2,000 Full - 12 Consultancy Engagements Up to K 1,000,000 Full - Notes:▲ ▲ Income Up to K 500,000 Authorization of the expenses shall be obtained from the first authority. The second authority can be exercised only when the first authority level is not available for approval. 9 CHAPTER 6 BUDGET 40. A budget is a statement of the anticipated income and expenditures for a given period, established on the basis of the plan of action and an estimation of the respective costs. 41. It is mandatory that the operational budget is approved by the Central Council in accordance with the provisions of these regulations before the commencement of the financial year. 42. In exigency where for reasons beyond control the operational budget has not been approved by the Central Council, the President shall approve an interim operational plan and the financial operational budget proposal submitted by the Executive Director for a maximum period of three months. 43. The Society's funds shall be expended on the basis of an approved budget and every expenditure whether core cost, project cost, program cost or operational cost must have a formally approved budget. 44. The budget shall be prepared in three parts: (a) Income ( 1 ) Expected Income for general core activities ( 2 ) Expected program receipts. (b) Expenditure ( 1 ) Expected (core) expenditure ( 2 ) Expected Project-wise Program expenditure (c) Capital expenditure Responsibility for Budget preparation Budget Committee. 45. Budget preparation is the responsibility of the Budget Committee which shall be formed by the Executive Committee and chaired by the Treasurer and to which all the departmental heads will be the members and the Executive Director will act as the Vice Chairperson. 46. The Head of Finance will act as the Secretary – coordinator to the Budget Committee. 47. The budget shall reflect the strategy of Myanmar Red Cross Society. Following the planning sessions and annual work plans of the divisions, the Budget Committee shall agree on broad budget guidelines and critical budget assumptions for budget preparation by all the divisions. The guidelines will cover all process of budgeting including a timetable. 48. The Head of Finance shall provide professional guidance and necessary financial information to all departmental heads as is necessary for preparing the budget for the coming year. 49 The Budget Committee shall be responsible for:(a) Issuing guidelines for preparation of annual budget. (b) Checking and consolidating departmental budgets into a Master Budget which shall be prepared by Head of Finance. (The heads of departments have overall responsibilities for ensuring that the departmental budgets are produced and submitted to the Head of Finance in accordance with agreed timetables.) 10 (c) Submitting the budget to the Executive Committee for approval. (d) Revising the budget whenever necessary. 50. Heads of Divisions shall be responsible to draw the budget i.e. the income & expenditure for all program activities in their respective divisions. Thereafter each divisional head shall submit the budget to Head of Finance who will be responsible to prepare the consolidated budget ( Master Budget ) to give an overall view of the budgeted financial plan. Steps for preparation of Annual Budget 51. The Society shall prepare an annual work plan for every division and for each of the continuing program. The yearly plans and activities shall be subdivided in monthly activities and budgets. 52. Each division shall prepare the budget in three parts: (a) Income i.e. expected program receipts. (b) Expenditure i.e. Project-wise Program expenditure (c) Capital expenditure 53. Budget shall be prepared under the guidelines of the Budget Committee. With regard to revenue income, the support which will be received from donors shall be negotiated with the donors. 54. The revenue income and expenditure codes in the budget shall be the same as in the existing Chart of Account. 55. All budgets should be supported with a commentary and working papers that will assist in explaining the basis upon which computations were arrived at. 56. The Budget Committee shall submit the proposed budget to the Executive Committee. The Executive Committee shall examine the proposed budget and make a decision on it and submit it to the nearest Central Council meeting for approval. 57. The Central Council shall then examine the proposed budget and make a decision. Budget Revisions 58. If it is considered necessary during the course of the year to revise the budget, for example, to cover unforeseen costs, over-expenditure or re-appropriate funds from one budget to another, the following procedures must be followed: (a) Heads of Divisions should write through the Head of Finance to the Budget Committee formally requesting a budget revision. (b) Requests for revisions should provide details of the accounts for which revisions are requested, reasons for the revisions, the original budgeted amount and proposed revised amount. Prescribed format should be used to reappropriate the budget item and must be approved by the Budget Committee. (c) Approval of the revised budget by the Executive Committee and the Central Council must be obtained. 11 (d) If the revisions are approved by the Central Council, the Head of Finance will inform the Heads of Divisions concerned of the alterations that have been made to the budget to incorporate the approved revision. Funding Budgets 59. The budget of Myanmar Red Cross Society shall be financed by membership fees, grants and financial assistance from Red Cross Movement Partners, public and private institutions, private individuals and government organizations, income derived from investments and fundraising, and any other funds to which Myanmar Red Cross Society become entitled. Budgetary Control 60. The Head of Finance is responsible for preparing the "Monthly Appropriation Account" for each division showing actual expenditure against budgeted expenditure. 61. The Head of Finance shall by every 7th of the next month send the divisional operating statements to the divisional heads asking each one to examine the results, confirm them and prepare explanations on the variance and the action to rectify the situation. 62. Each divisional head is responsible for preparing detailed analysis of the variations from the budget. Each divisional head is required to examine the details on the operating statement to satisfy him that his division has been charged correctly. If there are any disagreements, these should be sorted out with the Head of Finance immediately. 63 When the divisional head is satisfied that the charges have been raised correctly, he examines the reasons behind the variations from the budget, assesses their long-term effect on future expenditure and whenever necessary decides on the remedial action. The divisional head writes his report on the causes and effects of the variations and his recommended action to the Head of Finance. Divisional heads must submit their explanations on positive and negative variances to the Head of Finance within one week of the receipt of the operating statement. 64. Upon receiving the divisional explanations on variations, the Head of Finance will examine and summarize them on monthly Operating Statement to highlight: (a) Actual results against budgeted results; (b) Variances, their causes and effect; (c) Decisions to be taken to remedy the situation. 65. The monthly operating statement is prepared by the Head of Finance and sent to the Executive Director by the 15th day of the following month. A copy is also sent to each divisional head. 66. The Executive Director is responsible for examining the actual results against the budgeted results and report to the Executive Committee on monthly basis. The Executive Director also takes remedial action, if necessary, in the light of the explanation given by the heads of divisions. 67. The Executive Committee shall prescribe the necessary procedures and instructions for budget preparation, applying for supplementary grants and re-appropriation. 12 CHAPTER 7 CASH AND BANK MANAGEMENT Cash Management 68. In managing Cash and Bank the followings guidelines should be adhered to:(a) The Head of Finance shall have the overall responsibility for cash and bank management. (b) The cash limit shall be fixed by the Executive Committee upon the recommendation of the Head of Finance. (c) The Cashier shall be responsible for receiving all the money and deposit the receipts into bank, and cash payments against approved vouchers and supporting bills and invoices. (d) The cash should be kept in a safe having two keys and one of the keys shall be with the Head of Finance. (e) The cash should be adequately insured against all risks. (f) The cash should be taken to the bank and vice versa in office vehicle with appropriate security commensurate with the amount involved. (g) Losses of keys of safe shall be reported in writing to Head of Finance who report immediately to the Executive Director. (h) At the end of the day the Cashier shall reconcile the closing balance of cash in hand and make certificate of cash denominations. The Cashier should ensure that the cash in hand agrees with the balance of the Cash Book maintained by Finance Officer. (i) The Head of Finance or anybody delegated by the Head of Finance shall verify the cash balance at least once a month and also conduct surprise cash checks. The verification report should be signed by the official making the verification. (j) Cash losses ( if any ) shall immediately be reported to the Head of Finance and the Executive Director. The Executive Director shall take necessary action for the loss in accordance with the provisions mentioned in paragraph 250 of these Regulations. will Bank Management 69. All bank accounts shall be opened in the name of the Society with banks authorized by the Executive Committee. Preference should be given to government banks wherever possible. 70. In case, the organization financing a programme or a project requests to open a separate new bank account for the programme or project, the Head of Finance should look into the case and submit to the Executive Committee. 71. A new bank account can be opened only upon a resolution passed by the Executive Committee in this respect. The Executive Director is authorized to forward the resolution and to make application to the bank for opening new bank account. 13 72. Closing of a bank account should be made only upon the resolution of the Executive Committee. 73. Cheque and Bank Payment Voucher shall be jointly signed by one of the two persons entrusted by the Executive Committee for this purpose and the Honorary Treasurer. When the Honorary Treasurer is unable to sign the cheque, it should be signed by two persons who are authorized to do so by the Executive Committee. Safety and Control of Bank Documents 74. documents. The following procedures should be observed for the safety and control of bank (a) All communications relating to bank operations shall be kept securely in a file maintained by Finance Division for the purpose. (b) A register shall be maintained to keep the records of the opening and closing of bank accounts and cheque books received from the bank. (c) When a cheque book is issued to the Cashier for preparing cheques it must be in serial number. The Cashier will acknowledge receipt of the cheque book in the register. (d) All unused cheques and cheque books shall be kept in a safe. (e) The cheque counterfoil shall be retained as record and the signatory on the cheque should initial it for record. (f) Cancelled cheques shall be attached with the counterfoil and retained as such. Month End Procedures 75. At the end of the month, a bank statement shall be obtained from the bank for each bank account and a reconciliation statement shall be prepared for the month latest by the 7th of every month..The Monthly Bank Reconciliation Statement shall be checked and signed by the Head of Finance, and submitted to the Executive Committee. 76. The Bank Reconciliation statement shall contain the following details:(a) Credits recorded in bank statement but not entered in the Cash Book. (b) Deposits recorded in the Cash Book but not credited in the bank statement. (c) The cheques issued and recorded in the Cash Book but not debited by bank. (d) The debits recorded in bank statement but not recorded in the Cash Book. 77. The official reconciling the bank accounts should also investigate the appropriateness of each of the above details and pass the accounting entries upon the approval of the Head of Finance. 78. Any cheque dishonoured by bank should be brought to the notice of Head of Finance who shall take appropriate action to look into the causes for such dishonour and for informing the payee. 79. In case any cheque issued is not presented to bank for payment by the payee within 30 days of its issue, the fact should be brought to the notice of the Head of Finance for investigation by him. After three months, the cheque issued should be recorded in stale cheque account as unclaimed by appropriate journal entry. 14 CHAPTER 8 ACCOUNTING FOR INCOME Type of Income 80. The Executive Director has overall responsibility and the Head of Finance has functional responsibility for ensuring that all revenue due is collected and properly accounted for in accordance with the procedures laid down in these Regulations. 81. account:- The income can be categorized and accounted for under the following sub-heads of (a) Rental income arising on letting office space or land; (b) Interest income arising on fixed term deposits and savings bank deposits; (c) Membership fees; (d) Service charges for use of assets and facilities by other institution; (e) Sale of scrap and waste materials; (f) Disposal of fixed assets; (g) Grants and Donations; (h) Sale of products and services; (i) Other Income. Accounting Routines 82. The following accounting procedures should be observed:(a) An official receipt shall be issued for all amount received by the Society. (b) All receipt books and receipts should be pre-printed and serially numbered. The receipt books and receipts should be issued and used in serial number. (c) Receipt should be written with double carbon process in three copies. The original shall be in white colour and should be given to the payer. The second copy shall be in red colour and marked as accounts copy to be attached to the receipt voucher. The third copy shall be in green colour and should be kept in the receipt book. (d) The unused receipts and blank receipt books should be kept in safe. (e) Only the Cashier shall issue the receipts. The receipts shall be countersigned by a Finance Officer. (f) A receipt issued in error should be cancelled and all three copies must be attached together and kept securely in the receipt book. (g) No duplicate receipt shall be issued. (h) The receipts for cheques / banks drafts etc. shall clearly mention that the receipt is subject to realization. (i) All money received during the course of day shall be deposited immediately into the bank. Money received cannot be used directly to meet any payment. 15 (j) While receiving the cheques the Cashier must ensure that:(1) It is not post dated (2) It is signed (3) The figures and words agree. (k) The receipt voucher shall contain other supporting documents such as letter from the payee, the copy of invoice against which the payment is received. (l) The donation / charity boxes shall be opened in the presence of Head of Finance, Administration Head and Fundraising Head or the Executive Director. The amount should be certified by the above-mentioned officials before it is accepted by the cashier. (m ) There shall be maintained a register to record the receipt of printed receipt books, issue of receipt books to the cashier for use and the stock of unused receipt books. Accounting of Revenue Income: General Donations 83. basis. The donations and collections from the donation boxes shall be accounted for on cash Earmarked Donations 84. If donations are specifically earmarked for specific purpose, such donation shall be credited to the respective earmarked fund. The programme manager / project manager having the obligation to use this fund should be informed. Rent 85. The Head of Administration must inform the Head of Finance every month to raise an invoice on the lessee at the rates agreed for rent and other services. The invoice shall be raised in three copies. The original shall be sent to the lessee, second copy shall be sent to the Head of Administration and the third copy shall be kept by Finance Division. Investments 86. Income from fixed deposits with bank and other financial institutions at the predetermined rates shall be accounted for on accrual basis. The amount received from such investments shall be checked for accuracy. 87. At every quarter end, the Investment account shall be reconciled and a report thereto shall be submitted to the Executive Committee. Sale of Goods 88. With regard to sale of goods, the following procedures should be followed: (a) The person in charge shall raise the invoice in triplicate for any sale of goods at the rates fixed by the management. The invoice shall be pre-numbered and the original invoice shall be given to the customer. The duplicate shall be forwarded to the accountant. The third copy shall be retained by the shop/stores department. (b) The goods shall be delivered to the customer upon presentation of cash receipt issued by the cashier. The cash receipt shall be stamped "Goods Delivered" after the goods are delivered. 16 (c) In case the goods are sold on credit basis the stores officer should ensure that there is proper authorization to sell on credit basis. Sale of Scrap/ Waste materials 89. With regard to sale proceedings of scrap and waste materials, the following procedures should be adhered to:(a) The sale of general scrap or waste material should be done through a three member committee formed by the Procurement and Disposal Committee. (b) The proposal for sale of any scrap material shall be submitted to the Procurement and Disposal Committee for approval. This does not cover the sale of any fixed asset, the procedure relating to which is covered under the chapter on management of fixed assets. (c) The sale would be conducted by inviting sealed tenders/ public auction if the floor price is above K 500,000 ( Kyat Five Hundred Thousand Only ). (d) No sale of scrap shall be done without the final approval of the Procurement and Disposal Committee. Monthly Account Control and Reconciliations 90. At the end of each month, the Head of Finance shall make the monthly account control and reconciliation in accordance with the following procedures:(a) Prepare a debtors' schedule which should be ready by the seventh working day following the end of the month; (b) Ensure that the total as per the debtors' schedule agrees with the balance on the debtors' control account in the general ledger; (c) Check that a reconciliation of the debtors' schedule to the balance in the general ledger is performed by Finance Officer; (d) Perform ageing analysis of the debtors and take steps for recovery where the credit period has exceeded. The report must be forwarded to the Executive Director for comment and the Sales Section for information and necessary action. (e) Credit/ Debit notes 91. Credit / Debit notes are issued to customers when goods are faulty or goods and / or services have been incorrectly priced or priced for a wrong quantity. 92. Credit/ Debit Notes can only be raised with the approval of the Head of Finance. If adjustment involves a cash refund, then payment should be made according to the cash payment procedures. If adjustment requires a book entry to the customer's account, then an entry is posted to debtor’s ledger using a copy of Credit Note. A journal voucher should be raised by Finance Officer to post the Credit Note to the general ledger. 93. The Credit/ Debit Note shall be issued in triplicate. The original shall be given to the customer, the second copy shall be forwarded to the Head of Finance and the third copy shall be retained by store- in- charge. 17 CHAPTER 9 EXPENDITURE / PAYMENT ACCOUNTING 94. The Head of Finance shall be responsible to ensure that the expenditure incurred from the funds of the Society is governed by the following essential conditions: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) There is an approved budget for the expenditure. The expenditure incurred conforms with the relevant financial rules and regulations. There is sanction or approval by a competent authority. The expenditure is supported by adequate bills, vouchers and receipt. Expenses are recorded to the correct classification as per the Chart of Account. Standards of Financial Propriety 95. Every Red Cross executive, staff or member/volunteer should comply with the general principles, which have been recognized as standards of financial propriety. (a) The expenditure should not be prima facie more than the occasion demands. (b) Every Red Cross staff, volunteer and executive is expected to exercise the same vigilance in respect of expenditure incurred from the Society's funds as a person of ordinary prudence would exercise in respect of his/her own money. (c) No executive or authority should exercise its powers of sanctioning expenditure to pass an order which will be directly or indirectly to its own advantage. (d) The Society's funds should not be utilized for the benefit of a particular person or group of persons. (e) The amount of allowances, such as traveling allowances, should be so regulated that the allowances are not on the whole sources of profit to the recipients. Preparation of Claim Bill 96. expenses:- The following basic principles should be fulfilled when preparing claim bills for (a) Prescribed forms should be used as far as possible. (b) Entries and signatures should be in ink or ball pen. Pencil and erasable ink should not be used. (c) The total amount claimed should be written both in figures and words. (d) Each and every correction and amendment of entries should be initialed by the person making the correction and amendment. Erasures and over-writings must be avoided. (e) The claimant shall put a dated signature on every claim bill. Rubber stamp shall not be used in lieu of signature. If a cross mark ( x ) or his/her thumb impression is taken due to illiteracy of the recipient, it should be certified by a reliable and trustworthy person. 18 (f) Claim bills should be addressed to the Society and not to any individual. (g) All sub-vouchers attached to the claim bill should be signed by the claimant and should also be cancelled in such a manner that they cannot be subsequently used or stamped " cancelled " (h) Although the person who claims the bill is primarily responsible for the arithmetical accuracy of the claim, the disbursing officer should also be responsible. 97. With regard to pay, honorarium and fees, the following entitlements should be prescribed by the Executive Committee. (a) Entitlement of pay to the staff appointed for full time service of the society. (b) Entitlements of honorarium granted from the fund of the society and fees granted from other funds which are not the funds of the society to the staff with the permission of Executive committee for carrying out any special duty other than that of the official duty. (c) Entitlements of honorarium and compensatory allowance granted from the fund of the Society and fees granted from other funds which is not the fund of the Society for carrying out the activities of the Myanmar Red Cross Society either full time or occasionally by the volunteer. Pay, Honorarium and Fees 98. employee:- The following basic conditions shall be fulfilled before pay bill is prepared for an (a) (b) (c) (d) 99. The post shall be duly sanctioned. The employee shall be substantively appointed to the sanctioned post. The employee takes charge of his duties. There is a provision of funds. The Following procedures shall be followed when drawing pay bills of employees: (a) Pay bill shall be prepared in the prescribed format. (b) Appointment Orders for new appointees, Duty List, Increment Certificates, Absentee Statements, Office Orders and other relevant documents shall be attached to the pay bill. (c) Average Pay Statement shall be attached for those who are enjoying leave. (d) For deductions from pay, e.g. recoveries of overpayment of salary and other deductions for any other reasons, full details should be mentioned against the name of the staff concerned. When a name is included in the pay bill for the first time, it should be supported by a last pay certificate if the employee was transferred from another post. If the employee was newly appointed a copy of appointment order, duty report and a health certificate should be attached. (e) (f) Only one original copy of pay bill should be prepared and signed in full with date by the drawing officer. 19 100. The due date for disbursement of pay is the last working day of the month. 101. Pay bill shall be prepared by the respective divisions/projects and validated by Finance Division before disbursement. Finance Division shall disburse the pay and allowances of employees. 102. In case the employee cannot draw his/her pay personally, an authorized person shall draw the pay if a letter of authorization endorsed by the Head of Division is produced and approved by the Head of Finance Division. 103. Pay and allowances not drawn on due date shall be treated as undisbursed. Undisbursed pay not claimed within one year after due date shall not be disbursed. 104. procedures:- Pay of a deceased employee shall be disbursed in accordance with the following (a) (b) (c) (d) 105. The following deductions can be made from the pay of an employee: (a) (b) (c) (d) 106. Pay shall be calculated up to the date of death. The claimant shall be investigated before payment. Indemnity bond shall be signed before payment. In any case of doubt, payment should be made only to the person producing valid documents. Recoveries of overpayments. Recoveries of overdue advances. Social Security subscriptions. Any other deduction approved by the Executive Committee. Employees are entitled to salary from one source only. Travelling Allowance 107. Travelling allowance shall be granted under the following basic principles. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) The journey is in the interest of the Society. The journey is authorized by a competent authority. The journey is actually performed by the claimant. There is budget provision. The journey as whole shall not be a source of profit for the recipient. The amounts claimed as expenses are actually incurred by the claimant. 108. The rates of travelling allowance admissible for staff such as means of conveyance, per diem (daily allowance) and accommodation shall be prescribed by the Executive Committee. 109. Allowances for domestic travel such as mode and class of transport, per diem, etc. shall be prescribed by the Executive Committee. 110. Per diem is a compensation granted to cover the expenses in terms of meals and any out of pocket expenses incurred while performing duties outside the normal workplace. When reckoning per diem, a day means a day of 24 hours beginning and ending at midnight. If the absence from headquarters exceeds twelve hours per diem is entitled at full rate and if the absence is less than 12 hours per diem is entitled at half rate. 111. Per diem for travels undertaken on account of the activities of bilateral donors shall be governed and paid as per the respective rules of bilateral donors. 20 112. Public transport such as rail and bus shall be utilised as much as possible. For air transport the lowest priced carrier shall be utilised. 113. Allowance for foreign travel such as outfit allowance, per diem, mode and class of transport, etc, shall be prescribed by the Executive Committee. 114. When claiming travelling allowance the actual cost for transport, the actual cost for overnight accommodation, and per diem at the approved rate shall be reimbursed. 115. The following points shall be followed when preparing travelling allowance bills:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) The prescribed format for travelling allowance shall be used. Diaries shall be attached with the travelling allowance bill. Time of departure and arrival shall be mentioned together with the date. Purpose of journey shall be mentioned fully. Tour programme, movement order and other relevant documents shall be attached with the bill. Original tickets for bus, train, ship and air shall be attached with the bill. For foreign travels relevant deputation orders, invitation letters, flight schedule and other information regarding travel, per diem, meal and accommodation shall be attached with the bill. Original hotel bill/invoice and receipt shall be attached with the bill. Original freight receipt/ cash receipt for luggage shall be attached with the bill. When receipts or invoices are not given by the recipient, a Certificate of Payment form shall be used and signed by the recipient. When Certificate of Payment form cannot be utilized a Certificate of Expenditure shall be used which shall be checked and approved by the Head of Division. Advance of travelling allowance shall be adjusted in the bill when claiming travelling allowance for the journey. 116. The Executive Committee may prescribe standard cost for domestic travels for internal management of travelling expenses. 117. officers:- Travelling allowance bills must be countersigned by the following officials as controlling (a) ( b) (c) (d) Division/Project staff (except Head of Divisions ) Heads of Divisions Executive Director Executive Committee members Heads of Divisions Executive Director Honorary Secretary President 118. Once the travelling allowance bill is countersigned, it means that the whole claim is approved. The controlling officer should, therefore, countersign the bill only after the bill has been scrutinized to his satisfaction. 119. Travelling allowance bills countersigned by a competent authority shall be checked and validated by Finance Division before disbursement. 120. All payments of travelling allowance shall be acknowledged by the recipient. Expenses 121. When expenses are claimed, the following procedures shall be observed: (a) The purpose of incurring the expenses shall be mentioned. 21 (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) Invoices and receipts signed by supplier/vendor should be attached to the bill as supporting documents for the expenses. Supporting documents shall be classified according to the chart of account. If supporting documents are more than one page (such as purchase of fuel, telegraphic charges, postage, etc.) a summary statement shall be prepared and the total shall be claimed. The claimant shall sign on all pages including the last page. For meal and meeting expenses the bill should be documented with a statement showing the date and the number of participants in the party/ the number of attendees at the meeting. For purchase of machinery and office equipment the name of manufacturer, type, model, serial number, etc. shall be mentioned. Every source document shall mention the type of expense, the date, amount, the recipient's name, address and signature. All source documents including invoices, receipts, contracts, etc. shall be stapled securely. Alterations and erasures of the source documents shall not be accepted. In case an expense incurred is for more than one person such as bus fares and accommodations, only the person who makes the payment and not the other person shall make a claim for reimbursement of the payment. Correction of errors by over-writings, insertions, and deletions with correction fluid are not allowed. If correction is unavoidably needed to be made the following instructions should be followed:(1) The errors should be neatly struck off with a line in red ink and the correct figures and words should be written. (2) Each and every correction should be attested with a dated signature of the claimant. (j) If the claim bill contains too many errors, corrections and deletions, a new claim bill shall be prepared. Training and Workshop 122. Training and workshop expense include travelling expenses, per diem, accommodation, stationery, hand-outs, venue charges, honoraria and fees. 123. A standard cost should be used for management of training and workshop expenses. 124. Staff of the Society receiving salary shall not be paid honorarium for performing as facilitator or resource person. 125. expenses: The following procedures shall be observed for the claims of training and workshop (a) (b) (c) (d) The names and titles of participants and facilitators shall be approved by the Executive Director. Distribution list of stationery shall be signed by the participants/ recipients. Participants residing at the town/city where the activity is held are not entitled to per diem. For participants' accommodation and hall rental charges, bids or tenders should be called for from hotel and landlords and selection should be made after making comparative analysis. 22 (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) Accommodation charges and venue charges shall be supported by an official receipt from the landlord. Accommodation charges shall be supported by an invoice mentioning the names of participants and facilitators and by an official receipt from the hotel. Expenses not related to the training and workshop shall not be charged to the activity. Expense for opening and closing ceremony, dinner, etc. shall be supported by the number and list of persons attending the function. Participants from the same township or locality travelling together by the same conveyance should share the same taxi for the journey to and from airport / rail station / bus terminal. Payment for return journey of participants shall be made only upon submission of original return tickets for the return journey. A photocopy of the ticket for the return journey certified by the person in charge of the training/workshop or Head of Division shall be obtained and accepted as supporting document. Transport and Handling 126. Transport and handling charges includes expenses for transport of goods, clearing charges, handling charges, dock dues, warehousing expenses, loading / unloading charges, etc. 127. Selection of transport and clearing service provider shall be by competitive bidding as per procurement procedures. 128. Claims for transport of goods shall be supported by an acknowledgement of receipt of goods by the consignee / a responsible official of the Red Cross branch. Repair and Maintenance 129. claimed:- The following procedures shall be observed when repair and maintenance charges are (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Prior approval must be obtained for repair and maintenance works. If the estimate cost of repair is more than K 500,000( Kyat Five Hundred Thousand only ) the Executive Director shall form a Supervisory Committee to supervise the repair and maintenance work with the approval of Building Committee of the Society. Expense for repairs shall be only for those necessitated by fair wear and tear and by accidents. For repairs necessitated by negligence or carelessness of an employee, the liability of the employee shall be determined and payment should be made only for those items not included in the liability of the employee. Payment shall be made only on the basis of verification of performance of work by the supervising committee. Other expenses 130. All other expenses shall be paid on the basis of claim bills / invoices duly authorised by the responsible person. Purchase of Goods 131. Purchase of goods shall be in accordance with the procurement procedures prescribed by the Procurement and Disposal Committee 23 132. Claims for payment shall be supported by the following documents: (a) Purchase Requisition (b) Tender/quotation/bid (c) Comparative bid analysis (d) Purchase Order / Contract (e) Invoice (d) Goods Receipt Note or certificate for receipt of the goods. Unvalidated Vouchers 133. Payment vouchers without supporting documents or insufficient supporting documents, and vouchers which require explanations/remarks and not validated by Finance Division or Internal Audit shall be returned to the claimant. The claimant shall provide written explanations, details and supporting documents and resubmitted to Finance Division or Internal Audit as the case may be. Certificate of Payment / Expenditure 134. When a receipt cannot be obtained from the recipient (such as taxi hire charge, bus fare, etc.) the following procedures shall be observed:(a) (b) (c) A prescribed Certificate of Payment shall be utilized and signed by the recipient. In case the signature of the recipient cannot be obtained, a prescribed Certificate of Expenditure shall be utilized. The Certificate of Expenditure shall be signed by the payer and checked and approved by the Head of Division concerned. 135. Certificate of Expenditure shall be used only for expenses not exceeding Kyat 10,000 (Kyat Ten Thousand only). For expenses exceeding Kyat 10,000 (Kyat Ten Thousand only) a Certificate of Payment shall be utilized. Payment procedures 136. The following main principles shall be fulfilled when payment is made for expenses. (a) (b) (c) (d) No payment shall be made without a written authorization by a responsible person to whom authorization for expenditure has been delegated. Payment shall be made only if there is sufficient balance of budget at the time the payment is authorized. When there is partial delivery of goods or when delivery is short shipped, payment shall be made only for goods actually received as per Goods Received Note. All Bills / Invoices shall be stamped "Paid" after payment is made in order to make a second payment impossible. Payment for Purchase of Goods 137. Upon safe receipt of goods and an invoice from supplier, the Procurement Officer in charge shall forward the payment request form to the goods requisitioning department for verification and onward submission to the Head of Finance Division. The payment request form shall be accompanied by the following documents wherever applicable: (a) Original invoice. (b) Goods received note ( Finance copy ). 24 (c) (d) Goods requisition form. Copy of purchase order with all documents such as comparative bid analysis, etc. 138. Upon verification and due check, the requisitioning department head shall forward the invoice to the Head of Finance for final checking and release of payment. 139. Finance Division will release the payment after checking the documents, the codes to be charged, and the amount payable. 140. The payment shall be sent to supplier directly with a payment advice indicating the deductions made and the reasons therefore. 141. No payment to any supplier for supply of goods exceeding K 500,000 (Kyat Five Hundred Thousand only) shall be made in cash. Payments exceeding K 500,000 (Kyat Five Hundred Thousand only) shall made by cheque only. Advance to supplier 142. No advances to the suppliers should be released for supply of goods. However, if it is inevitable, the advances shall be released as per the terms and conditions of the agreement / purchase order subject to submission of Bank guarantee from a reputed bank for equivalent amount. Accounting routines 143. Upon release of the payment, the financial transaction shall be recorded in books simultaneously and the documents shall be filed securely in the payment file which shall be kept in chronological order. 25 CHAPTER 10 ADVANCES 144. The following advances can be disbursed to facilitate implementation of activities:(a) (b) Working Advance Staff Advance Working Advance 145. training, etc. Working Advance is granted for programme-related activities such as workshop, 146. Request for Working Advance shall be submitted 14 days before the commencement of the activity .The request shall contain a detailed estimate of the expense items. In preparing the estimates for expenses, it should not be merely a reproduction of budgeted estimates. The detailed estimates should be prepared by taking into consideration the kinds, the quantity, the rate, and the amount of the materials to be actually purchased and the activity to be actually performed. Project code, activity code and account code shall also be mentioned in the request. 147. Standard cost shall be used for estimation of expenses. The following is a list of standard cost for a training activity :(a) Transport cost of facilitators and participants (b) Per diem for facilitators and participants (c) Accommodation for facilitators and participants (d) Training and IEC material (e) Stationery (f) Other expenses directly related to the training activity 148. Request for Working Advance shall be sent to Finance Division by the requesting division. Finance Division shall verify the request with the plan of action, the budget, and whether the expenses are in accordance with Financial Regulations, procedures and directives. 149. Working Advance shall be disbursed to the Head of Division or Project Coordinator/Manager. The Head of Division or Project Coordinator/Project Manager holding the advance shall be responsible and accountable for the advance. 150. Working Advance for minor activities and administrative activities shall be disbursed only if the advance requested is more than K 50,000 ( Kyat Fifty Thousand Only ) Settlement of Working Advance 151. All Working Advances shall be settled as soon as possible, within 30 days after disbursement or 15 days after completion of the activity. Unspent cash balance shall also be refunded to Finance Division immediately after the completion of the activity. 152. If the working advance is overspent, the overspent amount shall be reimbursed only after approval of the report by the Executive Committee. 153. All expense paid from Working Advance shall be supported by original vouchers / invoices and receipts. The expenditure should also conform with the approved request. If there is an overspending or underspending of more than 10% of the approved advance, a written explanation shall be put up with the report. 154. A narrative report for the activity performed should also accompany the settlement of Working Advance. 26 155. A new working advance shall not be disbursed until the previous advance is totally settled. Partial settlements shall not be accepted for disbursement of new working advance. Transfer of Working Advances to Branches 156. The necessary funds as per the Working Advance requirements verified by the Program / Project Managers at HQ and approved by the Executive Director upon the recommendation of the Head of Finance, shall be transferred to the branches. 157. Procedures for safe custody, disbursement and settlement of the Working Advances shall be prescribed by the Executive Committee. 158. The Branches shall submit the reports for Working Advances to the Head of Division (Program Manager / Project Manager) once a month and all original bills, invoices and supporting documents shall also be submitted along with the Bank Statements. 159. The Working Advance Report received from the Branches shall be first verified by the Head of Division (Program / Project Manager at HQ) and then on being satisfied about the utilization, shall submit it to the Head of Finance for validation and accounting the expenses against the Working Advance drawn by the branch. Staff Advances 160. Advance for travelling allowance can be claimed for travelling on Red Cross duty. The estimated travelling expense shall be disbursed as an advance of travelling allowance. 161. Claim for advance travelling allowance should be submitted to the Head of Division for approval who shall forward the same to the Head of Finance. Claims for advance travelling allowance shall be supported by tour programme, movement order, etc. Settlement of Advance Travelling Allowance 162. A claim bill for travelling allowance shall be submitted within 15 days after returning from the journey. Relevant documents including tour programme, movement order, original tickets/receipts for transport and accommodation shall be attached with the bill. The travelling allowance bill shall be submitted to the Head of Division. The Head of Division shall check and countersign the bill, and submit the bill to Finance Division for validation. 163. The Head of Finance shall have the claim checked for the documents annexed thereto and the amount claimed. 164. In case the amount claimed is less than the amount of advance, the employee shall refund the balance when submitting the claim. 165. If the travelling allowance advance is not settled within 30 days after returning from the journey, the advance shall be deducted from the salary, and no further advance shall be entertained. 166. The accounting routine will require adjustment of the advance to the actual expense account by way of journal entry which should be done once the claim is approved. Security Money 167. Security money for emergency situation including emergency relief and emergency health situation shall be kept by Finance Division. The amount of security money shall be fixed by the Executive Committee. 27 168. Committee. Payment can be made from security money with the approval of the Executive Loans to Staff 169. Loans to staff shall be governed by the Human Resource Policy approved by the Executive Committee. 28 Chapter 11 PROCUREMENT PROCEDURES Scope 170. Procurement means and includes purchases of goods and services for the Society. Purchase of goods includes purchase of relief supplies, office equipment, workshop and training materials, information, education and communication materials, care and support goods, etc. Purchase of services includes hiring of consultants, lease of property, transport of goods, construction of buildings, etc. 171. The Executive Committee shall form a Procurement and Disposal Committee to carry out all the procurement and disposal of goods and services and a Building Construction Committee to supervise the construction and maintenance works of buildings. Procurement and Disposal Committee 172. (a) Procurement and Disposal Committee of Myanmar Red Cross Society consisting of the following persons shall be formed : (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) Full time Executive Committee Member Executive Director Head of Finance Head of Administration Head of Requesting Division Other suitable personnel Head of Procurement Section ( Chairman ) ( Member ) ( Member ) ( Member ) ( Member ) ( Member ) ( Secretary ) (b) In the absence of the Head of Procurement Section the Head of Finance Division shall take the responsibility of the Secretary of Procurement and Disposal Committee. (c) The Procurement and Disposal Committee shall monitor whether the policies for procurement and disposal prescribed by the Executive Committee are followed by the Procurement Teams. (d) For procurement of goods with donors’ fund, the requirements of the donors shall be complied with in addition to the procurement procedures of Myanmar Red Cross Society. Building Committee 173. (a) The Building Committee of Myanmar Red Cross Society shall be formed with the following persons : (1) Executive Director ( Chairman ) (2) Head of Finance ( Member ) (3) Head of Administration ( Member ) (4) Other suitable personnel ( Member ) (5) Project Engineer ( Secretary ) (b) In the absence of Project Engineer the Head of Administration shall take the responsibility of the Secretary of the Building Committee. 29 (c) The Building Committee shall monitor whether the policies for construction and maintenance of buildings prescribed by the Executive Committee are followed by the construction and maintenance teams. (d) For construction and maintenance works funded by donors, the requirements of donors shall be complied with in addition to the procurement procedures of Myanmar Red Cross Society. Purchase Procedure 174. The user division shall initiate the request for purchase of the goods by filling the standard purchase requisition form with the following information: (a) particulars of goods required with technical specifications and design; (b) quantity required; (c) required delivery date; (d) the expenditure code to be charged i.e. the account code, project code, activity code and the donor code; (e) the purpose for which it is required; (f) signature and division requesting the purchase of the goods, and (g) date. 175. The purchase requisition shall be validated by the Head of Finance to ensure that there is sufficient budget provision for the purchase. 176. copies. The purchase requisition form shall be pre-numbered and shall be raised in three 177. Upon validation from Head of Finance and approval by the Executive Director, the user division shall forward the original and the duplicate copy to the Procurement and Disposal Committee and the triplicate copy shall be retained by the division. Authorization for approval 178. The Table below provides authorization levels which apply to purchase as well as the contracting of services including recurring expenses. Requisition value Procedure Supplier Authority Level No quotation Any one Head of user Division No quotation Any one Executive Director Level III ( up to K 5,000,000 ) At least 3 quotations Registered Supplier Level IV ( above K 5,000,000 ) Tender Open Level I ( up to K 500,000 ) Level II( up to K 2,000,000 ) Procurement Committee Procurement Committee 179. For purchases not exceeding K 500,000 ( Kyat Five Hundred Thousand Only ) the Head of Division may form a purchasing team comprising of persons from the Division that will undertake the actual purchase of the goods. 180. For purchases above K500,000 (Kyat Five Hundred Thousand Only) and not exceeding K 2,000,000 (Kyat Two Million Only) the Executive Director shall form a team comprising suitable persons that will undertake the actual purchase of the goods. 30 181. For purchases exceeding K 2,000,000 (Kyat Two Million Only) the Procurement and Disposal Committee shall form a Purchasing Committee. The Purchasing Committee shall be responsible for the calling of tender/bid, making a comparative bid analysis and selection of supplier, and receiving the goods. Registration of Suppliers 182. The Society shall keep a list of registered vendors which are shortlisted and approved for supply of goods and services. The list of registered vendors shall contain the following basis criteria: (a) (b) (c) The firm is registered with appropriate authorities as per local laws. The firm has a bank account. The firm is reputed, reliable and deals in goods that are likely to be procured. 183. The registration of suppliers shall be approved by the Procurement and Disposal Committee. The Procurement and Disposal Committee shall meet every six months to update the list of registered vendors for supply of goods. Procedure for consultancy engagements 184. The procedures enumerated above shall be adhered to for engagement of services of any professional consultant. However if it is deemed necessary to obtain the services requiring engagement of reputed individual professional consultant, the proposal shall be obtained from the consultant based on a Terms of Reference. The Terms of Reference shall include an implementation schedule and should clearly state the nature, timeliness, and measures of performance required, and may include standards for accomplishing work. 185. Prior approval must be obtained from the President for recruitment of any consultant. Tender Procedure 186. The procedures with regard to calling for tenders are as follows: (a) (b) (c) (d) 187. Publication in minimum two leading newspapers about the work required and tender terms and conditions at least 10 days in advance of sale of tenders. The submission of tenders with Earnest Money Deposit at 1/2% of the proposed contract price failing which the tender shall not be accepted. The tender document should mention about the time, date and place of the opening of tender. Tenders received shall be opened by the Procurement and Disposal Committee members at the time and date mentioned in the tender document. The Society shall not recognize tenders / bids / quotations in case of the following:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) It is not submitted within the prescribed time. It is not submitted in prescribed format. Earnest Money Deposit / Bank guarantee is not attached. The bid/tender submitted does not contain the signature and stamp of the bidder. Terms and conditions are attached by the person who submits the tender. 31 Selection of Supplier 188. The bids submitted by suppliers shall be analyzed using the Comparative Bid Analysis form. Purchase order should be placed only to supplier which has quoted the best appropriate quality goods with the lowest possible price. 189. Preference is to be given for procurement of goods manufactured locally and supplies readily available locally in the quality and quantity required at competitive prices. 190. Procurement and Disposal Committee shall record in writing the reasons for selection recommended by the Procurement team. International Procurement of Supplies 191. When supplies and materials are not readily available in the country in the quality and quantity required at competitive prices, the Procurement and Disposal Committee, with the approval of the Executive Committee, may contact neighbor National Red Cross Societies for procurement of supplies. Issue of Purchase Order 192. After selection of supplier in accordance with the above procedures the Head of Procurement Section shall submit the selection list to the Executive Committee for approval. When the approval is obtained, the Head of Procurement Section shall issue a Purchase Order to the approved supplier for supply of goods mentioning:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) 193. Purchase Order number and date. Particulars of goods ordered. Quantity. Price basis. Place of Delivery and packing of goods if any. Insurance / Risk. Time frame of delivery. Security deposit. The Purchase Order shall be raised in four copies and distributed as below: (a) (b) (c) (d) Original and duplicate copy of the purchase order should be issued to supplier. The duplicate copy of the purchase order must be signed and stamped by the supplier as a token of acceptance and must be given back to the buyer. The triplicate copy should be sent to Finance Division. The fourth copy shall be retained by Procurement Section as reference. 194. For purchase of Kyat 5,000,000 ( Kyat Five Million Only ) or above a purchase contract shall be signed with the selected supplier. The contract shall mention penalty for non-performance, terms of payment, and for international procurement the application of ICC INCOTERMS. 195. For consultancy engagements a service contract shall be signed with the contractor. Receipt of goods 196. When goods are received, the Purchasing Committee shall inspect and check the goods promptly and carefully as soon as they are delivered to ensure that they fully conform to the Purchase Order or Contract. The Stores Officer shall prepare a Goods Received Note (GRN) which shall have a pre-printed serial number. 32 197. It is the responsibility of the Purchasing Committee and Stores Officer / user division receiving the goods to ensure that: (a) (b) (c) Goods received agree with the delivery order delivered together with the goods; The goods appear undamaged and are received in good condition; In case goods are short or damaged, it should be mentioned in the GRN as well as delivery note of the supplier. Receipt of Supplier's Invoices 198. The supplier shall submit an Invoice to the Head of Procurement Section. Upon receiving the supplier's invoices, the procurement section will: (a) (b) (c) (d) extract the respective Purchase Order ( PO ) / Purchase Contract and Goods Receipt Note (GRN) from files and match them to the Invoice. Invoice number should be endorsed on the PO and the GRN. The GRN number, together with PO number, are endorsed on the invoice; compare the invoices with the appropriate PO and GRN to agree the quantity invoiced with the quantity actually ordered and received; compare the invoice price and payment terms with those indicated on the Purchase Order. If there is any disagreement the matter should be referred to and rectified with the supplier, and recompute the Invoice. 199. In case problems, such as loss, damage, wrong quality and wrong quantity arise upon delivery, the non-conforming goods should not be accepted and the vendor should be informed immediately. The following action can be taken for all non-conforming deliveries: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Reject the delivery or part of it. Return the goods. Request replacement or repair free of charge. Terminate the contract. Sign a new contract with the second-in-line vendor of the bidding process and collect penalty from the defaulting vendor. Settlement of the vendor's bill 200. On receipt of goods or services and suppliers' invoices, the Head of Procurement Section shall forward to the Head of Finance a request for release of payment to the supplier attaching therewith the following documents :(a) Original suppliers' Invoices (b) Finance copy of the Purchase Order (c) Goods Received Note (GRN) (d) Copy of the approved Purchase Requisition (e) The code numbers under which the purchase is to be charged 201. Normally no advance payment shall be made for procurement. All payments shall be made only upon delivery of the goods. If advance payment is necessary the Procurement and Disposal Committee shall recommend advance payment only if the advance payment does not present a financial risk to the Society. 202. Payment shall invariably be made by an account payee cheque. However, in circumstances where the purchase does not exceed Kyat 5,000,000 ( Kyat Five Million Only ) the 33 payment can be released by order cheque. If uncrossed cheque is requested in writing, the claimant should submit an Indemnity Bond. Payment for purchase of less than K 500,000 (Kyat Five Hundred Thousand Only) can be released in cash with the approval of the Executive Director. Emergency Procurement of Supplies 203. Procurement of supplies in emergency situations shall be in accordance with the directives of the Executive Committee. Standards of Conduct 204. conduct: All employees of the Society engaged in procurement shall observe the following code of (a) (b) (c) (d) Business will be conducted ethically in a manner above reproach and with total impartiality. Conflict between professional duty and personal interest should be avoided. Any gift, favour, entertainment, loan or anything of monetary value (except for inexpensive public relations gifts such as business diaries, calendars or pens) shall not be accepted or solicited. Bids shall not be solicited from, nor contracts awarded to, any business concern that is owned , controlled or actively influenced by any employee of the Society or an immediate relative to that employee. Documentation of Procurement 205. All procurement activities must be fully and transparently documented. A completed purchase must be supported with a fully referenced file. The procurement file should contain the following documents: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (d) (e) (f) (g) 206. Purchase Requisition. Company name and contact persons for vendors solicited. Copy of the invitation to bid or request for quotation. Original proposals / offers from vendors Comparative Bid Analysis and the selection of vendor and the price. Copy of Purchase Order /Purchase Contract. Copy of Invoice from vendor. Payment receipt. Other documents and correspondences related to the procurement. Documents regarding procurements shall be maintained by the Procurement Section. 34 Chapter 12 FIXED ASSETS ACCOUNTING 207. Fixed assets shall be purchased in accordance with the procurement policy and procurement procedures of the Society. 208. Expenditure on the purchase of all fixed assets as well as donated fixed assets received in-kind as gift or donation value more than Kyat 100,000 (Kyat One Hundred Thousand only) shall be capitalized. All cost incurred till bringing the asset to a usable condition shall be included in the cost of the asset. 209. Fixed asset received as donation shall be recorded at the value indicated in the shipment documents at the first instance. In case where no shipment documents are available it shall be recorded at a value approved by the Procurement and Disposal Committee. 210. All assets shall be given an identification number which shall be affixed to the asset. 211. The physical count of the fixed assets shall be done at least once a year in coordination with the Administration Division and any shortages shall be reported to the Executive Director who shall in turn inform the Executive Committee. 212. When there is a change of Head of Division, Project Coordinator/Manager or management personnel responsible for maintaining the assets, the assets shall be physically verified and shall form part of the hand-over process. 213. All the assets shall be adequately insured against all natural and human risks. 214. A fixed asset register shall be maintained by the Administration Division for all divisions. Heads of Divisions shall also maintain a fixed asset register for each division. The fixed asset register shall contain the following particulars:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Cost and date of purchase with invoice details. Location. Quantity and the make Estimated life. Rate of depreciation. Accumulated depreciation and written down value at a given date. Sale/Disposal of Fixed Assets 215. The procedures for sale and disposal of fixed assets are as follows:(a) The sale and disposal of assets shall be made by the Procurement and Disposal Committee. (b) Procurement and Disposal Committee shall report any sale or disposal of an asset to the Executive Committee. (c) Loss or gain on account of the disposal of fixed asset shall be charged to the income and expenditure account. Depreciation 216. Depreciation shall be charged on fixed assets at the end of each fiscal year. The depreciation rates and methods of depreciation shall be as prescribed by the government for tax law. 35 Chapter 13 INVESTMENTS 217. Investments shall be made to generate income for the Society. 218. All investments should preferably be made in bank deposits. Any long term investment (more than 12 months) shall be made after due approval from the Executive Committee. Before granting approval, the Executive Committee shall ensure availability of funds for investment. Financial experts should also be consulted before making significant investments. 219. decision: The following points should be considered carefully before making an investment (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Safety of the investment Liquidity Capital appreciation Yield or return Legal requirements 220. The stock and shares and investments in banks shall be valued at cost or net realizable value whichever is less. Sufficient provision for loss should be made in books if the market value of investment falls below the cost. 221. Funds received for programs and projects shall not be invested. 222. Income from investments shall be accounted for as credits under the account head "Specific Fund". 223. Investments should be monitored whether interests or dividends are being received on the due dates. The maturity date should also be kept tracked for reinvestments. 224. The Head of Finance shall provide the Executive Committee a statement of the investments made with details of rates of interest every three months. 36 Chapter 14 STORE PROCEDURES AND STOCK CONTROL 225. The Officer in charge of the Procurement Section or Warehouse in-charge has overall responsibility over stocks under his custody as defined in the following procedures. Procedure for Control of Stock 226. The followings are the procedures for stock control:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) The Store Officer receives all goods purchased into the store. The Store Officer examines the goods for any visible damage and in collaboration with the user division, ensures that the goods are of good quality and agree with the Purchase Order. On being satisfied with the physical condition of goods received, the Store Officer raises a Goods Received Note ( GRN ) as evidence of the receipt of goods and issues copies to supplier, the Procurement Section and the requesting division. The Store Officer then records receipts per the GRN on the bin cards. The Store Officer updates bin cards on every issue and receipt of the goods. Goods are issued from the Stores when the Store Officer receives a duly authorized Material Requisition & Issue Note ( MRIN ) from the requesting division. Each month a physical stock count of selected items is taken by the Store Officer; At the end of the year an annual stock count is carried out under the overall supervision of the Executive Director. Any shortages or damages encountered during the course of physical stock taking should be reported to the Executive Committee. Receipts into Stores 227. When a supplier delivers goods to Stores the following procedures should be followed:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) The Purchasing Committee and the Store Officer must ensure that the goods supplied are as per the purchase order and establish that goods delivered are of good quality and agree to the details recorded on the delivery note; The Store Officer acknowledges the receipt of goods by stamping, signing and retaining the original copy of the supplier's delivery note; The Store Officer raises a goods received note (GRN) which is the basic document for recording and evidencing receipt of goods; The Store Officer updates bin cards to show stocks received; When a division returns goods to the store, the Head of Division should ensure that a Material Return Note (MRN) is provided. The Store Officer must then examine the goods returned to ensure that they are in good condition and agree with the MRIN and must issue a GRN and update bin cards. 228. The Goods Received Note (GRN) should be raised in four parts on pre-numbered and pre-printed forms. GRNs shall record the followings:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) GRN number; Description of goods; Quantity received; PO reference number and date; Supplier's name; Remarks as to the condition of goods; and 37 (g) 229. Signature of Store Officer. The Store Officer should distribute copies of GRN as follows:(a) (b) (c) (d) Original: Duplicate: Triplicate: Quadruplicate: to supplier; to the Procurement Section to the user division to be retained as office copy 230. The Store Officer should use GRN to update store bin cards. If the items received are of the same item which have been previously in the store, the Store Officer should continue with the old bin cards currently in use. For new lines of item, new bin cards should be opened. After posting receipts on store bin cards, the Store Officer should file GRN copies in order of serial number and keep in the stores. 231. The Store Officer must issue materials from stores only on receipt of the Material Requisition and Issue Note (MRIN) in 3 copies submitted by the requisitioning division. All MRINs must be signed by the Head of the requisitioning division and approved by the Executive Director. 232. Issue of relief goods for relief operation (including emergency response) and for replenishment of warehouse at branches shall be approved by the Executive Committee. 233. On receipt of a MRIN, the Store Officer should: (a) issue the goods and complete the following details on the MRIN :(1) Goods Issue Date (2) Quantity Issued (3) Name and Signature of the Store Officer (4) Stock Balance (b) ensure that persons collecting goods sign for them on the space provided on the MRIN; (c) distribute copies of MRIN as follows :(1) Original: (2) (3) Duplicate: Triplicate: to the Head of Store who use it as a source document for posting to the stores ledger cards. to the requisitioning division; and to be retained by the Store Clerk to update bin cards with the quantity of stock issued Physical Stock taking 234. There are three types of physical stock-takes as mentioned below:(a) Perpetual inventory counts Perpetual inventory stock counts should be carried out by the Store and Administration personnel on a monthly basis under the check of Store Officer. At least 10% of the stock items must be selected and counted. In doing so more weight should be given to the items which are of higher value and fast moving. The physical counts should then be reconciled with bin card and store ledger balances and any discrepancies revealed must immediately be reported to the Executive Director for the further action. 38 (b) Periodic independent counts Periodic independent counts should be carried out by the Store and Administration personnel delegated by the Executive Director at irregular intervals, at least once every three months. The physical counts should then be reconciled with bin card and store ledger balances and any discrepancies revealed must immediately be reported to the Executive Director for further action. (c) Annual physical stock counts Annual physical stock counts should be carried out by the stock taking team in the following manners during the last two week of December in every year. (a) (b) (c) A full and comprehensive annual stock count of goods held in warehouses and all divisions must be carried out at the end of each year under the overall supervision of the Executive Director. All stock counts must be recorded on the Stock Taking Sheets, which should be dated, stamped and signed by the stocktaking team. Each Head of Division shall sign the stock taking sheets or stock records of stores under his control, if he is satisfied that the particulars shown therein are correct and shall forward a certificate to the Executive Director. 235. The Executive Director, after ensuring that all discrepancies between the book and the actual physical stock balances are analyzed and investigated thoroughly, shall forward the stock reconciliation statement to the Executive Committee. Ground Stock Report 236. After annual ground stock taking a report of the findings shall be submitted to the President within a week after completion of stock taking. Discrepancies (if any) and reconciliations shall be included in the report. Damaged and obsolete goods 237. Damaged stock must be clearly marked and kept separately from other stocks. The Store Officer shall maintain a list of damaged materials which records the following particulars:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) Item code Index number Name and description Location Unit of quantity Quantity Cost Total value of the damaged stock 238. The Store Officer should report the nature, quantity and existence of damaged stock to the Store Officer of the main user division and the Head of Finance Division so that they can advice on the action to be taken. 239. Obsolete stock can also be identified during the annual stock-take when all bin cards are reviewed. If an item has not been moved during the year, the user division is required to comment on the possibility of the goods being obsolete. 39 240. After obtaining the approval of the user division, the Store Office must compile a schedule of the obsolete stocks and present it to the Executive Director for review. A list of stock items which the Executive Director agrees are obsolete should then be passed on to the Head of Finance who will prepare and submit a proposal to the Executive Committee to write off the obsolete goods. 241. The closing stock of saleable stock shall be valued at the lower of the cost or the net realizable value. 40 Chapter 15 LOSSES OF CASH AND STORES Handling of cash and stores 242. The Executive Committee, staff at all levels of the Society and volunteers who are carrying out the activities of the Society are expected to exercise the same vigilance in respect of receiving, handling, custody and utilizing of the cash and stores of the Society as a person of ordinary prudence would exercise in respect of receiving, handling, custody and utilizing of his own cash and stores. 243. If any loss or damage has occurred due to non-compliance of the above-mentioned standards of propriety, the responsibility will rest upon the individual concerned. With regard to the term "responsibility" it should be realized that the individual concerned will be held personally responsible for any loss sustained by him through negligence or dishonesty on his part and that he will also be held personally responsible for any loss arising from fraud or negligence on the part of any other individual if there is evidence that he has contributed to the loss by his own action or negligence. 244. Likewise, in exercising the power to write-off the loss and damages of cash and stores, the write-off should be made only after proper investigation has been made without negligence. If not, the responsibility will rest upon the authority that sanctions the write-off. 245. The term "cash" in addition to legal tender coins or currency notes, includes: (a) Overpayment of pay and expenses (b) Irrecoverable advances (c) Irrecoverable debts (d) Loss of cash due to other causes 246. The term "stores" includes: (a) Store materials (b) Marketable goods (c) Raw materials, goods in process and finished goods (d) Fixed assets and other capital assets such as buildings , plant and equipment, furniture, agricultural farms etc. 247. The term "loss" includes: (a) Shortages (b) Damages (c) Wastes (d) Lost 248. However, commercial losses, deterioration due to long use of tools and plant and normal waste in the process of manufacturing are not included in the meaning of loss. 249. If there is any abnormal loss necessary action should be taken after proper investigation has been made. Investigation of Losses 250. Head of Division or the Project-in-charge should put up a report at once to the Executive Director as and when loss of cash or stores occurs. The Executive Director should make a preliminary investigation immediately to ascertain the nature of loss and circumstances which made it possible and extent of the loss, after which a report must be submitted to the Executive Committee. 251. On receipt of the report, the Executive Committee shall appoint an Enquiry Commission with personnel who are not responsible for the loss. 41 252. The Enquiry Commission shall make necessary enquires so as to reveal whether there is any defect in the respective laws , rules , regulations , directives and procedures; whether there is dishonesty on the part of the responsible official, and whether it is due to negligence of some individual officer . In determining whether any individual officer is responsible or not, the fact that he has exercised or not the same vigilance in respect of handling, custody and utilizing of the cash and stores as a person of ordinary prudence would exercise in respect of handling, custody and utilizing of his own cash and stores should mainly be taken into consideration. The Enquiry Commission should report its findings to the Executive Committee through the Executive Director as soon as possible. 253. If the Enquiry Commission finds that the loss is due to dishonesty and negligence on the part of some individual officer, its opinions and recommendations as to whether there is any means of effecting a recovery for the value of cash or stores lost from the responsible official, or what action should be taken against the responsible official for the loss, or how much of the value of cash or stores lost should be written-off, must be mentioned in the investigation report. 254. On receipt of the Enquiry Commission's report, the Executive Committee should review the nature of loss and circumstances which made it possible and extent of the loss. If the loss is within the power of the Executive Committee to write off, necessary action should be taken to write-off the loss. In case the loss is beyond the power of the Executive Committee, the report of the Executive Committee should be submitted to the Central Council, even when such loss has been made good by the responsible official. 255. If the shortage, damage, waste, or loss has occurred during transit, the investigation should be made by the official who will receive the stores, and shall report the findings to the Executive Committee. 256. If the loss is due to shortage, waste or loss, the value of stores or cash so lost and the cost for repairs if the loss is due to differences in the condition when the materials are originally accepted and when the stores were examined, the cost for repairs should be mentioned in the report. When compensation for the loss is to be claimed from the responsible official, how it should be computed and claimed shall be recommended in the report. Write-off of Losses 257. The power to write-off the losses of cash and stores are as shown below: Sr. No (1) (2) (3) Authority to write-off President Executive Committee Central Council Cash Value ( Kyat ) 500,000 1,000,000 Above 1,000,000 Stores Value (Kyat) 1,000,000 2,000,000 Above 2,000,000 258. The amount that can be written off under the above-mentioned powers represents the total value of cash or stores of all cases of losses relating to the same nature and circumstances. Hence, no authority competent to sanction the write-off of the loss shall have the right to split the amount of the loss of one case into smaller ones so that it will fall within the limit of his write-off powers. 259. If the Enquiry Commission is of the opinion that the loss of cash or stores is not due to pilferage or fraud or negligence, and the opinion is accepted by the Executive Committee, the value of cash or stores so lost may be written-off under the above-mentioned powers. 260. If the Enquiry Commission is of the opinion that the loss of cash or stores is due to pilferage or fraud or negligence, and the opinion is accepted by the Executive Committee, action should be taken as follows: (1) The whole value of the loss of cash or stores may be written-off . 42 (2) May ask for compensation of the whole or part of the value of the loss of cash or Stores. If only part of the value of the loss of cash or stores is compensated, the balance should be written-off with the record of reasons in writing. (3) If departmental action is deemed necessary, departmental enquiry may be held. (4) If it is deemed necessary to prosecute in a court of law, legal prosecution should be initiated. 361. If the loss of cash or stores discloses some defects in the law and regulations in addition to the nature and causes of the loss mentioned in paragraph 245 and 247 of these Regulations the fact should be mentioned in the report submitted to the Executive Committee. The Executive Committee shall submit to the Central Council the defect that should be amended. 43 Chapter 16 FINANCIAL REPORTS Introduction 262. This section sets out the procedures for the preparation of financial management reports to be submitted to management, governance, government and other stakeholders. 263. Accurate financial information will assist management in the following matters: (a) (b) (c) Developing policies and planning for future operations; Making informed and effective decisions on the allocation of resources; Measuring the performance and controlling and monitoring the operation. Responsibilities 264. The Head of Finance shall be responsible for preparation and submission of financial management reports to the Executive Director. Forms of reports 265. The Society shall prepare the following financial statements for each accounting year: (a) (b) (c) Balance Sheet to show the true and fair view of the financial position of the Society as at the end of the financial year Income and Expenditure account to show the operational results for the financial year Cash Flow statement to show the cash receipts and utilization during the financial year. 266. The above statements shall be prepared in accordance with the norms and standards as prescribed by the Myanmar Accountancy Council in the Myanmar Accounting Standards. 267. The Head of Finance shall ensure the preparation of the annual accounts (financial statements) within three months of the end of the financial year. 268. The above financial statements shall be required to be audited and certified by independent external auditors to be appointed by the Executive Committee. 269. The audit report of the auditors shall be placed before the Executive Committee and the auditors shall submit the financial statements along with the audit report. Year-end cut-off dates 270. A few weeks before the year end, all Finance staff should be notified in writing by the Head of Finance on the financial period and cut-off procedures. Guidance provided should include the followings: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) the date on which books should be closed; guidance on the types of accruals and prepayments that should be considered and computed; a schedule of new books to be opened to record transactions relating to the next financial year; guidance to certify stocks, fixed assets and cash in hand; and guidance on stocks and debtors' provisions. 44 Monthly Financial Reports 271. This section sets the reports to be produced on the monthly basis and submitted to the Executive Director and the Executive Committee every month. These reports shall include the following and wherever necessary, shall be accompanied by a written commentary drawing attention to its most significant features and action required:(a) (b) c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) Trial Balance Budget Vs. Actual Expenditure Analysis Statement Income and Expenditure Statement Cash Position Statement Receipts and Payment Statement Bank Reconciliation Statement Income Analysis Report Debtors Outstanding List Creditors Outstanding List Unutilized Working Advances received from Donors 272. Monthly accounts shall be closed by 7th of the next month. The reports shall be prepared by the Finance Division, signed by the Head of Finance and submitted to the Executive Director. Quarterly Financial Accounts 273. The monthly reports should be consolidated into sets of quarterly accounts. The Finance Division shall prepare the following financial statements by 15th of the next month of the end of the quarter: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) Income and Expenditure Statement Budge vs Actual statement Balance Sheet Statement as at the end of the quarter. Cash Flow Statement Reports on working advances received from donors and reports submitted to them. Report on procurement and sale of fixed asset Income analysis report Expenditure analysis report Accounts receivable and payable report with ageing analysis 274. The quarterly financial reports shall be submitted by the Executive Director to the President through the Honorary Secretary. Report to Central Council Meeting 275. A report including the followings shall be submitted to the Central Council plenary meeting held every six months:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Income and Expenditure Statement Balance Sheet Cash Flow Statement Budget and Actual Comparison Statutory Auditors' Report and Management Letter and compliance of recommendations Financial Reporting to Donors 276. Financial report to the donors shall be regulated as per the program agreements/ memorandum of understanding with respective donors. 45 277. prescribed. The Financial reports shall be submitted to donors in the standard formats as may be 278. The Head of Finance shall prepare the donor financial reports and submit it to the Executive Director. 279. The Executive Committee shall submit the financial reports verified by the Program Manager to the donor. The financial report shall be released to the donors only after being approved by the President. 46 Chapter 17 EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL AUDIT 280. The management is responsible for keeping the books of account in accordance with the law and rules framed by the government. The financial statements are subject to the audit of the external auditor. The opinion expressed by the external auditors on the financial statement shall authenticate as to: (a) (b) whether the Society has kept proper books of account as required by law, and whether the financial statements audited by them present fair and true view of the affairs of the Society and adhere to generally accepted principles and procedures consistent to that of the previous year. Annual Statutory Audit 281. The following procedure should be followed regarding the annual statutory audit of the financial statement of the Society:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) The Society shall have its annual account audited by the external auditors. The auditors shall be appointed by the Executive Committee every year. Audit Fees may be decided by the Executive Committee. The auditors shall express their opinion on the yearly financial statements on the use of funds, and send a Management Letter which summarizes findings, highlight weaknesses in internal control, and recommendations for improvements. Audit Report and Management Letter shall be placed before the Central Council along with the yearly financial statements. Preparation for Annual Audit 282. Immediately upon the close of the accounts at the financial year end, the Head of Finance Division shall send a timetable for audit to the external auditor. The timetable should include the following information:(a) (b) (c) 283. A date on which a draft set of financial statements will be available; A date on which the auditors can commence their audit; and A date on which the audited financial statements have to be submitted to the Executive Committee. The following schedules may be made ready before the visit of the statutory auditors. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) The final Trial Balance Statement of fixed assets in columnar form showing: (1) Balances as at the end of the previous year (2) Additions and disposals (3) Depreciation charge (4) Balance at the balance sheet date; A schedule of any capital work in progress, if any. A schedule of accounts payable A summary of stock held at each store point at the balance sheet date and basis of valuation A list of goods in transit; A schedule of prepaid expenses; A schedule of cash and bank balances at the date of the balance sheet supported by reconciliation statements in respect of each bank balance; and Any other schedule that may be necessary. 47 Accounting/Audit standards 284. As far as possible, audit procedures should be performed in accordance with generally accepted International Audit Standards (IAS) and Myanmar Standard on Auditing (MSA)prescribed by the Myanmar Accountancy Council and the financial statements should be prepared in conformity with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and The Myanmar Accounting Standards (MAS) published by Myanmar Accountancy Council. Appointment of Statutory Auditor 285. An accountant who is registered as a Certified Public Accountant and hold a certificate of practice under Myanmar Accountancy Council Law can be appointed as Auditor to conduct the audit and certify the financial statements of the Society. The Auditor must have experience in auditing nonprofit organizations and also be familiar with legal requirements relating to non-government organizations. The Executive Committee, if required, may ask for the audit party of the office of the Auditor General to conduct audit. 286. The terms of reference should include the following:(a) (b) (c) 287. followed:- Audit certificate and auditor's report Management Letter with recommendation for improving financial ment practices Audit fee manage- When there is a need to change the Auditor, the following procedures should be (a) (b) Selection of a new auditor should be made by the Executive Committee Issue an appointment letter with a clear scope of work and mentioning the previous Auditor's name and obtain the acceptance of the new Auditor. 288. In carrying out their functions, the statutory auditors shall have access to the books and records of the Society at all times. They shall be entitled to such information or explanation as they may require from any employee of the Society, or any other persons the auditors deem necessary, with the agreement from the Executive Director. Audit Report 289. The statutory Auditor sends an audit report which expresses his opinion regarding the annual financial account stating whether or not the financial statements give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Society. The audit opinion may be unqualified, qualified, negative or disclaimer of opinion. The audit report is addressed to the President. 290 A management Letter is sent by the Auditor to the President to summarize audit findings, highlight weaknesses in the accounts and internal control system, and recommendations for improvement. 291. Head of Finance shall report to the Executive Director regarding compliance of the Auditor's recommendations in the Management Letter. The Executive Director shall ensure that the Auditor's recommendations are strictly followed and report action taken to the Executive Committee within the specified time frame. Internal Audit 292. Internal Audit Department of MRCS is required to perform on-going internal audit of the MRCS operations focusing on: (a) efficiency and effectiveness of its management functions 48 (b) (c) (d) assessment of financial and administrative operational areas to ensure proper utilization of the resources for the benefit of the vulnerable people adequacy, appropriateness and effectiveness of the systems and procedures in place for delivery of the services and management of MRCS as a whole including branches investigative functions 293. The Executive Committee shall prescribe the scope of the audit functions of the Internal Audit Section. 294. The audit report of the Internal Audit Section shall be submitted to the President. Donor Agency Audit 295. Donor Agency audit shall be governed as per the provisions of the memorandum of Understanding/Agreement with the donor agencies. 49 Chapter 18 GENERAL PROVISIONS Compliance of Financial Regulations 296. The provisions of the Financial Regulations shall be strictly complied by all executives, staff members and Red Cross volunteers at Headquarters and Branches. Directives and procedures made by the Executive Committee in accordance with the Financial Regulations shall also be observed strictly. Directive and Procedures 297. The Executive Committee may prescribe directives and procedures including amendments to existing regulations from time to time as and when necessary. Amendments 298. The Financial Regulations may require amendments due to: (a) (b) (c) A change in the existing procedures A deletion of existing procedures Addition of new or previously omitted procedures 299. When a change in any financial procedure is required, a request for change in the Financial Regulations should be submitted to the Head of Finance, who shall be responsible for updating the Regulations. 300. Any stakeholder of the Society holding this Financial Regulations may propose changes, and the Head of Finance shall make a recommendation to the Executive Director and the Executive Committee. The Executive Committee shall put the matter to the Central Council for adoption. Repeal of former Financial Regulations 301. The Financial Regulations shall come into force on the 29th February 2008 at the end of the session of the 62nd Meeting of the Central Council at which time the former Financial Regulations will stand repealed. 302. All financial directives and procedures made or issued before, in so far as they are not inconsistent with these Regulations, shall continue to be in force.