Decomposition reactions
advertisement

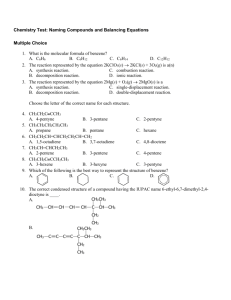
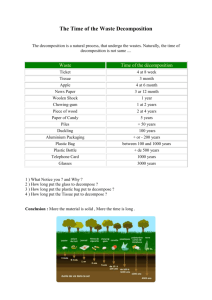
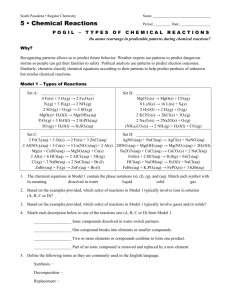
Chemical Reactions Part 1: Decomposition and Synthesis Reactions Objectives • -To identify decomposition and synthesis chemical reactions • -To predict the products of these two types of reactions 2 Symbols in Equations • The arrow (→) separates the reactants from the products • (s) = solid: Fe(s) • (g) = gas: CO2(g) • (l) = liquid: H2O(l) Symbols in Equations • double arrow indicates a reversible reaction (more later) heat • , heat is supplied to the reaction • a catalyst is supplied (i.e. Pt platinum) Classifying and Predicting Chemical Reactions • Oxidation-Reduction reactions - electrons are transferred from one atom to another • There are 5 classifications: – Decomposition – Synthesis – Combustion – Single displacement – Double displacement (ionic) 5 Decomposition Reactions • Decompose = fall apart • Decomposition reactions- one compound decomposes into two or more elements or compounds • Key: only 1 reactant • Usually involves energy or heat 6 Decomposition • Binary compounds (two elements) will split into those two elements: AB A + B • Tertiary compounds (three elements) will have one element in BOTH products ABC AB + BC 7 Decomposition Reactions A. Electrolysis (adding electricity) of compounds produces the elements 2 H2O 2 H2 + O2 2 NaCl 2 Na + Cl2 8 Decomposition Reactions B. Metallic (any positive ion) chlorates decompose into metallic chlorides and oxygen when heated 2 KClO3 2 KCl + 3 O2 C. Metallic carbonates decompose into metallic oxides and carbon dioxide when heated CaCO3 CaO + CO2 9 Decomposition Reactions D. Hydrated compounds yield the anhydrous compound and water when heated CuSO4 5 H2O CuSO4 + 5 H2O E. Oxides of the less active metals (see activity series) form the metal and oxygen when heated 2 HgO 2 Hg + O2 10 Decomposition Reactions F. Acids (hydrogen with negative ion) decompose into water and nonmetallic oxides H2CO3 H2O + CO2 2 H3PO4 P2O5 + 3 H2O G. Bases (metallic hydroxides) decompose into water and metallic oxides Ca(OH)2 CaO + H2O 11 Decomposition Reactions H. Peroxides decompose into oxides and oxygen. 2 K2O2 2 K2O + O2 2 H2O2 2 H2O + O2 water is the oxide of hydrogen 12 Synthesis Reactions • Synthesize = to make or put together • Synthesis reactions-two or more elements or compounds unite to form one product • Key: 2 elements OR two compounds when both are oxides with only one product 13 Synthesis Reactions A. Oxygen combines with most elements to form oxides 2 Mg + O2 2 MgO C + O2 CO2 B. Metallic elements + nonmetallic elements yield ionic compounds (ionic compounds called salts) 2 Al + 3 Cl2 2 AlCl3 2 K + I2 2 KI 14 Synthesis Reactions C. Nonmetallic elements tend to combine with each other to form covalent (molecular) compounds S8 + 8 F2 8 SF2 P4 + 6 Cl2 4 PCl3 15 Synthesis Reactions D. Oxides of metals + water form bases (metallic hydroxides) Water is an oxide! CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 Na2O + H2O 2 NaOH 16 Synthesis Reactions E. Oxides of nonmetals + water form acids- acids usually made from an “ate” ion P2O5 + 3 H2O 2 H3PO4 SO3 + H2O H2SO4 F. Oxides of metals + oxides of nonmetals yield ionic compounds- usually contain an “ate” ion 17 Na2O + SO3 Na2SO4 Objectives • -To identify decomposition and synthesis chemical reactions • -To predict the products of these two types of reactions 18